Pragmatic theory explores how context influences the interpretation of meaning in communication, emphasizing the relationship between language and its practical use. It examines how speakers convey intended meanings beyond literal words, considering factors like speaker intention and situational context. Discover how this theory shapes your understanding of language by reading the full article.
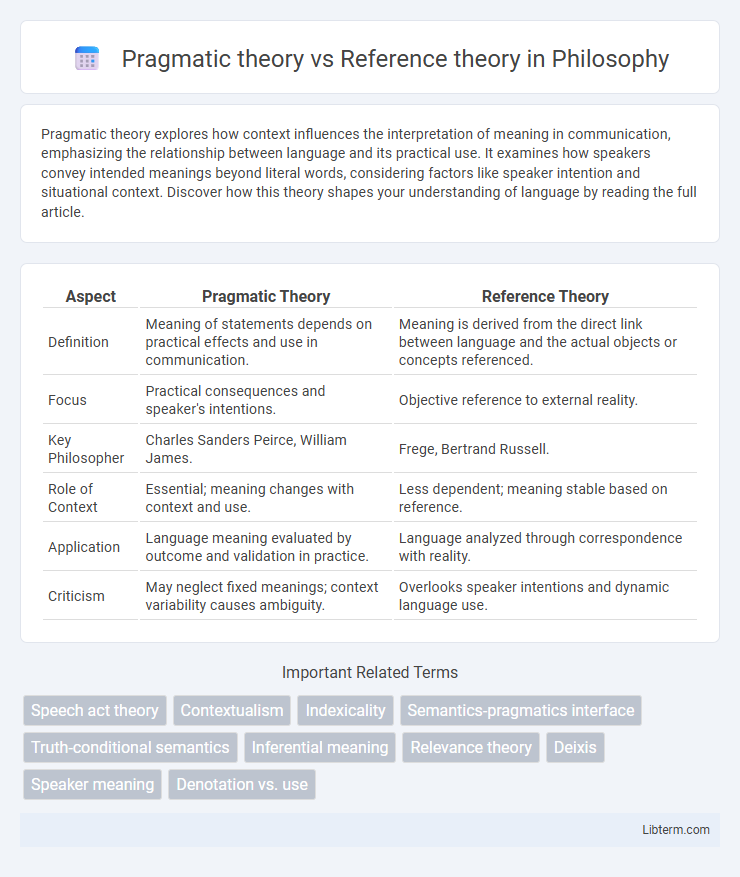
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pragmatic Theory | Reference Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meaning of statements depends on practical effects and use in communication. | Meaning is derived from the direct link between language and the actual objects or concepts referenced. |
| Focus | Practical consequences and speaker's intentions. | Objective reference to external reality. |
| Key Philosopher | Charles Sanders Peirce, William James. | Frege, Bertrand Russell. |
| Role of Context | Essential; meaning changes with context and use. | Less dependent; meaning stable based on reference. |
| Application | Language meaning evaluated by outcome and validation in practice. | Language analyzed through correspondence with reality. |
| Criticism | May neglect fixed meanings; context variability causes ambiguity. | Overlooks speaker intentions and dynamic language use. |
Introduction to Pragmatic Theory and Reference Theory
Pragmatic theory examines how context and speaker intention influence meaning beyond literal expressions, emphasizing communication's social and situational aspects. Reference theory focuses on the relationship between linguistic expressions and the actual objects or concepts they denote, highlighting direct links between language and the real world. Both theories play crucial roles in semantics and linguistics by explaining different dimensions of meaning and interpretation.
Defining Pragmatic Theory
Pragmatic theory defines meaning through the context of language use, emphasizing how speakers and listeners interpret utterances based on situational factors and intentions. Unlike Reference theory, which links meaning directly to objects or entities in the real world, Pragmatic theory accounts for implied meanings, speech acts, and conversational implicatures. This approach highlights the dynamic interaction between linguistic expressions and the social environment to capture the true function of communication.
