Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have similar meanings and can often be used interchangeably in various contexts without altering the intended message. Understanding synonymy enhances your vocabulary, allowing you to express ideas more precisely and avoid repetition in writing or speech. Explore the rest of this article to discover how mastering synonymy can improve your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
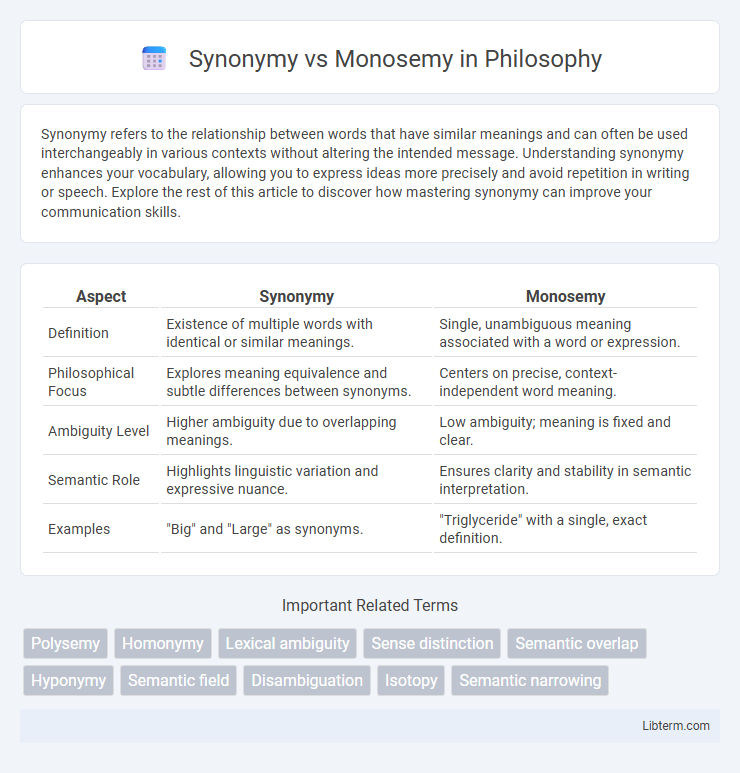
| Aspect | Synonymy | Monosemy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Existence of multiple words with identical or similar meanings. | Single, unambiguous meaning associated with a word or expression. |
| Philosophical Focus | Explores meaning equivalence and subtle differences between synonyms. | Centers on precise, context-independent word meaning. |
| Ambiguity Level | Higher ambiguity due to overlapping meanings. | Low ambiguity; meaning is fixed and clear. |
| Semantic Role | Highlights linguistic variation and expressive nuance. | Ensures clarity and stability in semantic interpretation. |
| Examples | "Big" and "Large" as synonyms. | "Triglyceride" with a single, exact definition. |
Introduction to Synonymy and Monosemy
Synonymy refers to the phenomenon where different words or expressions share the same or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," which enhances lexical variety in language. Monosemy describes words that have a single, clear meaning without ambiguity, like "photosynthesis," providing precise communication. Understanding the distinction between synonymy and monosemy is essential for lexical semantics, natural language processing, and effective language learning strategies.
Defining Synonymy: Meaning and Examples
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words with similar or identical meanings, such as "big" and "large," which convey comparable concepts in various contexts. These synonymous words allow for nuanced expression while maintaining semantic overlap, enhancing language flexibility and richness. Understanding synonymy helps in identifying interchangeable vocabulary that preserves meaning across sentences and discourse.
Understanding Monosemy: Concept and Illustration
Monosemy refers to a linguistic phenomenon where a word or expression possesses a single, unambiguous meaning, enhancing clarity and precision in communication. For example, the term "thermometer" consistently denotes an instrument used to measure temperature, leaving no room for alternative interpretations. Understanding monosemy is crucial for computational linguistics and natural language processing, as it facilitates accurate word sense disambiguation and semantic analysis.
Historical Perspectives on Semantic Relations
Historical perspectives on semantic relations reveal that synonymy has long been debated due to its apparent overlap in meaning between words, while monosemy emphasizes a single, distinct meaning for each lexical item. Early linguistic traditions from scholars such as Wilhelm von Humboldt stressed the uniqueness of word meanings, aligning with monosemy principles to avoid ambiguity in language analysis. Over time, semantic theories evolved to balance the nuanced spectrum between synonymy's subtle distinctions and monosemy's clarity, influencing modern approaches to lexicography and language processing.
Key Differences between Synonymy and Monosemy
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have similar or identical meanings, such as "big" and "large," allowing for interchangeable use in many contexts. Monosemy describes a word having a single, clear meaning without ambiguity, like "thermometer," which uniquely denotes an instrument measuring temperature. The key difference lies in synonymy involving multiple words with shared meanings, whereas monosemy involves one word with one unambiguous meaning.
Synonymy in Linguistic Theory
Synonymy in linguistic theory refers to the relationship between words that have identical or nearly identical meanings, such as "big" and "large," enabling nuanced expression and stylistic variation. This phenomenon challenges lexicographers and computational linguists to distinguish true synonyms from words with subtle semantic differences, impacting natural language processing tasks like word sense disambiguation. Research on synonymy enhances understanding of semantic hierarchies and lexical networks, contributing to more accurate thesauri and semantic databases.
Monosemy and Lexical Economy
Monosemy refers to a word having a single, clear meaning, which enhances lexical economy by reducing ambiguity and streamlining communication. This semantic precision supports efficient language processing and learning, making vocabulary acquisition more straightforward. In contrast to synonymy, where multiple words share similar meanings, monosemy promotes clarity and specificity in lexical choice.
Challenges in Identifying True Synonyms
Identifying true synonyms poses challenges due to subtle differences in connotation, context, and usage frequency that affect word interchangeability in natural language processing. Lexical ambiguity complicates automatic synonym detection, as words may share similar meanings in specific contexts but diverge semantically elsewhere. Advanced semantic analysis and contextual embedding models are essential for distinguishing monosemy from polysemy and accurately mapping synonym relationships in computational linguistics.
Practical Implications in Language Learning
Synonymy involves multiple words with similar meanings, which can enhance vocabulary depth but may cause confusion in language learning due to subtle differences in usage and connotation. Monosemy, where a word has a single clear meaning, simplifies comprehension and reduces ambiguity, aiding beginners in grasping foundational vocabulary more easily. Understanding these distinctions helps educators design targeted learning strategies, optimizing both vocabulary acquisition and contextual application for learners at varying proficiency levels.
Conclusion: The Role of Synonymy and Monosemy in Semantics
Synonymy enhances semantic richness by providing multiple lexical options with similar meanings, facilitating nuanced expression and language flexibility. Monosemy contributes clarity and precision by assigning a single, unambiguous meaning to a word, reducing interpretive confusion. Together, synonymy and monosemy balance variety and exactness, playing crucial roles in effective communication and semantic interpretation.
Synonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com