Practical reason enables individuals to make decisions based on real-world considerations and tangible outcomes, emphasizing logic and efficiency over abstract theory. It plays a crucial role in problem-solving and everyday decision-making, guiding actions that align with achievable goals. Explore the rest of the article to understand how practical reason shapes your choices and influences effective reasoning.
Table of Comparison
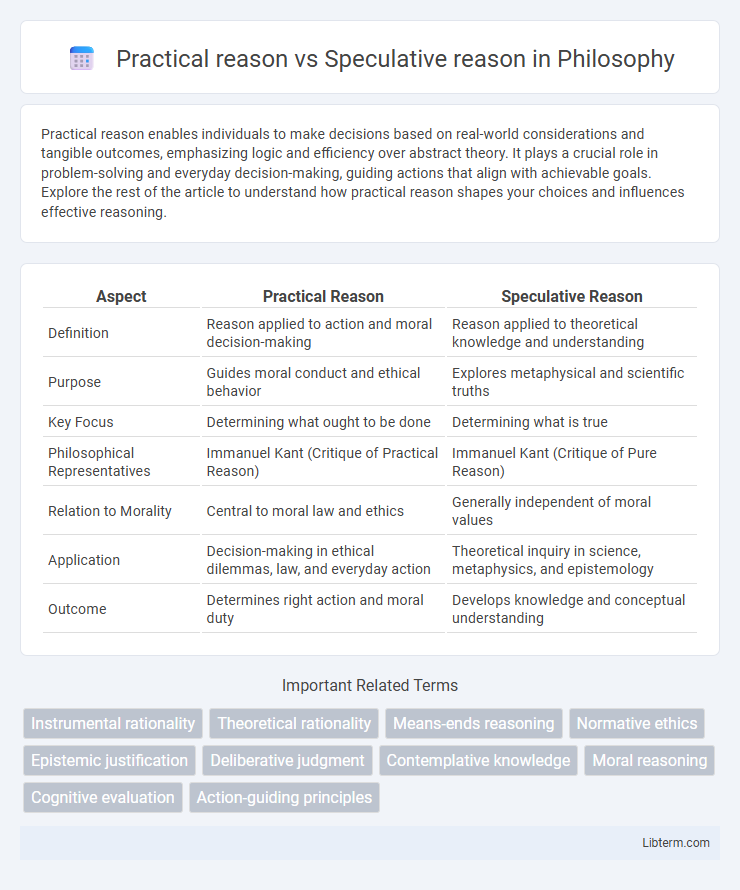
| Aspect | Practical Reason | Speculative Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reason applied to action and moral decision-making | Reason applied to theoretical knowledge and understanding |
| Purpose | Guides moral conduct and ethical behavior | Explores metaphysical and scientific truths |
| Key Focus | Determining what ought to be done | Determining what is true |
| Philosophical Representatives | Immanuel Kant (Critique of Practical Reason) | Immanuel Kant (Critique of Pure Reason) |
| Relation to Morality | Central to moral law and ethics | Generally independent of moral values |
| Application | Decision-making in ethical dilemmas, law, and everyday action | Theoretical inquiry in science, metaphysics, and epistemology |
| Outcome | Determines right action and moral duty | Develops knowledge and conceptual understanding |
Understanding Practical Reason: Definition and Scope
Practical reason refers to the capacity of the mind to decide upon actions based on moral principles and real-world goals, distinct from speculative reason which is concerned with theoretical knowledge and understanding. It involves deliberation about how to act in various situations, emphasizing ethical decision-making and purposeful behavior. The scope of practical reason encompasses ethics, law, and everyday decision-making, guiding individuals to align actions with values and societal norms.
What is Speculative Reason? Core Concepts Explained
Speculative reason involves the theoretical analysis of abstract concepts and aims to acquire knowledge for its own sake, focusing on metaphysics, epistemology, and logic. It engages in the investigation of universal truths and principles without immediate concern for practical application. Core concepts include the distinction between necessary and contingent truths, the pursuit of objective knowledge, and the use of deductive reasoning to understand the nature of reality.
