Absurdism explores the conflict between humans' desire to find inherent meaning in life and the universe's indifferent silence. It emphasizes accepting this paradox without despair, highlighting how embracing the absurd can lead to personal freedom and authenticity. Discover how understanding absurdism can transform your perspective by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
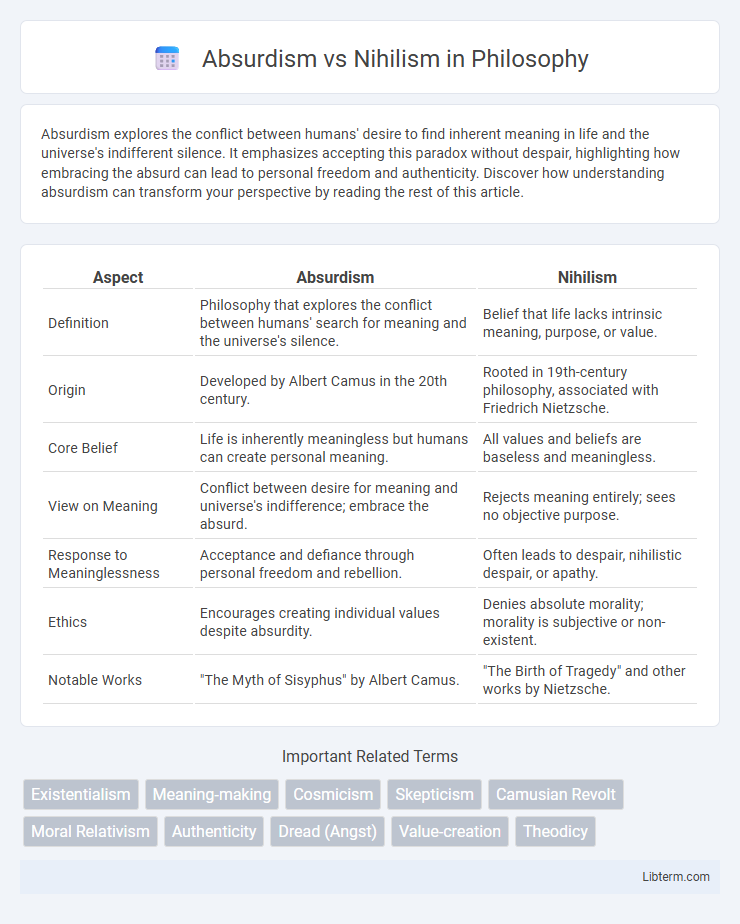
| Aspect | Absurdism | Nihilism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy that explores the conflict between humans' search for meaning and the universe's silence. | Belief that life lacks intrinsic meaning, purpose, or value. |
| Origin | Developed by Albert Camus in the 20th century. | Rooted in 19th-century philosophy, associated with Friedrich Nietzsche. |
| Core Belief | Life is inherently meaningless but humans can create personal meaning. | All values and beliefs are baseless and meaningless. |
| View on Meaning | Conflict between desire for meaning and universe's indifference; embrace the absurd. | Rejects meaning entirely; sees no objective purpose. |
| Response to Meaninglessness | Acceptance and defiance through personal freedom and rebellion. | Often leads to despair, nihilistic despair, or apathy. |
| Ethics | Encourages creating individual values despite absurdity. | Denies absolute morality; morality is subjective or non-existent. |
| Notable Works | "The Myth of Sisyphus" by Albert Camus. | "The Birth of Tragedy" and other works by Nietzsche. |
Understanding Absurdism: Core Concepts
Absurdism centers on the conflict between humans' inherent desire to find meaning and the universe's apparent indifference, highlighting the tension without seeking resolution. Key concepts include the acceptance of life's inherent absurdity and the freedom that emerges from confronting meaninglessness directly. Unlike nihilism, which often denies all meaning, absurdism embraces the paradox and encourages living authentically amidst uncertainty.