Understanding Reference Theory
Reference theory asserts that the meaning of a word or phrase is directly tied to the actual object or concept it denotes in the real world. This theory emphasizes the relationship between linguistic expressions and their external referents, making meaning dependent on the context in which terms are used. Understanding Reference theory involves recognizing that communication relies on the accurate identification of these referents to convey precise information.
Historical Background and Evolution
The Pragmatic theory, rooted in early 20th-century philosophical works by Charles Sanders Peirce and later expanded by philosophers like Charles Morris and H.P. Grice, emphasizes the role of context, speaker intention, and conversational implicature in meaning interpretation. Reference theory, with origins tracing back to Frege and Russell in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, focuses on the direct relationship between linguistic expressions and their real-world referents or objects. Over time, linguistic philosophy evolved as pragmatic considerations challenged the limitations of pure reference theory, leading to a more integrated understanding of meaning in semantics and pragmatics.
Key Differences Between Pragmatic and Reference Theories
Pragmatic theory emphasizes the role of context, speaker intention, and listener interpretation in deriving meaning, focusing on how utterances function in communication rather than just their linguistic form. Reference theory concentrates on the direct relationship between words and the objects or concepts they denote in the real world, highlighting the importance of truth conditions and semantic reference. Key differences lie in pragmatic theory's dynamic, use-based approach versus reference theory's static, denotational framework, with pragmatics addressing meaning beyond literal content and reference theory grounded in the linkage between language and reality.
Major Proponents and Influential Works
Pragmatic theory, prominently advanced by Charles Sanders Peirce and later by philosophers like H.P. Grice with his influential work "Logic and Conversation" (1975), emphasizes meaning derived from context and speaker intention. Reference theory, championed by Gottlob Frege and Saul Kripke, focuses on the direct relationship between language expressions and their referents, with Kripke's "Naming and Necessity" (1980) significantly shaping contemporary understanding. These theories differ fundamentally in their approach to semantics: pragmatic theory prioritizes use and inference, while reference theory centers on denotation and linguistic reference.
Applications in Linguistics and Communication
Pragmatic theory emphasizes the role of context and speaker intention in interpreting meaning, making it essential for analyzing conversational implicatures and speech acts in linguistics. Reference theory focuses on the direct relationship between linguistic expressions and the objects or concepts they denote, which aids in semantic analysis and the development of formal language models. Both theories are applied in communication studies to enhance natural language understanding, improve human-computer interaction, and develop more accurate language processing algorithms.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Theory
Pragmatic theory excels at explaining meaning through context and speaker intention, effectively capturing nuances in everyday communication but struggles with ambiguity and subjective interpretation. Reference theory provides clear semantic grounding by linking linguistic expressions directly to real-world entities, offering precision and objectivity, though it often fails to account for metaphorical language and context-dependent meanings. Each theory's strength lies in either contextual adaptability or referential clarity, while their weaknesses emerge in handling ambiguity or abstract uses of language.
Contemporary Debates and Developments
Contemporary debates in pragmatics focus on the tension between Pragmatic theory, which emphasizes context and speaker intentions in meaning determination, and Reference theory, which centers on the relationship between words and actual entities in the world. Developments in dynamic semantics and inferential pragmatics challenge traditional Reference theory by highlighting how meaning evolves through discourse and social interaction. Experimental studies using corpus linguistics and cognitive neuroscience provide empirical support for pragmatic accounts, reshaping theoretical models within philosophy of language and linguistic semantics.
Conclusion: Comparing the Impact on Language Studies
Pragmatic theory emphasizes the role of context and speaker intention in meaning, highlighting how language functions dynamically in communication. Reference theory centers on the relationship between linguistic expressions and real-world entities, providing a more static and objective approach to semantics. Comparing both, pragmatic theory offers greater insights into language use and interpretation, while reference theory contributes foundational clarity in meaning, together shaping a comprehensive understanding in language studies.
Pragmatic theory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com