Motivational force drives individuals to pursue goals by igniting internal desires and shaping external behaviors. Understanding this force helps you harness your energy and sustain focus in challenging situations. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how motivational force influences success and practical ways to enhance it.
Table of Comparison
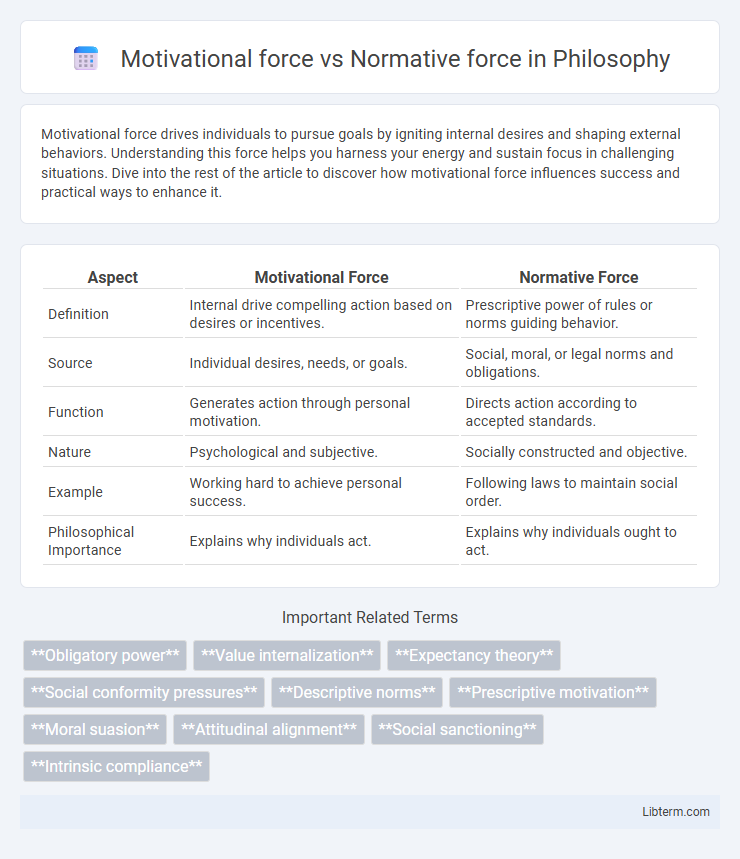
| Aspect | Motivational Force | Normative Force |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal drive compelling action based on desires or incentives. | Prescriptive power of rules or norms guiding behavior. |
| Source | Individual desires, needs, or goals. | Social, moral, or legal norms and obligations. |
| Function | Generates action through personal motivation. | Directs action according to accepted standards. |
| Nature | Psychological and subjective. | Socially constructed and objective. |
| Example | Working hard to achieve personal success. | Following laws to maintain social order. |
| Philosophical Importance | Explains why individuals act. | Explains why individuals ought to act. |
Understanding Motivational Force: Definition and Key Concepts
Motivational force refers to the internal drive that compels individuals to perform actions or adopt behaviors based on personal desires, beliefs, and goals, distinct from social obligations or external pressures. This force is crucial in shaping decision-making processes and behavioral intentions by aligning actions with intrinsic motivations rather than external norms. Understanding motivational force involves key concepts such as autonomy, self-determination, and individual value systems that influence goal-directed behavior within various psychological and organizational contexts.
What is Normative Force? An Overview
Normative force refers to the influence exerted by societal norms, values, and collective expectations that guide individuals' behavior and decision-making. It shapes actions by establishing what is considered appropriate or acceptable within a given social context, often reinforcing conformity and internalized rules. Unlike motivational force, which drives behavior through personal desires or goals, normative force operates through social pressure and shared standards.
Core Differences Between Motivational and Normative Forces
Motivational forces drive behavior based on personal desires, goals, and intrinsic rewards, emphasizing individual agency and psychological incentives. Normative forces, by contrast, shape behavior through social norms, cultural expectations, and collective values, enforcing conformity and social approval. The core difference lies in motivation stemming from internal personal factors versus external social pressures guiding decision-making.
Psychological Foundations of Motivational Force
Motivational force in psychology refers to the internal drives and desires that activate and sustain goal-directed behavior, rooted in intrinsic needs and personal values. It is significantly influenced by cognitive appraisals, emotional states, and self-determination theory, emphasizing autonomy and competence as core psychological foundations. Unlike normative force, which stems from social expectations and external pressures, motivational force originates within the individual's psyche, shaping persistence, effort, and goal commitment.
The Role of Social Norms in Shaping Behaviour
Social norms exert a powerful normative force that guides individual behavior by establishing expectations within a community, often leading people to conform to avoid social sanctions. Motivational force, on the other hand, drives behavior through internal desires and personal goals, occasionally conflicting with social norms. Understanding the interplay between normative force and motivational force is crucial for analyzing how social norms shape behaviors in contexts such as public health, environmental practices, and organizational conduct.
Motivational Force in Goal Setting and Achievement
Motivational force in goal setting drives individuals to initiate and sustain effort towards achieving specific objectives by generating intrinsic desires and aspirations. This force enhances persistence, focus, and resilience, directly influencing goal commitment and performance outcomes. Understanding motivational force enables the design of effective strategies that align personal values and rewards with goal attainment.
Normative Force in Cultural and Societal Contexts
Normative force in cultural and societal contexts shapes behavior by establishing shared expectations, values, and social norms that guide individual and group actions. It exerts influence through social approval, sanctions, and the internalization of cultural standards, reinforcing conformity and cohesion within communities. This force is critical in maintaining social order and transmitting cultural heritage across generations, impacting laws, traditions, and social roles.
Applications of Motivational and Normative Forces in the Workplace
Motivational forces in the workplace drive employee behavior through personal incentives such as rewards, recognition, and career advancement opportunities, enhancing productivity and job satisfaction. Normative forces influence workplace conduct by shaping employees' adherence to organizational values, ethical standards, and cultural norms, fostering a cohesive and compliant work environment. Applying both motivational and normative forces strategically boosts employee engagement, aligns individual actions with company objectives, and supports sustainable organizational success.
Case Studies: Motivational vs Normative Influences
Case studies highlight that motivational forces drive individuals by internal desires such as personal goals and aspirations, while normative forces operate through societal expectations and cultural norms. Research in consumer behavior demonstrates that motivational influences often result in unique, personalized decisions, whereas normative influences lead to conformity and adherence to group standards. Distinguishing these forces is essential for effectively tailoring interventions in marketing, organizational behavior, and social policy development.
Integrating Motivational and Normative Forces for Effective Change
Integrating motivational and normative forces is essential for effective organizational change, as motivational force drives individual willingness through incentives and personal goals, while normative force aligns behavior with shared values and social expectations. Research shows that blending both forces enhances commitment and reduces resistance by addressing both individual desires and collective norms. Leaders should design change strategies that simultaneously appeal to intrinsic motivation and reinforce cultural norms to sustain long-term transformation.
Motivational force Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com