Nihilism Explained: Philosophical Foundations
Nihilism, rooted in the philosophical foundations laid by thinkers such as Friedrich Nietzsche and Jean-Paul Sartre, asserts the absence of inherent meaning, value, or purpose in life and the universe. This worldview challenges traditional beliefs and moral frameworks by positing that existence is fundamentally void of objective truth, leading to a rejection of absolute values and norms. Nihilism's impact spans existential philosophy, influencing debates on morality, ontology, and epistemology by emphasizing the subjective nature of meaning and confronting the void of objective significance.
Historical Roots of Absurdism and Nihilism
Absurdism originated in the 20th century, heavily influenced by existentialist philosophy and the works of Albert Camus, who emphasized the conflict between humans' desire for meaning and the indifferent universe. Nihilism traces back to 19th-century thinkers like Friedrich Nietzsche and Russian nihilists, focusing on the rejection of established moral values and the inherent meaninglessness of life. Both philosophies arose from critical responses to Enlightenment rationalism and the decline of religious authority in Western thought.
Key Thinkers in Absurdism: Camus and Beyond
Albert Camus, a pivotal figure in Absurdism, argued that life's inherent meaninglessness prompts a confrontation with the absurd without resorting to nihilism. Philosophers like Kierkegaard and Beckett expanded on Camus' ideas, embracing the absurd condition while seeking personal meaning and freedom. Absurdism distinguishes itself from nihilism by advocating for the creation of individual purpose despite the universe's indifference.
Major Nihilist Philosophers: Nietzsche and Others
Major nihilist philosophers like Friedrich Nietzsche challenge traditional values by proclaiming the "death of God," emphasizing the resulting void of inherent meaning in life. Nietzsche's concept of nihilism unveils the collapse of objective morality, urging the creation of personal values through the will to power. Other figures such as Arthur Schopenhauer and Jean-Paul Sartre also contribute to nihilistic thought by exploring themes of existential despair and meaninglessness without relying on cosmic or divine purpose.
Absurdism vs Nihilism: Key Differences
Absurdism centers on the inherent conflict between humans' desire for meaning and the chaotic, indifferent universe, emphasizing the struggle to find purpose despite this contradiction. Nihilism asserts that life is fundamentally meaningless, rejecting all religious, moral, and existential principles as baseless. Key differences lie in Absurdism's call to embrace the absurd condition and continue seeking meaning, whereas Nihilism often leads to the denial of meaning altogether.
Life’s Meaning: Contrasting Perspectives
Absurdism posits that life inherently lacks meaning, but humans continuously seek purpose, creating a tension between desire and reality that must be embraced. Nihilism asserts that life is entirely meaningless, rejecting all moral and existential values as baseless. While Absurdism encourages acceptance and personal rebellion against meaninglessness, Nihilism leads to complete negation of any value or purpose.
Impact on Modern Culture and Literature
Absurdism and nihilism have significantly shaped modern culture and literature by influencing existential themes and character archetypes. Absurdism, rooted in the belief that human efforts to find meaning are inherently futile, inspires works that highlight life's inherent contradictions and the search for personal significance, as seen in Albert Camus' "The Stranger." Nihilism, with its assertion that life lacks objective meaning or value, often manifests in darker, more existential narratives that question morality and purpose, influencing authors like Friedrich Nietzsche and modern postmodern literature.
Personal Responses to Absurdity and Meaninglessness
Personal responses to absurdity and meaninglessness vary significantly between Absurdism and Nihilism. Absurdism encourages embracing the inherent contradictions between human longing for meaning and the chaotic universe, promoting personal freedom and subjective meaning despite the absurd. In contrast, Nihilism often leads to the rejection of all inherent values and meanings, resulting in a more skeptical or despairing worldview regarding purpose and existence.
Absurdism and Nihilism Today: Relevance in Contemporary Thought
Absurdism, rooted in the works of Albert Camus, emphasizes the conflict between humans' search for meaning and an indifferent universe, influencing existential and ethical discussions in contemporary philosophy. Nihilism, with its assertion that life lacks inherent meaning or value, informs cultural critiques and challenges in postmodern thought, impacting art, literature, and social theory. Today, both philosophies highlight the tension between meaning-making and meaninglessness, shaping debates in psychology, ethics, and political theory.
Absurdism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com