Aesthetic appeal significantly enhances the value and experience of any space or product by blending beauty with functionality. Understanding how design elements influence perception can transform your surroundings and evoke desired emotions. Explore this article to discover key principles that elevate aesthetic quality effectively.
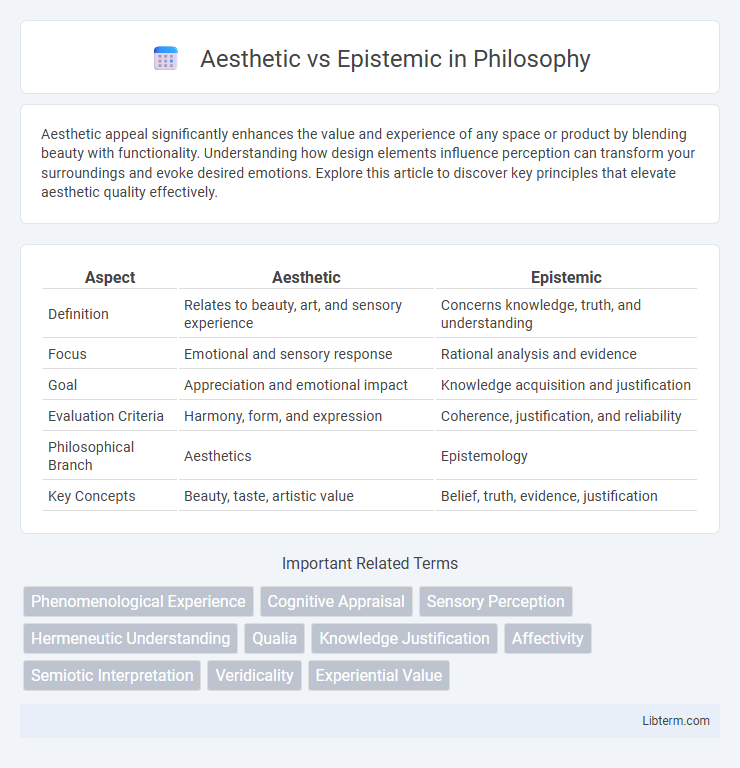
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aesthetic | Epistemic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relates to beauty, art, and sensory experience | Concerns knowledge, truth, and understanding |
| Focus | Emotional and sensory response | Rational analysis and evidence |
| Goal | Appreciation and emotional impact | Knowledge acquisition and justification |
| Evaluation Criteria | Harmony, form, and expression | Coherence, justification, and reliability |
| Philosophical Branch | Aesthetics | Epistemology |
| Key Concepts | Beauty, taste, artistic value | Belief, truth, evidence, justification |
Introduction: Defining Aesthetic and Epistemic
Aesthetic relates to the appreciation of beauty and sensory experiences, emphasizing emotional and perceptual engagement with art, nature, or design. Epistemic concerns knowledge acquisition, understanding, and justification, focusing on cognitive processes and truth-seeking methods. Distinguishing between aesthetic and epistemic domains highlights the difference between valuing sensory appeal versus valuing intellectual insight and evidence.
Historical Origins of Aesthetic and Epistemic Concepts
The historical origins of aesthetic concepts trace back to Ancient Greece, where philosophers like Plato and Aristotle explored beauty, art, and sensory experiences as fundamental aspects of human perception. Epistemic concepts, rooted in epistemology, originate from early philosophical inquiries into knowledge, justification, and belief, with significant contributions from figures such as Socrates, Descartes, and Locke. Both domains evolved through centuries, influencing modern discussions on how humans perceive reality versus acquire and validate knowledge.
Core Differences Between Aesthetic and Epistemic Values
Aesthetic values prioritize sensory experience, beauty, and emotional impact, focusing on how objects or phenomena appear and affect the observer's feelings. Epistemic values emphasize knowledge acquisition, truth, and understanding, concentrating on cognitive processes and the reliability of information. Core differences lie in their objectives: aesthetic values seek to enhance enjoyment or appreciation, while epistemic values drive insight and intellectual growth.
The Role of Perception in Aesthetic Judgments
Perception shapes aesthetic judgments by influencing how sensory information is interpreted and valued emotionally, highlighting the subjective nature of beauty and artistic experience. In contrast, epistemic judgments rely on perception for gathering accurate information and forming justified beliefs, emphasizing objective understanding and truth. The role of perception in aesthetics involves emotional resonance and sensory engagement, whereas in epistemics it centers on clarity and factual accuracy.
The Importance of Truth in Epistemic Evaluations
Epistemic evaluations prioritize truth as a fundamental criterion, emphasizing knowledge accuracy and factual correctness over subjective experience. Unlike aesthetic judgments, which value beauty and sensory appeal, epistemic assessments seek to establish reliable understanding and justification based on evidence. Truth serves as the cornerstone in epistemic evaluation, ensuring that beliefs and claims align with reality and contribute to intellectual integrity.
Crossovers: When Aesthetic Meets Epistemic
The crossover between aesthetic and epistemic domains occurs when sensory experiences contribute to knowledge acquisition, demonstrating how beauty and truth intertwine in perception. Artworks often serve as epistemic tools by conveying complex ideas and emotions, enriching understanding beyond purely logical frameworks. This intersection highlights the cognitive impact of aesthetics in shaping beliefs and deepening wisdom through experiential engagement.
Philosophical Debates: Priority of Aesthetic vs Epistemic
Philosophical debates on the priority of aesthetic versus epistemic values center around whether beauty or truth holds greater fundamental importance in human experience and knowledge acquisition. Aesthetic value emphasizes sensory, emotional, and imaginative engagement, while epistemic value prioritizes truth, understanding, and cognitive clarity. Scholars argue that aesthetic appreciation can influence epistemic processes by shaping perception and interpretation, yet epistemic rigor remains crucial for validating knowledge claims.
Aesthetic and Epistemic in Art and Science
Aesthetic experience in art emphasizes sensory perception, emotional response, and the appreciation of beauty, playing a crucial role in how individuals engage with creative works. Epistemic value in science focuses on knowledge acquisition, truth-seeking, and understanding phenomena through empirical evidence and logical reasoning. The interplay between aesthetic and epistemic elements enriches both disciplines by fostering creativity in scientific discovery and deepening interpretative insights in art.
Real-World Applications: Design, Learning, and Technology
Aesthetic experiences in design prioritize visual appeal, user engagement, and emotional response, shaping product interfaces and environments through elements like color, form, and style. Epistemic experiences enhance learning and technology by emphasizing knowledge acquisition, problem-solving, and critical thinking, crucial in educational tools and AI development. Integrating both approaches leads to innovative solutions where aesthetic design improves usability while epistemic frameworks ensure functionality and meaningful content delivery.
Conclusion: Balancing Aesthetic and Epistemic Perspectives
Balancing aesthetic and epistemic perspectives involves integrating subjective appreciation with objective understanding to enrich experiences across art, science, and knowledge. Prioritizing aesthetic values enhances emotional engagement and creativity, while epistemic values ensure accuracy and credibility in knowledge acquisition. Achieving harmony between these dimensions fosters a comprehensive approach that respects both beauty and truth.
Aesthetic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com