Dualism explores the concept that reality consists of two fundamental and distinct substances, often characterized as mind and body or physical and non-physical entities. This philosophical view addresses how these substances interact and influence each other, posing questions about consciousness, identity, and existence. To understand how dualism shapes perspectives in metaphysics and cognitive science, continue reading the article.
Table of Comparison
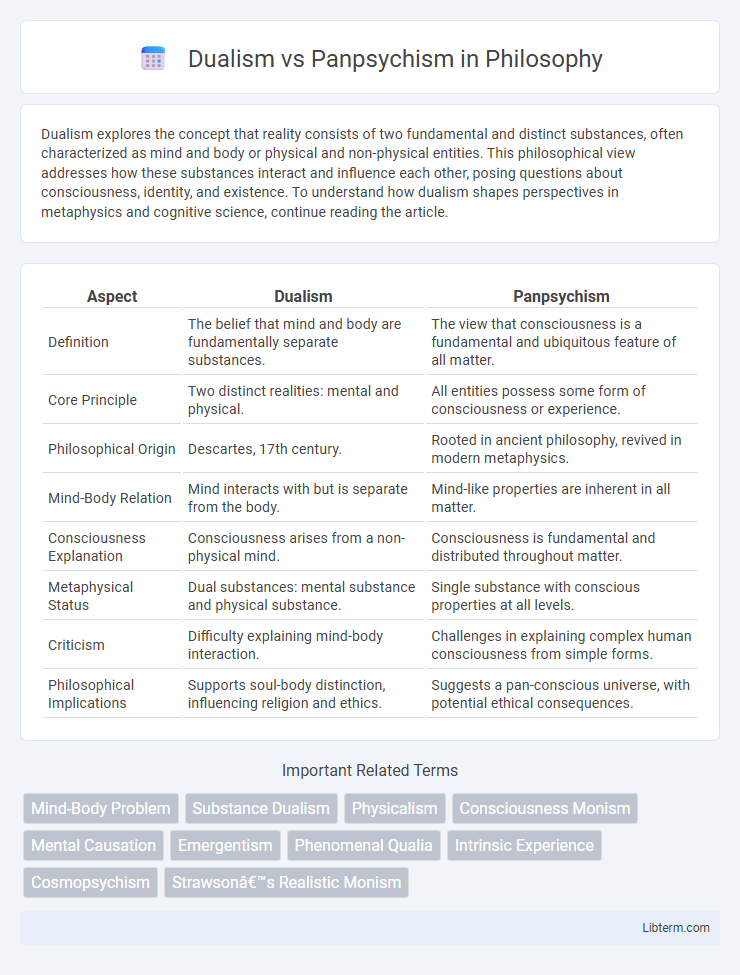
| Aspect | Dualism | Panpsychism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The belief that mind and body are fundamentally separate substances. | The view that consciousness is a fundamental and ubiquitous feature of all matter. |
| Core Principle | Two distinct realities: mental and physical. | All entities possess some form of consciousness or experience. |
| Philosophical Origin | Descartes, 17th century. | Rooted in ancient philosophy, revived in modern metaphysics. |
| Mind-Body Relation | Mind interacts with but is separate from the body. | Mind-like properties are inherent in all matter. |
| Consciousness Explanation | Consciousness arises from a non-physical mind. | Consciousness is fundamental and distributed throughout matter. |
| Metaphysical Status | Dual substances: mental substance and physical substance. | Single substance with conscious properties at all levels. |
| Criticism | Difficulty explaining mind-body interaction. | Challenges in explaining complex human consciousness from simple forms. |
| Philosophical Implications | Supports soul-body distinction, influencing religion and ethics. | Suggests a pan-conscious universe, with potential ethical consequences. |
Introduction to Mind-Body Philosophies
Mind-body philosophies explore the relationship between consciousness and the physical body, with dualism asserting that mind and body are fundamentally distinct substances. Panpsychism posits that consciousness is a universal feature inherent in all matter, suggesting a continuum rather than a strict separation. These perspectives address the challenge of explaining subjective experience within the framework of physical reality.
Defining Dualism: Mind and Matter
Dualism posits that mind and matter are fundamentally distinct substances, with the mind characterized by non-physical consciousness and the body composed of physical matter. This philosophical doctrine asserts that mental phenomena cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone, establishing a clear ontological divide between mental states and material entities. Rene Descartes' Cartesian dualism famously encapsulates this view, distinguishing res cogitans (thinking substance) from res extensa (extended substance).
