Noesis and Dianoia represent different levels of thinking in philosophy, where Noesis signifies direct, intuitive understanding, and Dianoia refers to discursive, logical reasoning. These concepts are crucial for grasping how knowledge is structured and accessed through different cognitive processes. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how Noesis and Dianoia shape philosophical thought.
Table of Comparison
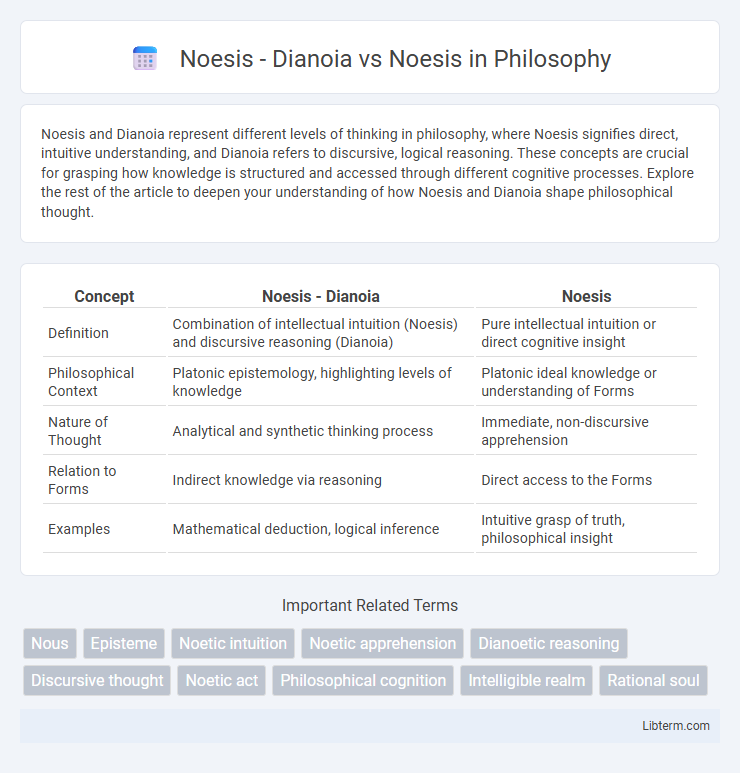
| Concept | Noesis - Dianoia | Noesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of intellectual intuition (Noesis) and discursive reasoning (Dianoia) | Pure intellectual intuition or direct cognitive insight |
| Philosophical Context | Platonic epistemology, highlighting levels of knowledge | Platonic ideal knowledge or understanding of Forms |
| Nature of Thought | Analytical and synthetic thinking process | Immediate, non-discursive apprehension |
| Relation to Forms | Indirect knowledge via reasoning | Direct access to the Forms |
| Examples | Mathematical deduction, logical inference | Intuitive grasp of truth, philosophical insight |
Introduction to Noesis and Dianoia
Noesis and Dianoia are key concepts in Platonic philosophy representing different modes of cognition. Noesis refers to direct, intuitive understanding or intellectual insight, often linked with grasping the Forms or ultimate realities. Dianoia, in contrast, denotes discursive reasoning and analytical thought, characterized by step-by-step logical processes used in mathematics and empirical investigation.
Defining Noesis: The Highest Form of Knowledge
Noesis represents the highest form of knowledge in classical philosophy, characterized by intuitive understanding and direct apprehension of truths without reliance on sensory experience or discursive reasoning. Unlike Dianoia, which involves analytical and logical thinking processes, Noesis embodies immediate cognition of eternal and unchanging realities, often linked to intellectual insight or pure thought. This concept, central to Platonic epistemology, highlights a transcendent mode of knowing that surpasses empirical observation and rational deduction.
Understanding Dianoia: Discursive Thought Explained
Dianoia, in classical philosophy, refers to discursive thought characterized by rational, step-by-step reasoning and logical analysis, often contrasted with noesis, which denotes immediate, intuitive understanding. Understanding dianoia involves recognizing its role in processes such as mathematical reasoning, scientific inquiry, and dialectical thinking, where conclusions are drawn through a sequence of premises. This form of cogitation emphasizes conceptual manipulation and systematic exploration, forming the basis of analytic cognition in epistemology.
Plato’s Divided Line: Where Noesis and Dianoia Belong
In Plato's Divided Line, Noesis represents the highest form of knowledge, characterized by direct intellectual insight into the Forms, while Dianoia involves discursive reasoning or mathematical thinking, situated just below Noesis in the realm of understanding. Noesis belongs to the intelligible segment focused on the Forms themselves, whereas Dianoia pertains to the realm of hypotheses and abstract reasoning, offering a step towards true knowledge but not complete apprehension. This division emphasizes the hierarchy in Platonic epistemology, where Noesis provides absolute, non-empirical comprehension and Dianoia serves as a methodical, rational intermediate stage.
Key Differences Between Noesis and Dianoia
Noesis refers to direct, intuitive understanding or intellectual insight, while dianoia involves discursive, analytical thinking or reasoning processes. Noesis captures immediate awareness of truths without mediation, whereas dianoia involves step-by-step conceptual elaboration and logical inference. These distinctions highlight noesis as immediate cognitive apprehension and dianoia as reflective, methodical thought.
The Role of Noesis in Philosophical Inquiry
Noesis, in philosophical inquiry, serves as the direct intellectual intuition or immediate awareness of concepts, contrasting with dianoia, which involves discursive reasoning and analytical thought processes. Noesis enables the apprehension of fundamental truths and essences without mediation, situating itself as the foundation for genuine knowledge in Platonic and phenomenological traditions. Its role is crucial for transcending mere opinion (doxa) and achieving true understanding (episteme) through an intuitive grasp of the forms or ideal objects of thought.
Dianoia’s Function in Everyday Reasoning
Dianoia in everyday reasoning functions as the process of discursive thinking, involving step-by-step analysis and logical deduction based on sensory experience and empirical data. It contrasts with Noesis, which refers to direct, intuitive intellectual apprehension of truths without intermediate reasoning. Dianoia enables practical problem-solving and decision-making by structuring thoughts through concepts, definitions, and syllogisms in daily cognitive tasks.
Noesis and Dianoia in Modern Cognitive Science
Noesis refers to the direct, intuitive apprehension of concepts, while dianoia involves analytical, discursive thinking, crucial in understanding cognitive processes. In modern cognitive science, noesis aligns with immediate perception and non-conceptual awareness, whereas dianoia corresponds to reasoning, problem-solving, and symbolic manipulation. Research on these modes illuminates the interplay between intuitive cognition and deliberate thought, enhancing models of human intelligence and decision-making.
Practical Implications of Noesis vs Dianoia
Noesis represents direct, intuitive knowledge or intellectual insight, whereas Dianoia involves discursive, analytical reasoning through logical processes. The practical implications of Noesis lie in its immediate grasp of truths and creative problem-solving without reliance on step-by-step analysis, benefiting fields like design and philosophy. In contrast, Dianoia supports structured decision-making, detailed planning, and systematic investigation essential in scientific research and engineering.
Conclusion: Integrating Noesis and Dianoia in Pursuit of Truth
Integrating Noesis and Dianoia fosters a comprehensive approach to truth by blending intuitive insight (Noesis) with analytical reasoning (Dianoia). This synthesis enables deeper understanding, as immediate intellectual apprehension complements methodical thought processes. Emphasizing their interdependence promotes balanced cognition essential for holistic knowledge acquisition and authentic truth comprehension.
Noesis - Dianoia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com