Nominal values represent fixed or stated amounts that do not change with market conditions, often used in finance and economics to denote face value without adjusting for inflation. Understanding how nominal figures differ from real values can help you make more informed decisions regarding investments and budgeting. Explore the rest of the article to discover the practical implications of nominal data in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
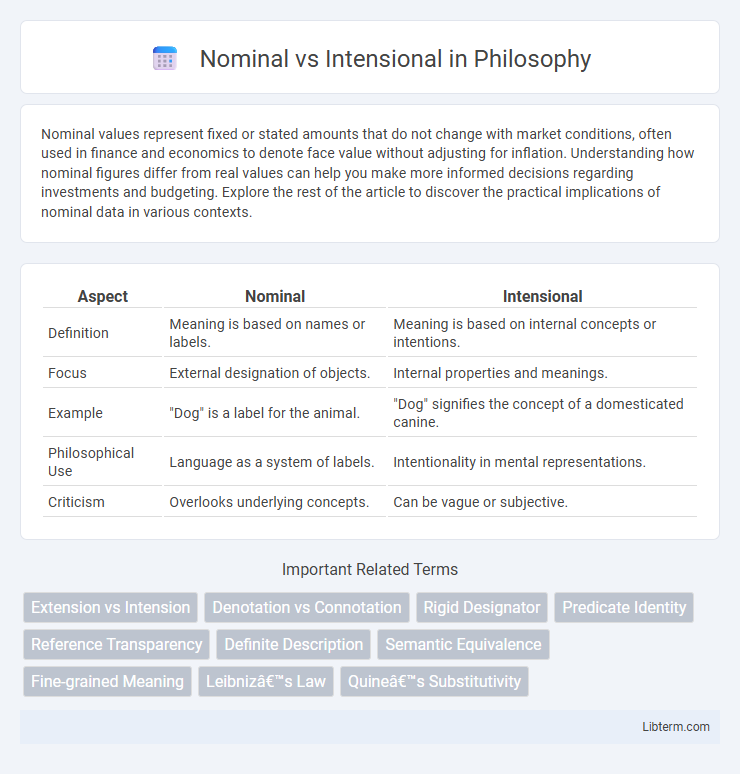
| Aspect | Nominal | Intensional |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meaning is based on names or labels. | Meaning is based on internal concepts or intentions. |
| Focus | External designation of objects. | Internal properties and meanings. |
| Example | "Dog" is a label for the animal. | "Dog" signifies the concept of a domesticated canine. |
| Philosophical Use | Language as a system of labels. | Intentionality in mental representations. |
| Criticism | Overlooks underlying concepts. | Can be vague or subjective. |
Understanding Nominal vs Intensional Definitions
Nominal definitions specify the meaning of a term by assigning it a name or label, focusing on linguistic usage rather than inherent properties. Intensional definitions describe the essential attributes or properties that an entity must have to fall under the defined concept, emphasizing necessary and sufficient conditions. Understanding the distinction helps clarify how terms are categorized and interpreted in logic, philosophy, and semantics.
Key Concepts: Nominal and Intensional Meaning
Nominal meaning refers to the explicit, dictionary definition or the literal sense of a word or phrase, focusing on its surface-level understanding. Intensional meaning involves the deeper, inherent properties or concepts that a term conveys, capturing the essence and context behind the nominal term. These distinctions are crucial in semantics for interpreting language accurately, as nominal meaning addresses explicit reference while intensional meaning concerns implicit conditions or attributes.
Historical Background of Nominal and Intensional Approaches
The historical background of nominal and intensional approaches traces back to the development of logic and semantics in the early 20th century, with nominalism rooted in medieval philosophy rejecting abstract universals in favor of individual entities. Intensional approaches emerged in the mid-20th century with the works of Rudolf Carnap and Richard Montague, focusing on meanings, properties, and context-dependent interpretations rather than mere extensions. These contrasting perspectives laid the foundation for modern theories in linguistic semantics, formal logic, and cognitive science.
Comparative Analysis: Nominal versus Intensional
Nominal and intensional approaches differ fundamentally in their treatment of meaning: nominal focuses on the explicit naming and classification of entities, while intensional emphasizes the underlying properties and concepts defining those entities. Comparative analysis reveals that nominal methods excel in straightforward categorization tasks due to their reliance on fixed labels, whereas intensional techniques provide greater flexibility by capturing the semantic relationships and contextual nuances. This contrast highlights the strengths of nominal for static taxonomies and intensional for dynamic or context-sensitive semantic modeling.
Examples of Nominal Definitions in Practice
Nominal definitions in practice often involve assigning a specific meaning to a term by stipulating its use within a particular context, such as defining "bachelor" as an unmarried man or a "triangle" as a three-sided polygon. These definitions aim to clarify language by specifying the exact criteria or conditions under which a term applies, without describing the essence or properties of the concept itself. For instance, a legal document may nominally define "vehicle" as any mode of transportation subject to registration, emphasizing practical classification over conceptual depth.
Illustrations of Intensional Definitions
Intensional definitions specify the essential properties or attributes that an object or concept must possess, providing a clear understanding of its nature. Illustrations of intensional definitions include defining a triangle as a polygon with three sides or water as a compound consisting of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. These examples emphasize the inherent characteristics that classify entities within a concept rather than merely listing instances, as in nominal definitions.
Advantages of Nominal Definitions
Nominal definitions offer clear advantages by providing precise and concise labels that facilitate effective communication and categorization within various disciplines. These definitions enable easier standardization and reduce ambiguity, making them essential for establishing consistent terminology in scientific research, law, and information systems. Their straightforward nature supports faster comprehension and application, enhancing clarity in educational and professional settings.
Benefits of Intensional Approaches
Intensional approaches enable precise modeling of concepts through definitions and properties rather than fixed labels, enhancing flexibility in knowledge representation. These methods support more effective reasoning and inference by capturing the inherent meaning of terms, facilitating better alignment with real-world contexts. Consequently, intensional approaches improve accuracy in semantic search, classification, and ontology development compared to nominal classification.
Limitations and Critiques: Nominal vs Intensional
Nominal approaches face limitations in capturing the underlying meanings or concepts behind terms, often leading to superficial categorization based only on labels or observable features. Intensional methods address this by emphasizing the inherent properties and definitions that constitute a concept, but they can be criticized for complexity and subjectivity in defining these inherent qualities. Both approaches struggle with boundary cases where clear distinctions between nominal labels and intensional meanings blur, challenging consistent application in knowledge representation and linguistic analysis.
Practical Implications and Applications
Nominal and intensional definitions differ fundamentally in their practical implications: nominal definitions provide explicit labels or names facilitating categorization and communication, essential for data labeling and database management, while intensional definitions focus on the inherent properties or criteria that determine category membership, crucial in rule-based systems and artificial intelligence for inference and decision-making. In software development, nominal definitions streamline coding by standardizing terms, whereas intensional definitions enable dynamic data classification and semantic search optimization. Understanding these distinctions enhances system design, ensuring accurate data processing and improved semantic clarity in applications like knowledge representation and ontology engineering.
Nominal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com