Materialism emphasizes the importance of physical possessions and wealth in defining success and happiness. This philosophy can shape your priorities, influencing decisions and lifestyle choices based on tangible assets rather than abstract values. Explore the rest of this article to understand how materialism impacts your life and mindset.
Table of Comparison
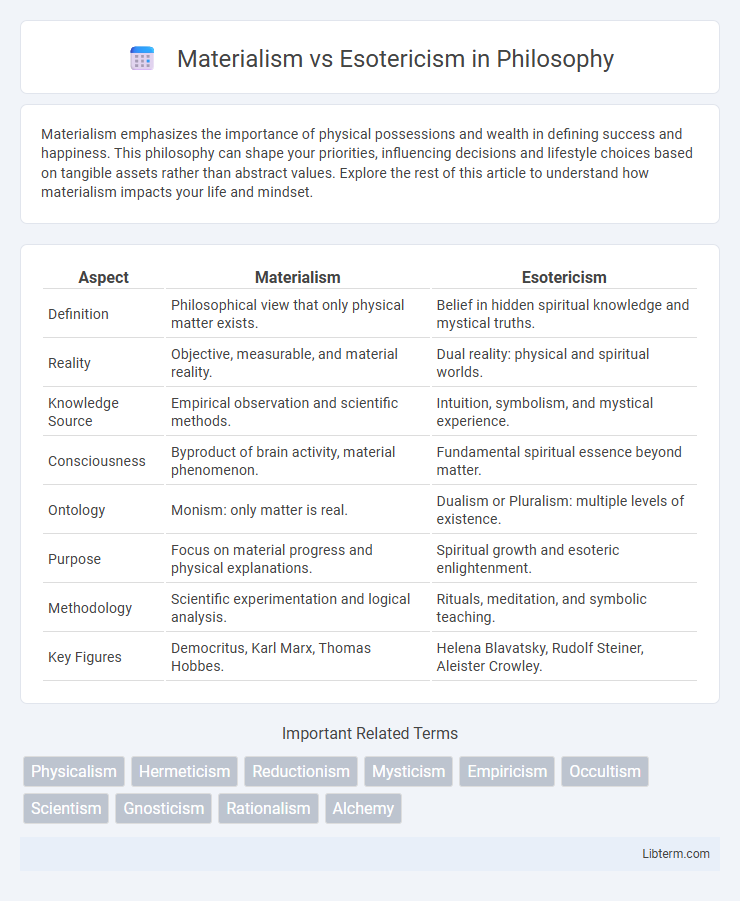
| Aspect | Materialism | Esotericism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical view that only physical matter exists. | Belief in hidden spiritual knowledge and mystical truths. |
| Reality | Objective, measurable, and material reality. | Dual reality: physical and spiritual worlds. |
| Knowledge Source | Empirical observation and scientific methods. | Intuition, symbolism, and mystical experience. |
| Consciousness | Byproduct of brain activity, material phenomenon. | Fundamental spiritual essence beyond matter. |
| Ontology | Monism: only matter is real. | Dualism or Pluralism: multiple levels of existence. |
| Purpose | Focus on material progress and physical explanations. | Spiritual growth and esoteric enlightenment. |
| Methodology | Scientific experimentation and logical analysis. | Rituals, meditation, and symbolic teaching. |
| Key Figures | Democritus, Karl Marx, Thomas Hobbes. | Helena Blavatsky, Rudolf Steiner, Aleister Crowley. |
Understanding Materialism: Foundations and Principles
Materialism, rooted in the belief that physical matter constitutes the fundamental reality, emphasizes empirical evidence and scientific inquiry as the basis for understanding existence. It asserts that all phenomena, including consciousness and thought, arise from material interactions governed by natural laws. This philosophical stance contrasts sharply with esotericism, which prioritizes hidden, spiritual knowledge beyond sensory perception and material explanation.
Delving into Esotericism: Key Concepts and Beliefs
Esotericism centers on hidden knowledge and spiritual truths accessible only to a select few through initiated practices and symbolic language. Core beliefs include the interconnectedness of all things, the existence of higher realities beyond material perception, and the transformative power of inner awakening. Its principles often emphasize mystical experiences, alchemical processes, and the pursuit of enlightenment beyond empirical materialism.
