Positivism emphasizes the importance of observable, scientific facts over metaphysical speculation, grounding knowledge in empirical evidence and logical reasoning. It shapes various fields, including sociology and philosophy of science, by promoting systematic observation and verification. Explore the rest of the article to deepen Your understanding of how positivism influences modern thought and research methods.
Table of Comparison
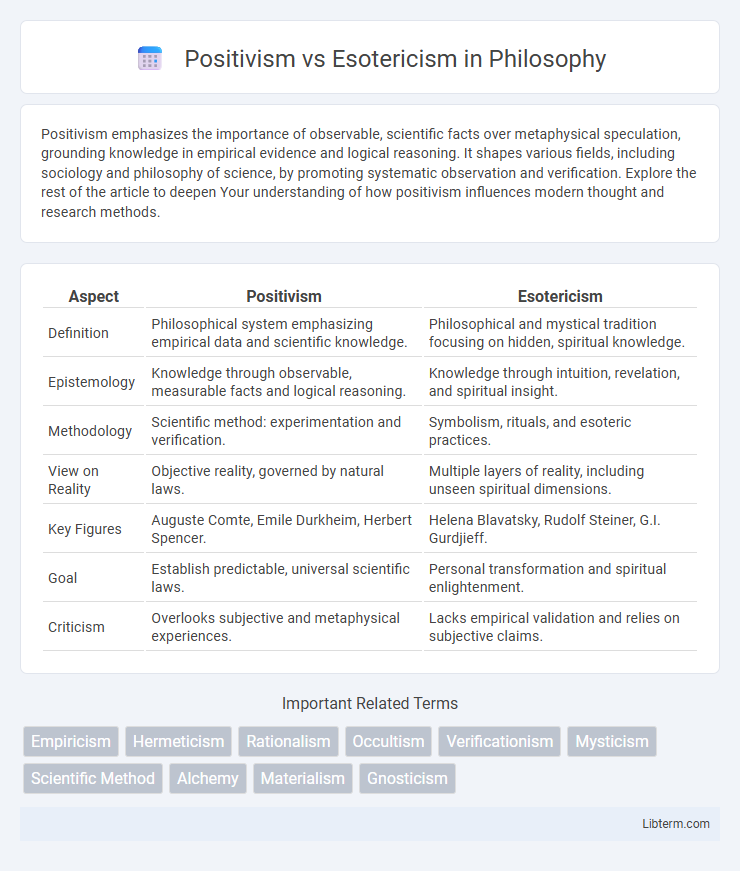
| Aspect | Positivism | Esotericism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical system emphasizing empirical data and scientific knowledge. | Philosophical and mystical tradition focusing on hidden, spiritual knowledge. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge through observable, measurable facts and logical reasoning. | Knowledge through intuition, revelation, and spiritual insight. |
| Methodology | Scientific method: experimentation and verification. | Symbolism, rituals, and esoteric practices. |
| View on Reality | Objective reality, governed by natural laws. | Multiple layers of reality, including unseen spiritual dimensions. |
| Key Figures | Auguste Comte, Emile Durkheim, Herbert Spencer. | Helena Blavatsky, Rudolf Steiner, G.I. Gurdjieff. |
| Goal | Establish predictable, universal scientific laws. | Personal transformation and spiritual enlightenment. |
| Criticism | Overlooks subjective and metaphysical experiences. | Lacks empirical validation and relies on subjective claims. |
Understanding Positivism: A Brief Overview
Positivism is a philosophical doctrine emphasizing empirical evidence and scientific methods as the sole sources of authentic knowledge, rejecting metaphysical speculations. Originating in the 19th century through Auguste Comte's work, positivism advocates for observation, experimentation, and logical analysis to understand social and natural phenomena. This approach contrasts sharply with esotericism, which relies on hidden meanings, mystical experiences, and spiritual insights beyond empirical verification.
