Idiographic approaches focus on the detailed understanding of individual cases or events, emphasizing unique factors and personal experiences rather than general laws. This method is often used in psychology, anthropology, and history to capture the complexity of human behavior and cultural phenomena. Explore the rest of the article to discover how idiographic research can deepen your insight into personalized data analysis.
Table of Comparison
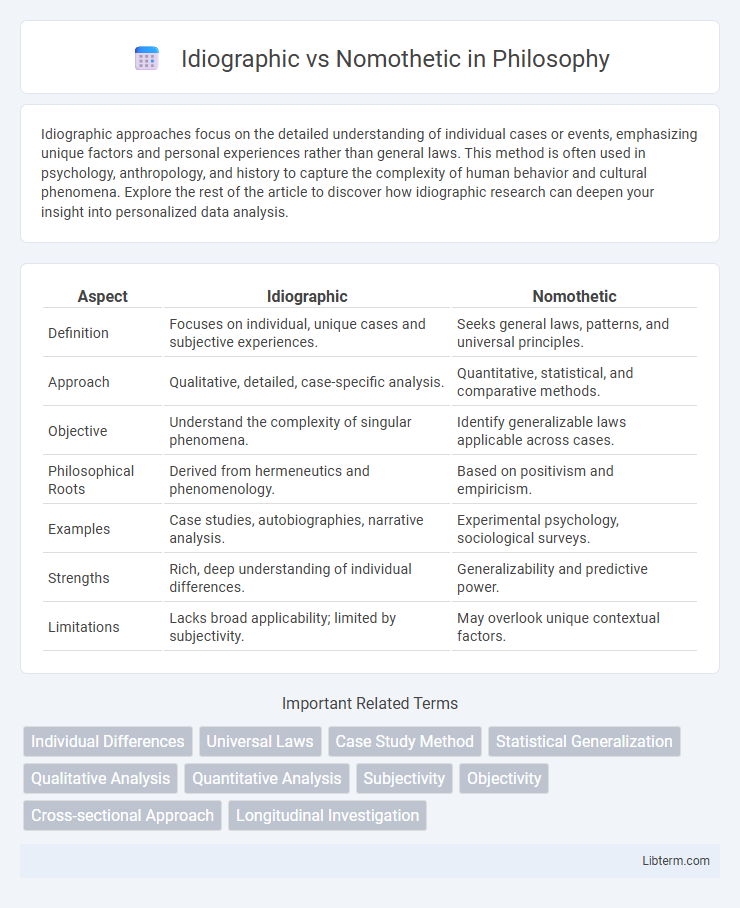
| Aspect | Idiographic | Nomothetic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on individual, unique cases and subjective experiences. | Seeks general laws, patterns, and universal principles. |
| Approach | Qualitative, detailed, case-specific analysis. | Quantitative, statistical, and comparative methods. |
| Objective | Understand the complexity of singular phenomena. | Identify generalizable laws applicable across cases. |
| Philosophical Roots | Derived from hermeneutics and phenomenology. | Based on positivism and empiricism. |
| Examples | Case studies, autobiographies, narrative analysis. | Experimental psychology, sociological surveys. |
| Strengths | Rich, deep understanding of individual differences. | Generalizability and predictive power. |
| Limitations | Lacks broad applicability; limited by subjectivity. | May overlook unique contextual factors. |
Introduction to Idiographic and Nomothetic Approaches
Idiographic and nomothetic approaches represent two fundamental methods in psychological research and social sciences for understanding human behavior. The idiographic approach emphasizes detailed, qualitative analysis of individual cases, aiming to capture the uniqueness and complexity of a single subject through methods such as case studies and narrative analysis. In contrast, the nomothetic approach seeks to identify general laws and patterns applicable across populations, relying on quantitative techniques like experiments and surveys to generate statistical generalizations.
Defining Idiographic: Focus on the Individual
Idiographic approaches prioritize the detailed understanding of individual cases, emphasizing unique personal experiences, traits, and behaviors over generalizations. This method seeks to capture the complexity of a single person by analyzing subjective data such as personal histories, qualitative interviews, and case studies. Idiographic research contrasts with nomothetic approaches by valuing depth over breadth, aiming to reveal insights specific to the individual rather than broad laws or universal principles.
Understanding Nomothetic: Emphasizing General Laws
Nomothetic approaches prioritize identifying general laws and patterns that apply broadly across populations, enabling the development of universal psychological theories. This method relies heavily on quantitative data, statistical analysis, and the search for consistent relationships between variables to explain behaviors. Emphasizing nomothetic research enhances predictive power and supports the creation of standardized assessments and interventions in fields like psychology and social sciences.
Historical Origins and Key Figures
Idiographic approaches originated with Wilhelm Windelband and Wilhelm Dilthey in the late 19th century, emphasizing the study of unique historical events and individual experiences. Nomothetic methods trace back to Auguste Comte and Emile Durkheim, who advocated for establishing general laws through empirical observation and statistical analysis. These foundational figures shaped the distinction between understanding the particularities of human life and identifying universal principles in social science.
Research Methods in Idiographic vs Nomothetic
Idiographic research methods emphasize in-depth, qualitative analysis of individual cases to capture unique personal experiences, often using case studies, interviews, and diaries. Nomothetic research methods employ quantitative techniques, such as experiments and surveys, to identify generalizable laws and patterns across large populations. The contrast lies in idiographic methods prioritizing subjective understanding, while nomothetic methods seek statistical regularities.
Strengths and Limitations of Idiographic Approach
The idiographic approach provides in-depth, detailed understanding of individual experiences, capturing the uniqueness and complexity that quantitative methods often overlook. Its strength lies in generating rich qualitative data through case studies and narrative analysis, allowing for personalized insights and advancing theories tailored to specific contexts. However, the idiographic approach faces limitations such as limited generalizability, potential researcher bias, and challenges in replicating findings across different populations or settings.
Strengths and Limitations of Nomothetic Approach
The nomothetic approach excels in identifying general laws and patterns by analyzing large data sets to create broad psychological theories applicable across populations. Its strength lies in its ability to produce quantifiable and replicable results, facilitating prediction and control of behavior. However, this approach often overlooks individual differences and subjective experiences, limiting its usefulness in understanding unique personal contexts and complex human behaviors.
Practical Applications in Psychology
Idiographic approaches in psychology emphasize individualized case studies and are extensively used in clinical settings for personalized therapy and tailored treatment plans. Nomothetic methods focus on generalized laws derived from large sample populations, facilitating the development of standardized psychological assessments and evidence-based interventions. Combining both approaches enhances diagnostic accuracy and improves mental health outcomes by integrating broad patterns with unique personal experiences.
Relevance in Contemporary Research
Idiographic approaches emphasize in-depth analysis of individual cases, providing rich, context-specific insights crucial for personalized interventions in psychology and social sciences. Nomothetic methods prioritize generalization through statistical analysis of large samples, enabling the identification of universal laws and patterns applicable across populations. Contemporary research increasingly integrates both, leveraging idiographic depth and nomothetic breadth to enhance the validity and applicability of findings in diverse fields such as clinical psychology, education, and behavioral science.
Integrating Idiographic and Nomothetic Perspectives
Integrating idiographic and nomothetic perspectives enhances psychological research by combining detailed individual case studies with generalizable population-level patterns, providing a comprehensive understanding of human behavior. Idiographic methods capture unique personal experiences through qualitative analyses, while nomothetic approaches utilize quantitative data to identify universal laws or trends. This integration facilitates personalized interventions grounded in broad empirical evidence, improving both theoretical models and practical applications in psychology.
Idiographic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com