The Historical Evolution of Materialism vs Esotericism
Materialism, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy with thinkers like Democritus and Epicurus, evolved through the Scientific Revolution, emphasizing empirical evidence and physical reality, while esotericism traces back to mystical traditions, secret knowledge, and spiritual practices from Hermeticism and Gnosticism. The historical evolution of materialism is marked by the rise of rationalism and natural sciences in the Enlightenment, contrasting with esotericism's resurgence during periods such as the Renaissance and 19th-century occult revival. This ongoing dialectic reflects the tension between measurable reality and hidden spiritual dimensions across intellectual history.
Core Differences Between Materialist and Esoteric Worldviews
Materialism centers on the belief that physical matter constitutes reality, emphasizing empirical evidence, scientific observation, and tangible phenomena as the sole basis of existence. Esotericism embraces metaphysical concepts, spiritual dimensions, and hidden knowledge accessible through intuition, mysticism, or sacred traditions beyond observable matter. The core difference lies in materialism's reliance on objective, measurable reality versus esotericism's acceptance of subjective, transcendent experiences as valid sources of truth.
Science and Spirituality: Where Materialism Meets Esotericism
Materialism emphasizes empirical evidence and physical phenomena as the basis of reality, driving scientific inquiry through measurable data and observable experiments. Esotericism explores spiritual dimensions, inner knowledge, and metaphysical experiences that transcend material existence, often emphasizing intuition and mystical insights. The intersection of science and spirituality occurs when empirical methods investigate consciousness and quantum phenomena, suggesting potential bridges between materialistic science and esoteric wisdom.
The Role of Perception and Consciousness
Materialism posits that perception is a byproduct of physical processes in the brain, emphasizing sensory data as the foundation of reality. Esotericism views consciousness as a fundamental, non-material essence shaping perception and unlocking hidden dimensions beyond physical senses. The contrasting roles of perception and consciousness highlight the divide between empirical observation and inner experiential knowledge in understanding existence.
Materialism and Esotericism in Modern Society
Materialism in modern society emphasizes tangible, scientific evidence and economic progress, driving technological innovation and consumer culture. Esotericism persists through spiritual practices, alternative healing, and metaphysical beliefs, offering a contrast to materialistic values by exploring hidden meanings and inner experiences. The dynamic tension between materialism and esotericism shapes contemporary debates on consciousness, reality, and the purpose of life.
Psychological Impacts of Materialist and Esoteric Beliefs
Materialist beliefs often emphasize external validation and tangible success, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and feelings of emptiness when material goals are unmet. Esoteric beliefs promote inner exploration, spiritual growth, and a sense of interconnectedness, which can enhance psychological well-being and resilience to life's challenges. However, intense esoteric focus may also result in detachment from reality or social isolation if not balanced with practical engagement.
Criticisms and Misconceptions Surrounding Both Philosophies
Materialism is often criticized for its reductionist view that dismisses subjective experiences and spiritual phenomena as mere byproducts of physical processes, leading to misunderstandings about its limitations in explaining consciousness. Esotericism faces misconceptions of being unscientific or irrational due to its reliance on mystical knowledge, symbolic interpretations, and non-empirical methods, which critics argue lack empirical validation. Both philosophies encounter the challenge of addressing skepticism from opposing viewpoints while striving to articulate the value and coherence of their perspectives in understanding reality.
Integrating Materialism and Esotericism: Is Harmony Possible?
Integrating materialism and esotericism requires acknowledging the empirical foundations of materialism alongside the introspective insights of esotericism, fostering a holistic worldview that bridges physical realities and metaphysical experiences. Recent interdisciplinary studies in consciousness research suggest that exploring quantum phenomena could offer a common framework where materialist science and esoteric spirituality converge, promoting harmony between these perspectives. Such integration challenges the dichotomy by encouraging an open dialogue that values both measurable evidence and subjective transcendence.
Materialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com