Mysticism explores the profound connection between the human soul and the divine, emphasizing direct personal experience beyond ordinary perception. Practices such as meditation, contemplation, and spiritual rituals foster deeper insight and transcendence. Discover how mysticism can enrich your inner journey by delving into its core principles throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
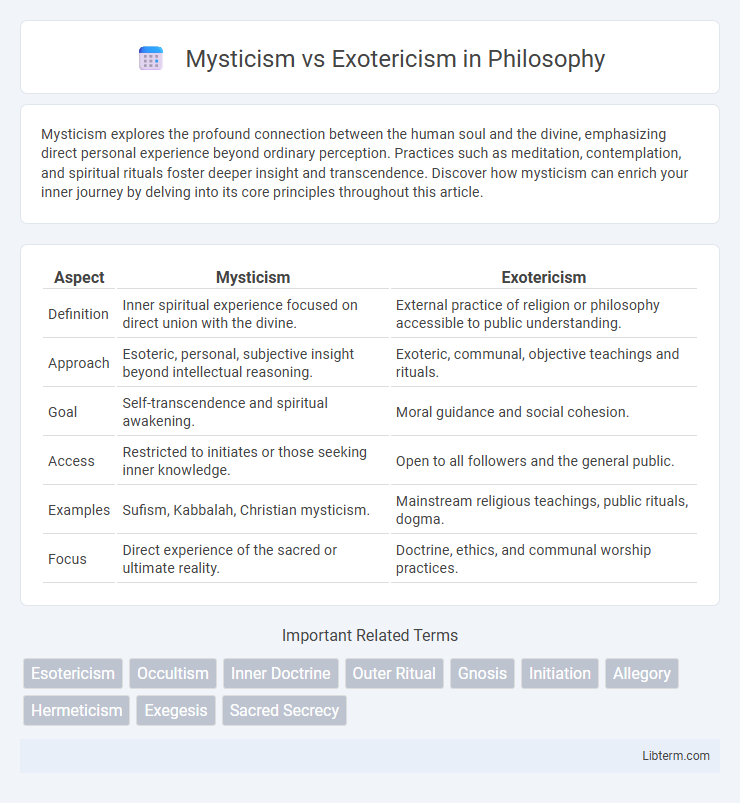
| Aspect | Mysticism | Exotericism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inner spiritual experience focused on direct union with the divine. | External practice of religion or philosophy accessible to public understanding. |
| Approach | Esoteric, personal, subjective insight beyond intellectual reasoning. | Exoteric, communal, objective teachings and rituals. |
| Goal | Self-transcendence and spiritual awakening. | Moral guidance and social cohesion. |
| Access | Restricted to initiates or those seeking inner knowledge. | Open to all followers and the general public. |
| Examples | Sufism, Kabbalah, Christian mysticism. | Mainstream religious teachings, public rituals, dogma. |
| Focus | Direct experience of the sacred or ultimate reality. | Doctrine, ethics, and communal worship practices. |
Understanding Mysticism: Key Concepts
Mysticism centers on the direct, experiential union with the divine or ultimate reality, emphasizing inner transformation and transcending ordinary consciousness. Core concepts include introspection, the role of meditation or contemplative practices, and the pursuit of spiritual insight beyond intellectual knowledge. Mystical traditions often highlight ineffability, the paradox of unity and duality, and a deeply personal connection to the sacred.
Defining Exotericism: Core Principles
Exotericism centers on accessible, outward religious practices and teachings designed for the general public, emphasizing communal rituals and clear moral codes. It seeks to convey spiritual knowledge through established doctrines, symbols, and ceremonies that reinforce social cohesion and cultural identity. Core principles include transparency, adherence to orthodox beliefs, and the dissemination of teachings in a form suitable for collective understanding.
Historical Origins of Mysticism and Exotericism
Mysticism traces its historical origins to ancient religious traditions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and early Christian Gnosticism, emphasizing inner spiritual experience and direct communion with the divine. Exotericism, rooted in organized religions and public doctrines like mainstream Christianity, Islam, and Judaism, focuses on external rituals, moral codes, and communal worship practices accessible to all adherents. The divergence between mysticism and exotericism highlights the contrast between esoteric knowledge reserved for initiates and exoteric teachings intended for broader societal adherence.
Inner Experience vs. Outer Practice
Mysticism emphasizes profound inner experience and direct personal encounter with the divine or ultimate reality, fostering transformation through contemplation and spiritual insight. Exotericism prioritizes outward rituals, communal practices, and codified teachings accessible to the broader public, ensuring religious or spiritual traditions are maintained and performed collectively. The distinction between mysticism's introspective journey and exotericism's external observance highlights complementary paths to spiritual understanding and expression.
Symbols, Rituals, and Language
Symbols in mysticism convey profound inner experiences and spiritual truths, often requiring personal insight for comprehension, while exotericism uses symbols as accessible tools for communal identity and shared meaning. Rituals in mysticism aim to transform consciousness and facilitate direct encounters with the divine, contrasting with exoteric rituals that emphasize social cohesion, tradition, and external observance. Language in mysticism is typically metaphorical and symbolic, designed to evoke ineffable states, whereas exoteric language tends to be literal and descriptive, serving educational and doctrinal purposes.
Accessibility: Private Insight or Public Doctrine?
Mysticism centers on private insight and personal spiritual experiences accessible primarily through inner practices and contemplation, emphasizing direct, often secretive knowledge. Exotericism promotes public doctrine and communal teachings, making spiritual or religious knowledge widely accessible and structured for collective understanding. This fundamental difference highlights mysticism's intimate, subjective approach contrasted with exotericism's open, organized dissemination of beliefs.
Roles of Authority and Tradition
Mysticism emphasizes direct, personal experience of the divine, often challenging established authority by valuing inner revelation over institutional doctrine. Exotericism upholds structured teachings and communal traditions, relying on religious hierarchies to preserve and transmit sacred knowledge. The tension between mysticism and exotericism reflects differing roles of authority: mysticism privileges individual spiritual insight, while exotericism reinforces collective rituals and orthodoxy.
Impact on Spiritual Communities
Mysticism fosters deep personal spiritual experiences and inner transformation, often leading to exclusive, tightly-knit communities centered on individual enlightenment. Exotericism emphasizes external rituals, shared beliefs, and inclusive practices, promoting broader community participation and cohesion. The contrasting approaches shape spiritual communities by either prioritizing inward, esoteric wisdom or outward, accessible expressions of faith.
Controversies and Misconceptions
Mysticism often faces controversy for its emphasis on personal, ineffable experiences that resist empirical validation, contrasting with exotericism's reliance on publicly accessible teachings and rituals. Misconceptions arise when mysticism is dismissed as purely irrational or when exotericism is seen as superficial, ignoring the complex interplay where both seek spiritual understanding through different means. Scholars debate the boundaries and overlaps between the two, highlighting challenges in categorizing spiritual practices within rigid frameworks.
Relevance of Mysticism and Exotericism Today
Mysticism and exotericism remain highly relevant today, with mysticism offering profound insights into personal spiritual experiences and inner transformation, while exotericism provides accessible frameworks for communal religious practices and societal ethics. The balance between mystical knowledge and exoteric teachings helps individuals navigate modern existential questions and fosters intercultural understanding in increasingly diverse societies. Their complementary roles support both individual enlightenment and collective cohesion in contemporary spiritual landscapes.
Mysticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com