Formal argumentation employs structured reasoning to support claims using clear premises and logical conclusions, ensuring validity and soundness in debates or discussions. This method enhances critical thinking by requiring evidence-based statements and the avoidance of fallacies. Discover how mastering formal argumentation can improve your persuasive skills throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
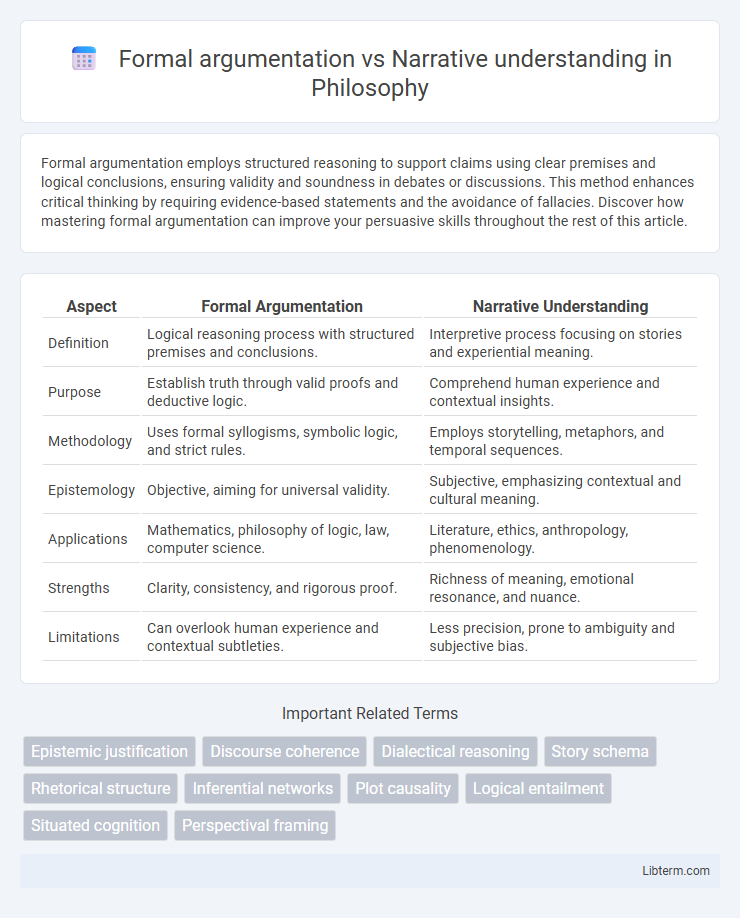
| Aspect | Formal Argumentation | Narrative Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical reasoning process with structured premises and conclusions. | Interpretive process focusing on stories and experiential meaning. |
| Purpose | Establish truth through valid proofs and deductive logic. | Comprehend human experience and contextual insights. |
| Methodology | Uses formal syllogisms, symbolic logic, and strict rules. | Employs storytelling, metaphors, and temporal sequences. |
| Epistemology | Objective, aiming for universal validity. | Subjective, emphasizing contextual and cultural meaning. |
| Applications | Mathematics, philosophy of logic, law, computer science. | Literature, ethics, anthropology, phenomenology. |
| Strengths | Clarity, consistency, and rigorous proof. | Richness of meaning, emotional resonance, and nuance. |
| Limitations | Can overlook human experience and contextual subtleties. | Less precision, prone to ambiguity and subjective bias. |
Defining Formal Argumentation
Formal argumentation is a structured approach to reasoning that utilizes well-defined rules and logical frameworks to evaluate the validity and soundness of arguments. It emphasizes clarity, consistency, and the systematic analysis of premises and conclusions, often employing symbolic logic and formal languages. This method contrasts with narrative understanding, which prioritizes context, interpretation, and the subjective meaning conveyed through storytelling.
Exploring Narrative Understanding
Narrative understanding emphasizes interpreting stories by capturing characters' motivations, contexts, and emotional dynamics, which contrasts with the rigid logic of formal argumentation. Through analyzing plot structures, causal relationships, and thematic elements, narrative understanding enables a more holistic comprehension of human experiences and social interactions. This approach leverages cognitive and linguistic frameworks to decode meaning from narratives, enriching communication beyond formal logical constructs.
Core Principles of Formal Argumentation
Formal argumentation centers on structured reasoning using clear premises, logical rules, and valid inferences to derive conclusions with rigor and precision. Core principles include validity, soundness, and argument strength, ensuring that arguments are both logically coherent and factually supported. This approach contrasts with narrative understanding, which emphasizes context, experience, and subjective interpretation over strict logical form.
Key Elements of Narrative Comprehension
Narrative understanding centers on key elements such as plot structure, character development, and causal relationships, which enable the reader to construct a coherent mental representation of the story. Unlike formal argumentation that relies on logical premises and conclusions, narrative comprehension emphasizes the integration of temporal sequences and thematic coherence to infer meaning. These elements facilitate empathy and predict outcomes, enriching the interpretive experience beyond objective analysis.
Cognitive Processes in Argumentation
Formal argumentation relies on structured logic and rule-based reasoning to evaluate claims and evidence, engaging analytical cognitive processes such as critical thinking, deduction, and systematic evaluation. Narrative understanding activates episodic memory and empathy, utilizing cognitive functions related to storytelling, perspective-taking, and contextual interpretation to grasp meaning within arguments. These distinct cognitive processes highlight the dual pathways through which humans process and assess information, balancing logical rigor with experiential insight.
Cognitive Processes in Narrative Engagement
Formal argumentation engages analytical cognitive processes, emphasizing logical reasoning, critical evaluation, and structured evidence assessment. Narrative understanding activates experiential cognition, involving empathy, memory integration, and emotional resonance to create immersive narrative engagement. Cognitive processing in narrative engagement often incorporates mental simulation and theory of mind to interpret characters' intentions and predict outcomes.
Strengths and Limitations of Formal Argumentation
Formal argumentation excels in clarity and logical rigor, enabling precise evaluation of premises and conclusions through structured frameworks such as deductive and inductive reasoning. Its limitations are evident in handling complex, context-dependent human experiences, where rigidity may overlook nuanced interpretations and emotional subtleties inherent in narrative understanding. While formal argumentation enhances critical analysis and objective assessment, it often struggles to capture the richness and depth of meaning conveyed through storytelling and subjective perspectives.
Strengths and Limitations of Narrative Understanding
Narrative understanding excels in capturing human experiences, emotions, and contextual nuances that formal argumentation often overlooks, making it powerful for empathy and meaning-making. Its limitations include susceptibility to bias, subjective interpretation, and less precision in logical rigor compared to formal argumentation frameworks. This approach thrives in scenarios demanding cultural sensitivity and storytelling but struggles with abstract, universally valid conclusions required in scientific or legal reasoning.
Applications in Education and Communication
Formal argumentation enhances critical thinking and logical reasoning skills in education by teaching students structured debate and evidence evaluation, which improves academic performance and decision-making. Narrative understanding fosters empathy and engagement through storytelling, making complex concepts more relatable and memorable in communication settings. Integrating both approaches creates a balanced educational environment where learners develop analytical abilities alongside emotional intelligence, optimizing comprehension and information retention.
Integrating Argumentation and Narrative Approaches
Integrating formal argumentation and narrative understanding enhances critical thinking by combining structured logic with contextual storytelling. This approach leverages argumentation frameworks like Toulmin's model alongside narrative techniques to facilitate coherent evidence presentation and emotional engagement. Bridging these methods supports richer knowledge construction and more effective communication in fields such as law, education, and artificial intelligence.
Formal argumentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com