Noesis and nous both refer to aspects of intellect and understanding in philosophy, with noesis representing the act of direct, intuitive insight, while nous denotes the faculty of mind responsible for thinking and perceiving. These concepts are central to classical and modern discussions on cognition and consciousness, highlighting different dimensions of human intellect. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of how noesis and nous shape philosophical thought and influence your perception.
Table of Comparison
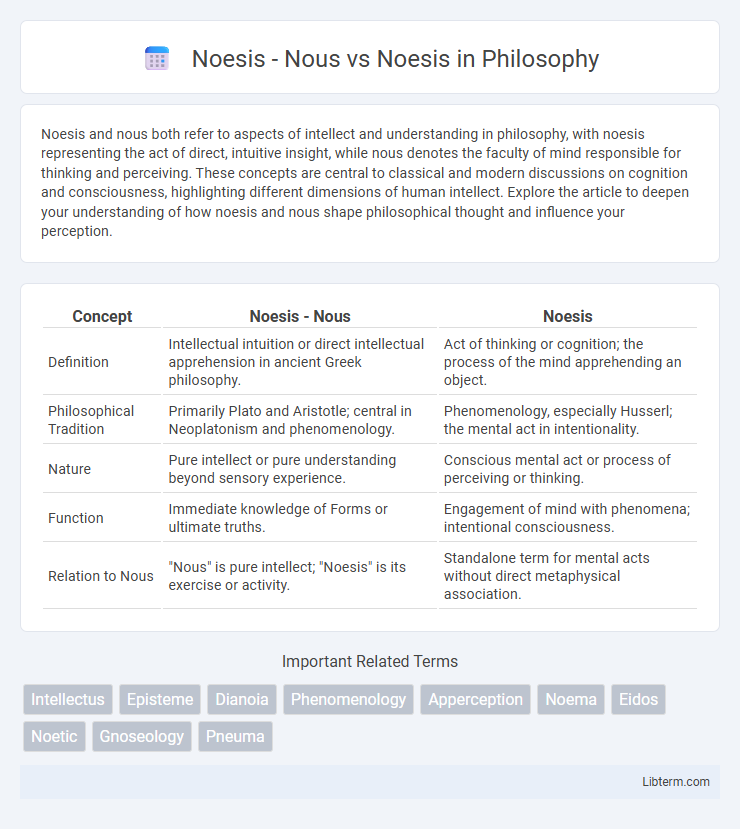
| Concept | Noesis - Nous | Noesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intellectual intuition or direct intellectual apprehension in ancient Greek philosophy. | Act of thinking or cognition; the process of the mind apprehending an object. |
| Philosophical Tradition | Primarily Plato and Aristotle; central in Neoplatonism and phenomenology. | Phenomenology, especially Husserl; the mental act in intentionality. |
| Nature | Pure intellect or pure understanding beyond sensory experience. | Conscious mental act or process of perceiving or thinking. |
| Function | Immediate knowledge of Forms or ultimate truths. | Engagement of mind with phenomena; intentional consciousness. |
| Relation to Nous | "Nous" is pure intellect; "Noesis" is its exercise or activity. | Standalone term for mental acts without direct metaphysical association. |
Understanding Noesis: Definition and Origins
Noesis originates from ancient Greek philosophy, referring to the faculty of intellectual insight or direct apprehension of truth, distinct from mere sensory perception. It involves the active process of the mind grasping the essence of objects or concepts through intuitive understanding rather than analytical reasoning. This concept forms a foundational element in phenomenology and epistemology, emphasizing the intrinsic link between consciousness and knowledge acquisition.
The Concept of Nous in Philosophy
The concept of Nous in philosophy refers to the faculty of intellect or divine mind responsible for true understanding and rational insight. Unlike Noesis, which denotes the act of thinking or the process of intellective apprehension, Nous embodies the underlying principle or source of intelligible knowledge. Philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle emphasize Nous as the foundational element in cognition that enables humans to grasp eternal truths beyond sensory experience.
