Via Negativa offers a powerful approach to understanding concepts by defining them through what they are not, rather than what they are. This method encourages deeper analysis and clarity by eliminating misconceptions and focusing on the essence beyond positive attributes. Discover how embracing Via Negativa can transform your thinking by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
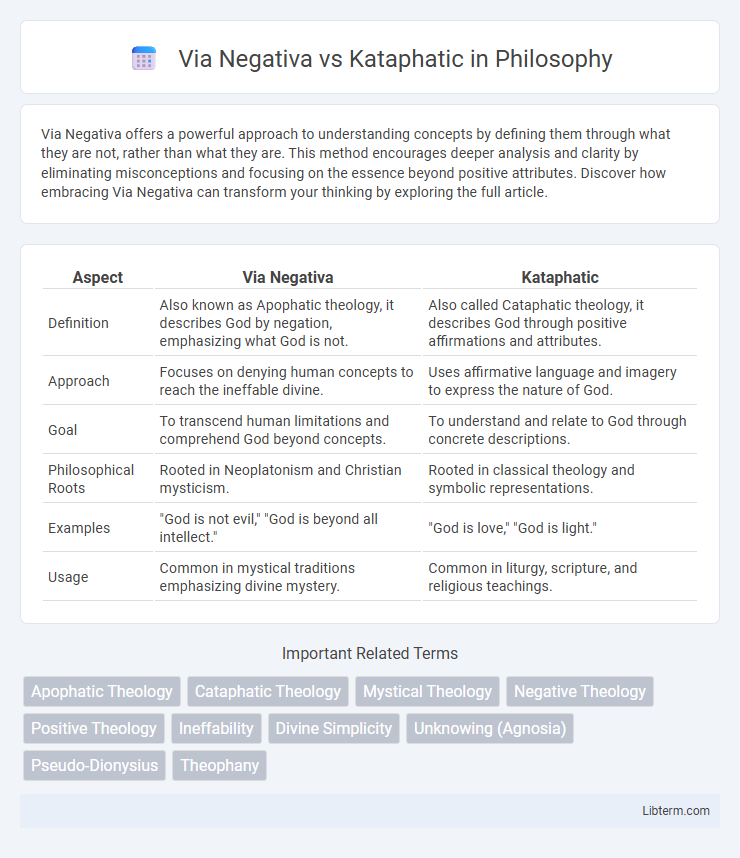
| Aspect | Via Negativa | Kataphatic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Also known as Apophatic theology, it describes God by negation, emphasizing what God is not. | Also called Cataphatic theology, it describes God through positive affirmations and attributes. |
| Approach | Focuses on denying human concepts to reach the ineffable divine. | Uses affirmative language and imagery to express the nature of God. |
| Goal | To transcend human limitations and comprehend God beyond concepts. | To understand and relate to God through concrete descriptions. |
| Philosophical Roots | Rooted in Neoplatonism and Christian mysticism. | Rooted in classical theology and symbolic representations. |
| Examples | "God is not evil," "God is beyond all intellect." | "God is love," "God is light." |
| Usage | Common in mystical traditions emphasizing divine mystery. | Common in liturgy, scripture, and religious teachings. |
Introduction to Via Negativa and Kataphatic Approaches
Via Negativa emphasizes understanding the divine through negation, describing what God is not, thereby highlighting the ineffable and transcendent nature of ultimate reality. Kataphatic theology uses positive affirmations and attributes to describe God, aiming to make the divine more relatable and accessible through imagery and metaphor. These complementary approaches represent contrasting pathways in spiritual discourse: one through denial and mystery, the other through affirmation and depiction.
Defining Via Negativa: The Apophatic Path
Via Negativa, also known as the Apophatic Path, defines the divine by negation, emphasizing what God is not rather than what God is. This approach highlights the ineffability and transcendence of the divine, suggesting that human language and concepts cannot adequately describe the ultimate reality. By embracing silence and negation, Via Negativa guides spiritual seekers toward an experiential understanding beyond positive assertions or descriptive theology.