Key Principles of Panpsychism
Panpsychism posits that consciousness is a fundamental and ubiquitous feature of the universe, with all matter possessing some form of experiential quality. Unlike dualism, which separates mind and matter into distinct substances, panpsychism integrates consciousness as an intrinsic property of physical entities, from subatomic particles to complex organisms. This principle challenges traditional materialist views by suggesting that mental aspects are pervasive throughout the natural world, potentially bridging the explanatory gap between physical processes and subjective experience.
Historical Origins and Founding Thinkers
Dualism traces back to Plato and was systematically developed by Rene Descartes, who distinguished mind and body as fundamentally separate substances. Panpsychism, with roots in pre-Socratic philosophers like Thales and later revived by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, posits that consciousness is a fundamental and ubiquitous feature of the universe. Both frameworks address the mind-body problem but differ in attributing mental properties either solely to human minds or universally to all matter.
Dualism: Arguments For and Against
Dualism posits the existence of two distinct substances: mind and matter, with proponents arguing that subjective experience cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone, as exemplified by Descartes' famous cogito argument and the explanatory gap concerning consciousness. Critics of dualism highlight the interaction problem, questioning how immaterial minds can causally affect physical bodies, and emphasize advances in neuroscience that increasingly correlate mental states with brain activity, challenging the need for a non-physical mind. The debate remains central in philosophy of mind, driving discussions about the nature of consciousness, mental causation, and the limits of scientific explanation.
Panpsychism: Evidence and Debates
Panpsychism posits that consciousness is a fundamental feature of all matter, supported by recent findings in quantum physics suggesting that particles may exhibit proto-conscious properties. Debates center on its explanatory power for the mind-body problem, contrasting with dualism's strict separation of mind and matter. Critics argue that panpsychism faces challenges in empirically validating subjective experiences at the atomic level, while proponents highlight its potential to unify consciousness with physical reality.
Consciousness Explained: Dualist vs Panpsychist Perspectives
Dualism posits consciousness as an immaterial substance distinct from the physical brain, emphasizing a separation between mind and matter, while panpsychism asserts that consciousness is a fundamental and ubiquitous feature of all matter, including particles and physical entities. Dualist theories often grapple with explaining the interaction between non-physical mind and physical body, whereas panpsychism avoids this problem by attributing proto-conscious properties to basic physical components. Contemporary debates center on which framework better addresses the hard problem of consciousness by reconciling subjective experience with objective physical processes.
Major Critiques and Counterarguments
Dualism faces criticism for its difficulty explaining the interaction between mind and body, often labeled as the "interaction problem," while Panpsychism is challenged for its lack of empirical evidence and the "combination problem," questioning how simple consciousness integrates into complex minds. Critics argue Dualism struggles with scientific compatibility, but proponents counter that subjective experience cannot be fully reduced to physical processes. Panpsychists respond to critiques by proposing that consciousness is a fundamental feature of matter, offering a potential bridge between physical science and experiential phenomena.
Implications for Science and Spirituality
Dualism posits a clear separation between mind and matter, which challenges scientific efforts to explain consciousness purely through physical processes, whereas panpsychism attributes consciousness to all matter, offering a unified framework that bridges the gap between science and spirituality. Scientific research benefits from panpsychism by providing testable hypotheses about the nature of consciousness embedded in fundamental particles, while spiritual traditions find resonance in the pervasive consciousness concept, aligning with experiential and mystical insights. The dualistic perspective often necessitates metaphysical assumptions beyond empirical science, limiting interdisciplinary integration, whereas panpsychism encourages collaboration between neuroscience, quantum physics, and spiritual philosophy to explore consciousness holistically.
Conclusion: Which Theory Best Explains the Mind?
Dualism posits a fundamental separation between mind and body, asserting consciousness as a non-physical substance, while panpsychism attributes consciousness as a universal property inherent in all matter. Evaluating empirical evidence and philosophical coherence, panpsychism offers a more integrated framework by bridging subjective experience with physical processes, minimizing the explanatory gap that dualism struggles to address. Therefore, panpsychism provides a promising avenue for understanding the mind's nature through its intrinsic link to the physical world.
Dualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com