Key Differences Between Practical and Speculative Reason
Practical reason involves decision-making and moral judgments aimed at guiding actions, whereas speculative reason focuses on theoretical inquiry and the pursuit of knowledge without direct concern for action. Practical reason addresses questions of what ought to be done, typically linked to ethics and human behavior, while speculative reason explores what is true, engaging with metaphysics, science, and logic. The key difference lies in their orientation: practical reason is action-oriented and normative, speculative reason is knowledge-oriented and descriptive.
Historical Perspectives on Reason in Philosophy
Historical perspectives on reason distinguish practical reason as the capacity guiding moral and ethical decisions, primarily explored by Immanuel Kant, who emphasized its role in autonomy and moral law formulation. Speculative reason, by contrast, pertains to theoretical understanding and knowledge acquisition, rooted in metaphysical inquiry as seen in the works of Aristotle and later German Idealists. This dichotomy shaped Enlightenment and post-Enlightenment philosophy, influencing debates on human cognition, ethics, and the limits of metaphysics.
Notable Philosophers on Practical vs Speculative Reason
Immanuel Kant significantly distinguished practical reason, which governs moral actions, from speculative reason, which aims at theoretical knowledge, emphasizing ethics and metaphysics respectively. G.W.F. Hegel built upon Kant by integrating practical and speculative reason within his dialectical method, seeing practical reason as the realization of freedom through ethical life. Contemporary philosopher Jurgen Habermas further expanded on this by highlighting communicative action's role in practical reason, contrasting it with the instrumental focus of speculative reason.
Real-World Examples of Practical Reason
Practical reason governs decision-making processes that involve moral judgments and actions, exemplified by a doctor choosing the best treatment for a patient based on ethical considerations and outcomes. In contrast, speculative reason seeks to understand theoretical truths, such as a physicist formulating laws of nature without immediate concern for practical application. Real-world examples of practical reason include a judge applying legal principles to deliver fair verdicts and a business leader making strategic choices that balance profit with social responsibility.
Applications of Speculative Reason in Theory
Speculative reason is primarily applied in theoretical contexts to explore metaphysical questions, formulate abstract principles, and develop frameworks for understanding the nature of reality beyond empirical observation. Its use is essential in disciplines like philosophy, mathematics, and theoretical physics, where it aids in constructing models and hypotheses that shape foundational knowledge. Unlike practical reason, which guides actions and decisions, speculative reason advances knowledge through contemplation and conceptual analysis, driving the formulation of theories that underpin scientific and philosophical inquiry.
The Role of Reason in Ethical Decision-Making
Practical reason directs ethical decision-making by applying principles to real-world contexts, enabling individuals to deliberate about moral actions and consequences. Speculative reason seeks theoretical understanding without immediate concern for action, focusing on knowledge and truth rather than ethical practice. In ethical contexts, practical reason bridges abstract moral concepts with concrete choices, guiding responsible and value-driven behavior.
Interplay Between Practical and Speculative Rationality
The interplay between practical and speculative reason reveals a dynamic relationship where speculative reason seeks theoretical knowledge and understanding of abstract principles, while practical reason applies these insights to ethical decision-making and action. Practical reason grounds speculative reason in real-world contexts, translating abstract concepts into moral imperatives and guiding behavior. This reciprocal interaction enriches both domains, ensuring that theoretical truths inform practical judgment and that lived experiences refine philosophical theories.
Conclusion: Integrating Practical and Speculative Reason
Integrating practical and speculative reason enhances decision-making by combining ethical considerations with theoretical insights, fostering well-rounded judgments. Practical reason guides actions based on moral values and goals, while speculative reason explores abstract truths and knowledge, creating a balance between doing and understanding. This synthesis supports comprehensive problem-solving, aligning purpose-driven actions with informed, reflective thinking.
Practical reason Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com