Understanding Kataphatic: The Affirmative Approach
Kataphatic theology emphasizes understanding the divine through positive affirmations and descriptive language, focusing on God's attributes such as love, mercy, and omnipotence. This approach uses metaphors and analogies to convey the nature of God, making the divine accessible and relatable to human experience. By affirming what God is, Kataphatic theology fosters a personal connection and deepens spiritual comprehension.
Historical Origins and Development
Via Negativa, rooted in early Christian mysticism and Neoplatonism, emphasizes understanding the divine by describing what God is not, originating from thinkers like Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite in the 5th century. Kataphatic theology, emerging alongside via negativa, focuses on positive affirmations and attributes of God, drawing from biblical texts and Church Fathers such as Augustine and Aquinas. Both approaches developed through medieval scholasticism, shaping Western theological discourse by balancing apophatic and cataphatic traditions in exploring the nature of the divine.
Key Figures in Apophatic and Kataphatic Traditions
Key figures in apophatic (Via Negativa) tradition include Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite and Meister Eckhart, who emphasized the ineffability of the divine by describing God through negations. In contrast, Kataphatic theology is represented by Thomas Aquinas and Saint Augustine, who employed positive affirmations and analogies to articulate God's nature. These traditions shape theological discourse by balancing affirmations of divine attributes with the acknowledgment of divine mystery.
Philosophical Foundations: Contrasting Worldviews
Via Negativa emphasizes the ineffability of ultimate reality by defining it through what it is not, rooted in apophatic theology and mysticism, highlighting the limits of human language and cognition. Kataphatic approaches affirmatively describe the divine or absolute using positive attributes and analogies, grounded in classical theism and metaphysical realism, asserting that human reason can apprehend aspects of transcendent truth. These contrasting worldviews reveal differing commitments about the relationship between the finite human mind and the infinite reality, shaping diverse philosophical and theological methodologies.
Spiritual Practices: Apophatic vs Kataphatic Methods
Apophatic spiritual practices emphasize approaching the divine through negation, focusing on what God is not, fostering a mystical experience beyond human comprehension. Kataphatic methods use positive affirmations and symbolic imagery to describe and connect with the divine, making spirituality more accessible through tangible concepts and devotional actions. Both approaches offer complementary paths for deepening spiritual understanding and experiential knowledge.
Theological Implications and Doctrinal Impact
Via Negativa emphasizes understanding God by asserting what God is not, fostering a theology rooted in divine mystery and ineffability that limits anthropomorphic descriptions. Kataphatic theology, by contrast, affirms positive attributes of God, supporting doctrines that describe divine nature and qualities affirmatively, which shapes devotional practices and creeds. The tension between these approaches influences doctrinal formulations on God's transcendence and immanence, affecting theological discourse on divine knowledge, worship, and the limits of human language in expressing the divine.
Comparative Analysis: Strengths and Limitations
Via Negativa emphasizes understanding the divine by defining what it is not, fostering a purer, apophatic spirituality that avoids limiting God to human concepts but may lead to abstractness and ambiguity. Kataphatic theology, by affirming positive attributes and descriptions of the divine, offers a more accessible and concrete framework for worship and comprehension, yet risks anthropomorphizing and constraining the ineffable nature of God. Comparative analysis reveals that Via Negativa excels in conveying mysticism and transcendence, whereas Kataphatic approaches effectively facilitate relational and doctrinal clarity within religious practice.
Contemporary Relevance in Modern Spirituality
Via Negativa emphasizes understanding the divine through negation, fostering a meditative approach that resonates with modern seekers valuing experiential spirituality over dogma. Kataphatic spirituality, characterized by positive affirmations and imagery of the divine, appeals to individuals craving concrete expressions of faith and personal connection. Contemporary relevance lies in their complementary use within diverse spiritual practices, including mindfulness and interfaith dialogues, enhancing inclusivity in modern spiritual experiences.
Via Negativa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com