Noesis vs Nous: Key Semantic Differences
Noesis refers to the intellectual apprehension or direct cognition of an object, emphasizing the act of thinking or understanding itself, whereas nous signifies the mind or intellect as an enduring faculty that enables perception and reasoning. In philosophical contexts, noesis is often the process of mental insight, while nous represents the foundational capacity for knowledge and consciousness. Distinguishing between noesis and nous is crucial for analyzing different layers of cognition, with noesis highlighting the dynamic act and nous the stable organ of intellect.
Historical Evolution: From Ancient Greece to Modern Thought
Noesis, originating in Ancient Greek philosophy, signifies the act of intellectual apprehension or pure thought, primarily explored by Plato and Aristotle in their metaphysical frameworks. Nous, often translated as "mind" or "intellect," represents the faculty of rational insight and was central to Stoic and Neoplatonic traditions, influencing the development of Western epistemology. Over time, the distinction between Noesis as an active cognitive process and Nous as the symbolic embodiment of intellect evolved, shaping contemporary philosophical and psychological theories of consciousness and knowledge acquisition.
Noesis in Phenomenology: Husserl’s Perspective
Noesis in Husserl's phenomenology refers to the intentional act of consciousness directed toward an object, highlighting the active process of perception and meaning-making. Husserl distinguishes noesis from noema, where noesis is the subjective act and noema is the intended content or object as it is experienced. This differentiation plays a crucial role in exploring the structures of experience and the foundation of knowledge within phenomenological analysis.
The Role of Noesis in Epistemology
Noesis in epistemology refers to the direct, intuitive act of cognition distinct from mere sensuous perception, often contrasted with the term Nous, which denotes the higher intellectual mind or reason. Noesis is crucial in understanding how knowledge is acquired through immediate awareness or insight, emphasizing the active engagement of the intellect in grasping essences and truths. This concept highlights the fundamental role of intellectual intuition in the formation and validation of knowledge claims within philosophical inquiry.
Applications of Noesis and Nous in Cognitive Science
Noesis in cognitive science refers to the direct intellectual apprehension or intuitive insight, often applied in understanding conscious experience and knowledge acquisition. Nous denotes the higher intellect or mind responsible for reasoning and abstract thought, playing a crucial role in theories of cognition and mental representation. Applications of noesis emphasize immediate, non-discursive awareness in perception and problem-solving, while nous is central to modeling reasoning processes, conceptual analysis, and the development of artificial intelligence frameworks.
Comparative Analysis: Noesis, Nous, and Intuition
Noesis represents the intellectual apprehension of truth through direct cognitive insight, whereas Nous is often described as the faculty of higher mind or the divine intellect in classical philosophy. Intuition, in contrast, involves immediate understanding without rational deliberation, acting as a subconscious form of knowledge acquisition. Comparative analysis reveals that Noesis and Nous emphasize active, intellectual comprehension, while intuition relies on instinctive awareness, highlighting distinct but interconnected modes of human cognition.
Noesis in Contemporary Philosophy and Psychology
Noesis in contemporary philosophy and psychology refers to the act of intellectual insight or direct apprehension of meaning, contrasting with Nous, which traditionally denotes a more abstract, universal intellect or mind. Scholars in cognitive science emphasize Noesis as the immediate, conscious experience underlying perception and understanding, integral to phenomenological and existential inquiries. The distinction highlights Noesis as the process of knowing, emphasizing subjective consciousness and intentionality central to modern philosophical psychology.
Conclusion: Bridging Noesis and Nous in Modern Discourse
Noesis and Nous represent complementary dimensions of intellect in philosophical contexts, with Noesis emphasizing the active process of understanding and Nous denoting the faculty of intuitive or rational insight. Bridging Noesis and Nous in modern discourse involves integrating analytical reasoning with intuitive comprehension to foster holistic cognitive awareness. This synthesis enhances critical thinking and innovation across disciplines such as cognitive science, philosophy, and epistemology.
Noesis - Nous Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com