Logical reasoning enhances your ability to analyze information and solve problems systematically. Developing this skill improves decision-making and helps you construct clear, coherent arguments. Dive into the rest of the article to sharpen your logical reasoning abilities further.
Table of Comparison
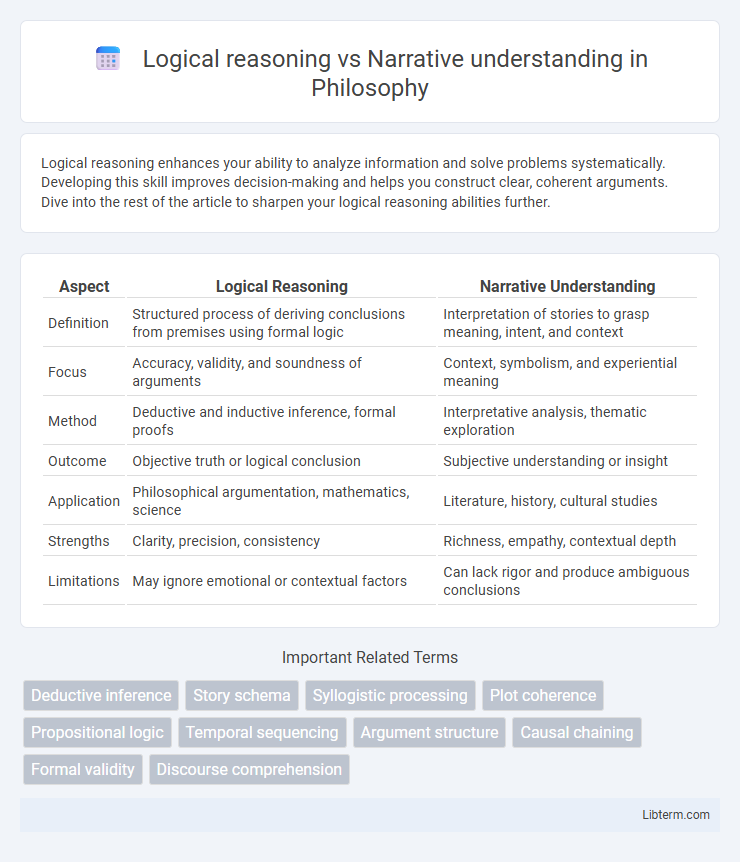
| Aspect | Logical Reasoning | Narrative Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured process of deriving conclusions from premises using formal logic | Interpretation of stories to grasp meaning, intent, and context |
| Focus | Accuracy, validity, and soundness of arguments | Context, symbolism, and experiential meaning |
| Method | Deductive and inductive inference, formal proofs | Interpretative analysis, thematic exploration |
| Outcome | Objective truth or logical conclusion | Subjective understanding or insight |
| Application | Philosophical argumentation, mathematics, science | Literature, history, cultural studies |
| Strengths | Clarity, precision, consistency | Richness, empathy, contextual depth |
| Limitations | May ignore emotional or contextual factors | Can lack rigor and produce ambiguous conclusions |
Introduction to Logical Reasoning and Narrative Understanding
Logical reasoning involves analyzing premises to draw valid conclusions through structured, rule-based thinking, crucial for problem-solving and decision-making tasks. Narrative understanding focuses on comprehending stories by interpreting characters, events, and contexts, emphasizing meaning and coherence in human communication. Both cognitive processes engage distinct mental frameworks: logical reasoning relies on formal logic, while narrative understanding draws on contextual and experiential knowledge.
Defining Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning involves the systematic evaluation of premises to reach a valid conclusion through deductive, inductive, or abductive methods. It emphasizes structured problem-solving based on formal rules, symbol manipulation, and critical analysis of arguments. This cognitive process contrasts with narrative understanding, which focuses on interpreting stories, contexts, and human experiences rather than abstract logic.
Defining Narrative Understanding
Narrative understanding involves interpreting stories by recognizing characters, motives, and plot structures to grasp the underlying meaning and emotional impact. Unlike logical reasoning, which relies on formal rules and objective analysis, narrative understanding emphasizes empathy, context, and the coherence of events over time. This cognitive process is crucial for effective communication, social interaction, and deriving lessons from complex human experiences.
Core Differences Between Logical and Narrative Thinking
Logical reasoning relies on structured, sequential thinking focused on facts, rules, and objective analysis, often used in problem-solving and decision-making processes. Narrative understanding emphasizes interpreting stories, context, and human experiences, highlighting emotions, motives, and subjective meaning. The core difference lies in logic's emphasis on clarity and consistency versus narrative's focus on coherence and meaning within a broader context.
Importance of Logical Reasoning in Everyday Life
Logical reasoning is crucial in everyday life as it enables individuals to make sound decisions by analyzing facts, identifying patterns, and drawing valid conclusions. It supports problem-solving in various contexts, from managing finances to making informed choices in professional and personal settings. Strong logical reasoning skills help in understanding complex information clearly, avoiding cognitive biases, and improving communication accuracy.
Role of Narrative Understanding in Communication
Narrative understanding plays a crucial role in communication by enabling individuals to interpret and convey complex experiences through stories, which foster emotional connections and shared meaning. Unlike logical reasoning, which focuses on structured arguments and factual accuracy, narrative understanding emphasizes context, perspective, and causality in human interactions. Effective communication relies on narrative competence to bridge gaps in knowledge, influence attitudes, and enhance empathy across diverse audiences.
Cognitive Processes Behind Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning engages cognitive processes such as working memory, pattern recognition, and analytical thinking to evaluate premises and derive valid conclusions. It involves systematic problem-solving techniques, applying formal rules of inference, and abstract rule manipulation to ensure coherence and consistency. Neural mechanisms primarily activate in the prefrontal cortex, supporting executive functions essential for deductive and inductive reasoning tasks.
Psychological Foundations of Narrative Comprehension
Logical reasoning involves structured problem-solving based on formal rules and abstract principles, while narrative understanding relies on interpreting stories through contextual and emotional cues. Psychological foundations of narrative comprehension emphasize the role of mental models, theory of mind, and memory integration in making sense of character intentions, plot coherence, and causal relationships. Research highlights that effective narrative understanding engages brain regions related to empathy and prediction, differentiating it from the more analytical processing seen in logical reasoning tasks.
Integrating Logic and Narrative for Effective Problem Solving
Integrating logical reasoning with narrative understanding enhances problem-solving by combining analytical precision with contextual insight, enabling a comprehensive approach to complex challenges. Logical reasoning structures arguments and evaluates evidence systematically, while narrative understanding captures human experiences and motivations, offering depth to otherwise abstract data. This fusion facilitates more effective decision-making by aligning quantitative analysis with qualitative storytelling, improving both clarity and persuasion in problem resolution.
Conclusion: Balancing Logical Reasoning and Narrative Understanding
Balancing logical reasoning and narrative understanding enhances decision-making by integrating analytical precision with contextual insight. Logical reasoning offers structured problem-solving skills, while narrative understanding provides empathy and perspective, enriching interpretation. Combining these cognitive approaches leads to more comprehensive and effective conclusions across diverse scenarios.
Logical reasoning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com