Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning behind information, art, or data to uncover deeper insights. It allows you to connect abstract concepts with practical understanding, enhancing comprehension across various contexts. Explore the rest of this article to discover essential techniques for mastering interpretation.
Table of Comparison
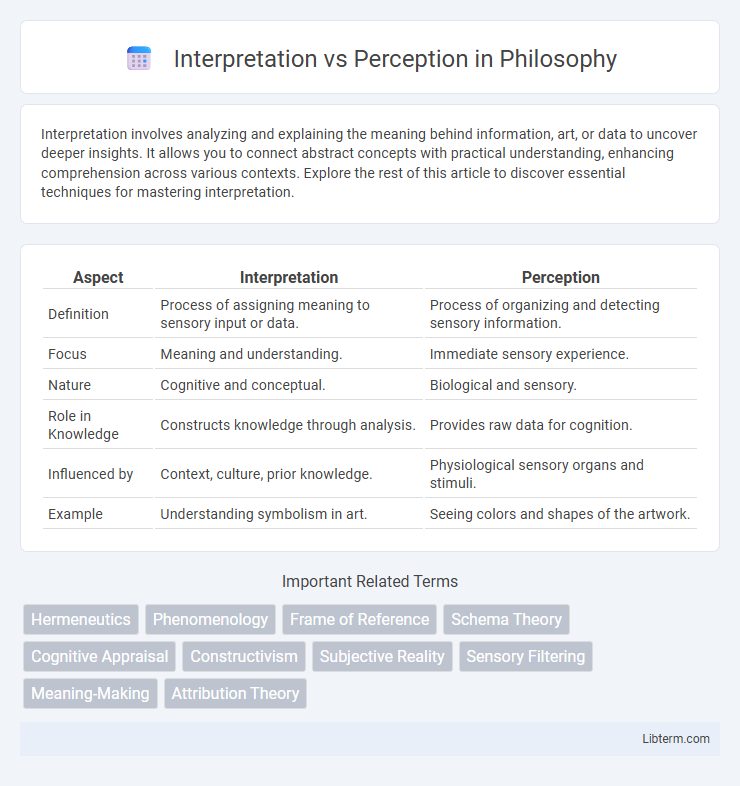
| Aspect | Interpretation | Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of assigning meaning to sensory input or data. | Process of organizing and detecting sensory information. |
| Focus | Meaning and understanding. | Immediate sensory experience. |
| Nature | Cognitive and conceptual. | Biological and sensory. |
| Role in Knowledge | Constructs knowledge through analysis. | Provides raw data for cognition. |
| Influenced by | Context, culture, prior knowledge. | Physiological sensory organs and stimuli. |
| Example | Understanding symbolism in art. | Seeing colors and shapes of the artwork. |
Understanding Interpretation: A Definition
Interpretation involves assigning meaning to sensory data or information based on prior knowledge, context, and cognitive processes, distinguishing it from perception, which is the immediate sensory experience. It requires mental organization and analysis to transform raw stimuli into comprehensible concepts, enabling individuals to derive significance beyond mere observation. Understanding interpretation is crucial for effective communication, problem-solving, and decision-making as it shapes how information is internalized and responded to.
What is Perception? Core Concepts
Perception is the cognitive process by which individuals organize and interpret sensory information to represent and understand their environment. Core concepts include sensory input, attention, and pattern recognition, which collectively shape how stimuli are detected and experienced. This process influences behavior by creating a subjective reality from objective sensory data.
Key Differences Between Interpretation and Perception
Interpretation involves the cognitive process of making sense of sensory information by assigning meaning based on prior knowledge and context, whereas perception refers to the immediate sensory experience and awareness of stimuli. Perception is a raw input stage shaped by sensory organs, while interpretation is a subjective, higher-level processing that influences understanding and response. Key differences include perception being more passive and automatic, whereas interpretation is active, conscious, and influenced by personal biases and cultural background.
How Interpretation Shapes Meaning
Interpretation shapes meaning by assigning context and personal experience to sensory information, transforming raw perception into understanding. While perception involves the immediate recognition of stimuli through senses, interpretation adds layers of cognitive processing that influence how information is comprehended and acted upon. This cognitive framing determines the significance and emotional impact of events, making interpretation central to meaning construction.
The Role of Perception in Human Experience
Perception serves as the fundamental process through which humans receive sensory information, shaping their immediate experience of the world. It filters and organizes stimuli, enabling individuals to construct meaningful interpretations based on prior knowledge and context. Thus, perception directly influences cognitive responses, emotional reactions, and decision-making in human experience.
Factors Influencing Interpretation
Interpretation is shaped by cognitive biases, cultural background, past experiences, and emotional state, all of which influence how information is processed and understood. Perception involves the sensory input received, but interpretation depends on the mental framework applied to that input. Factors like language proficiency, context, social norms, and individual values critically affect how people assign meaning to sensory data and construct their reality.
Factors Affecting Perception
Factors affecting perception include sensory capabilities, cultural background, past experiences, and psychological state, which collectively shape how individuals interpret sensory information. Attention and context heavily influence perception by filtering relevant stimuli and framing the environment in which information is processed. Social and environmental influences, such as expectations and language, also play crucial roles in altering perception before conscious interpretation occurs.
Interpretation in Communication and Language
Interpretation in communication and language involves decoding and assigning meaning to messages based on cultural, contextual, and individual factors. It shapes effective interaction by enabling speakers to understand nuances such as tone, intent, and implied meanings beyond literal words. Accurate interpretation minimizes misunderstandings and enhances clarity in diverse communicative exchanges.
Perception and Its Impact on Decision-Making
Perception shapes decision-making by filtering sensory information through prior experiences, beliefs, and emotions, leading to subjective reality construction. This cognitive process influences how individuals assess risks, opportunities, and intentions, frequently causing biases or heuristic shortcuts. Understanding perception's role helps improve decision quality by enhancing awareness of potential distortions and encouraging more objective data evaluation.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Interpretation and Perception
Bridging the gap between interpretation and perception enhances cognitive processing by aligning raw sensory data with contextual understanding, facilitating more accurate decision-making and communication. Integrating these processes involves leveraging neural mechanisms that transform perceptual inputs into meaningful interpretations through experience, memory, and cultural frameworks. This fusion promotes adaptive responses and deeper insights, optimizing how humans interact with complex environments and abstract information.
Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com