Determinate refers to something having a fixed or defined limit, extent, or nature, often used in science and mathematics to describe values or conditions that are precisely known. This concept ensures clarity and predictability, distinguishing it from indeterminate states that lack exact boundaries. Discover how understanding determinate elements impacts various fields and why it matters to your knowledge.
Table of Comparison
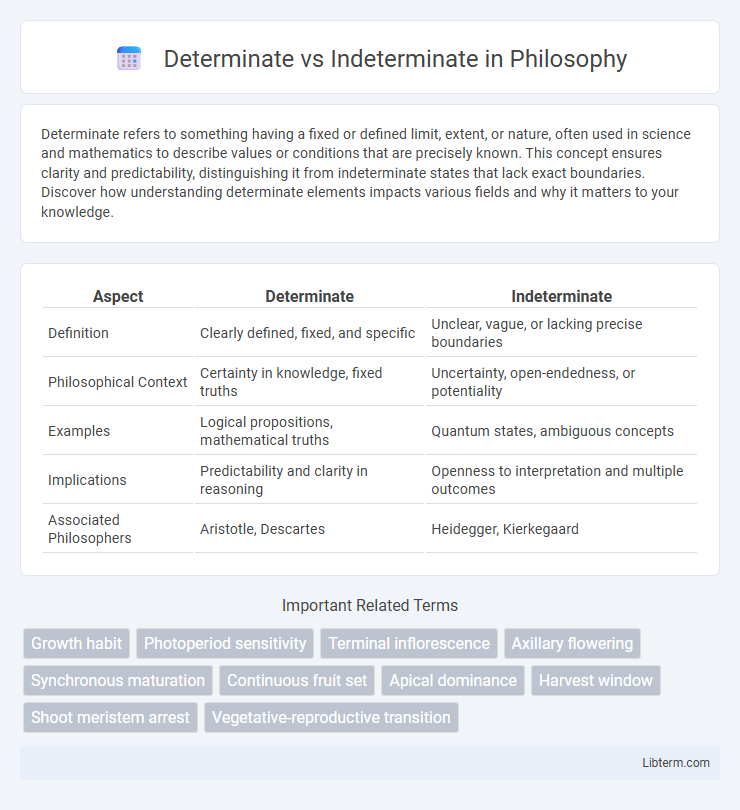
| Aspect | Determinate | Indeterminate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clearly defined, fixed, and specific | Unclear, vague, or lacking precise boundaries |
| Philosophical Context | Certainty in knowledge, fixed truths | Uncertainty, open-endedness, or potentiality |
| Examples | Logical propositions, mathematical truths | Quantum states, ambiguous concepts |
| Implications | Predictability and clarity in reasoning | Openness to interpretation and multiple outcomes |
| Associated Philosophers | Aristotle, Descartes | Heidegger, Kierkegaard |
Introduction to Determinate and Indeterminate
Determinate tomato plants exhibit a compact growth habit, typically reaching a fixed mature height and producing fruit within a shorter timeframe, making them ideal for container gardening and limited spaces. Indeterminate tomato plants continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the growing season, often reaching taller heights and requiring staking or support structures. Understanding the growth patterns of determinate and indeterminate tomatoes is essential for selecting the right variety based on space, harvest goals, and maintenance preferences.
Key Differences Between Determinate and Indeterminate
Determinate plants grow to a fixed mature size and then stop, producing fruit primarily in a single, concentrated harvest period, while indeterminate plants continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the growing season. Determinate varieties are typically bushier, making them ideal for container gardening and limited spaces, whereas indeterminate varieties have a vining growth habit requiring staking or trellising. The key difference lies in growth habit and fruit production timing, impacting harvest duration and cultivation methods.
Characteristics of Determinate Types
Determinate tomato plants exhibit a compact growth habit, typically reaching a fixed mature height of 3 to 4 feet, and produce fruit in a concentrated time frame, often within a few weeks. These varieties are predictable, making them ideal for container gardening and commercial harvesting due to their synchronized ripening. Their limited vine growth and early fruit set also reduce pruning needs and simplify care management.
Characteristics of Indeterminate Types
Indeterminate tomato plants exhibit continuous growth with vines that can reach several feet long, producing flowers and fruit throughout the growing season. These types require regular pruning and staking for optimal air circulation and support due to their sprawling habit. Indeterminate varieties are ideal for extended harvest periods, often yielding higher overall production compared to determinate types.
Growth Patterns Explained
Determinate plants exhibit a defined growth pattern, ceasing vertical expansion once they reach a certain size, concentrating energy on fruit production. Indeterminate plants continue growing and producing flowers throughout the growing season, enabling extended harvest periods. Understanding these growth patterns is vital for optimizing cultivation strategies and maximizing crop yields.
Advantages of Determinate Varieties
Determinate varieties offer the advantage of uniform fruit ripening, enabling efficient and simultaneous harvesting, which is ideal for commercial growers seeking streamlined production. Their compact growth habit requires less staking and maintenance, making them suitable for small spaces and reducing labor costs. Determinate plants also tend to have a concentrated fruit set, allowing for better pest and disease management throughout the growing season.
Benefits of Indeterminate Varieties
Indeterminate varieties continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the growing season, offering extended harvest periods and increased overall yield potential compared to determinate types. Their vining growth habit allows for larger plant size and more fruit clusters, which is advantageous for gardeners and commercial growers seeking prolonged production. The flexibility in harvesting times also reduces the risk of crop loss due to pest infestations or adverse weather conditions.
Choosing Between Determinate and Indeterminate
Choosing between determinate and indeterminate plant varieties depends on growing space, climate, and harvest timing preferences. Determinate plants, which grow to a fixed size and produce fruit simultaneously, suit limited garden areas and gardeners aiming for a concentrated harvest. Indeterminate plants continue growing and fruiting throughout the season, ideal for extended fresh produce supplies in larger spaces.
Common Examples and Applications
Determinate plants such as bush tomatoes and most beans stop growing once they reach a certain size, making them ideal for container gardening and short growing seasons. Indeterminate plants like tomatoes and cucumbers continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the season, suitable for vertical gardening and extended harvesting. Common applications in agriculture include determinate varieties for mechanized harvesting and indeterminate types for continuous fresh market supply.
Summary and Final Considerations
Determinate plants exhibit a fixed growth pattern, typically ceasing growth after reaching a certain size and producing fruit within a shorter timeframe, making them ideal for controlled environments and early harvests. Indeterminate plants continue to grow, flower, and produce fruit throughout the growing season, offering extended yields but requiring more space and support. Selecting between determinate and indeterminate varieties depends on factors such as available space, desired harvest period, and cultivation goals.
Determinate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com