Defining Esotericism: Key Concepts
Esotericism encompasses hidden knowledge, mystical experiences, and symbolic interpretations often accessible only to a select few, contrasting sharply with positivism's reliance on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning. Key concepts include initiation, sacred texts, ritual practices, and the belief in transcendent truths beyond ordinary perception. These elements highlight esotericism's emphasis on personal spiritual transformation rather than objective verification.
Historical Roots of Positivism and Esotericism
Positivism emerged in the 19th century with Auguste Comte, emphasizing empirical science and observable phenomena as the basis of knowledge, rejecting metaphysics and speculation. Esotericism traces back to ancient mystery traditions, Gnosticism, and Hermeticism, focusing on hidden knowledge, spiritual insight, and inner transformation beyond empirical understanding. These contrasting historical roots reflect positivism's foundation in rationalism and scientific progress versus esotericism's emphasis on mystical experiences and secret wisdom.
Core Philosophical Differences
Positivism is grounded in empirical evidence and scientific methodology, asserting that knowledge must be derived from observable phenomena and logical reasoning. Esotericism emphasizes hidden meanings, mystical experiences, and spiritual insights inaccessible through sensory observation or rational analysis. The core philosophical divergence lies in positivism's reliance on external validation and esotericism's focus on inner, subjective understanding beyond empirical proof.
Methodologies: Scientific Rigor vs Mystical Insight
Positivism emphasizes methodologies grounded in empirical observation, experimentation, and logical analysis to ensure scientific rigor and reproducibility. Esotericism relies on mystical insight, symbolic interpretation, and experiential knowledge often derived from intuition, meditation, or spiritual practices. The contrast highlights a foundational divide between objective validation in positivism and subjective revelation in esoteric traditions.
Worldview and Approach to Knowledge
Positivism emphasizes empirical evidence and scientific methods as the sole basis for knowledge, advocating a worldview grounded in observable, measurable phenomena and logical reasoning. Esotericism, by contrast, embraces hidden, mystical, and spiritual insights, promoting a subjective worldview that values intuition, symbolic interpretation, and inner experiences beyond empirical validation. The positivist approach prioritizes objective, testable facts, while esotericism seeks deeper, often non-material truths accessible through personal or transcendent understanding.
Influence on Modern Thought and Society
Positivism, grounded in empirical science and observable phenomena, significantly shaped modern thought by promoting rationality, scientific methods, and technological advancement, influencing education, policy, and social reforms. In contrast, Esotericism emphasizes mystical knowledge and spiritual insights, impacting contemporary spiritual movements, alternative medicine, and cultural expressions that challenge mainstream rationalism. The tension between these paradigms fosters ongoing debates about the balance between scientific progress and the quest for deeper existential meaning in society.
Criticisms and Controversies
Positivism faces criticism for its strict reliance on empirical data and scientific methods, often being challenged for neglecting metaphysical and spiritual dimensions of human experience, which esotericism seeks to explore. Esotericism, on the other hand, attracts controversy due to its reliance on hidden knowledge, mystical interpretations, and practices that lack empirical validation, often being dismissed as pseudoscientific or irrational. Both perspectives spark debate over the nature of knowledge, with positivism emphasizing objective evidence and esotericism valuing subjective insight and symbolic meaning.
Areas of Overlap and Interaction
Positivism and esotericism overlap in their exploration of knowledge, with positivism emphasizing empirical evidence and scientific methods while esotericism delves into mystical, spiritual insights often inaccessible to traditional science. Both approaches interact in fields such as psychology and philosophy, where empirical research examines esoteric concepts like consciousness and altered states. This intersection fosters interdisciplinary dialogue, revealing how measurable phenomena can coexist with intangible experiences in human understanding.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Perspectives
Positivism, emphasizing empirical evidence and scientific methodology, remains a cornerstone in contemporary research, shaping data-driven decision-making and technological advancements. Esotericism, with its focus on hidden knowledge and spiritual insight, continues to influence cultural practices and alternative healing modalities, reflecting a growing public interest in holistic and non-materialistic worldviews. Future perspectives suggest a potential synthesis where positivist frameworks integrate esoteric concepts, fostering interdisciplinary approaches that address both measurable phenomena and subjective human experiences.
Positivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com