The principle of beneficence emphasizes acting in the best interest of others by promoting good and preventing harm, serving as a core guideline in healthcare ethics and decision-making. It requires healthcare professionals to balance benefits against risks to ensure positive patient outcomes while respecting their dignity. Discover how understanding this fundamental ethic can enhance your approach to care throughout the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
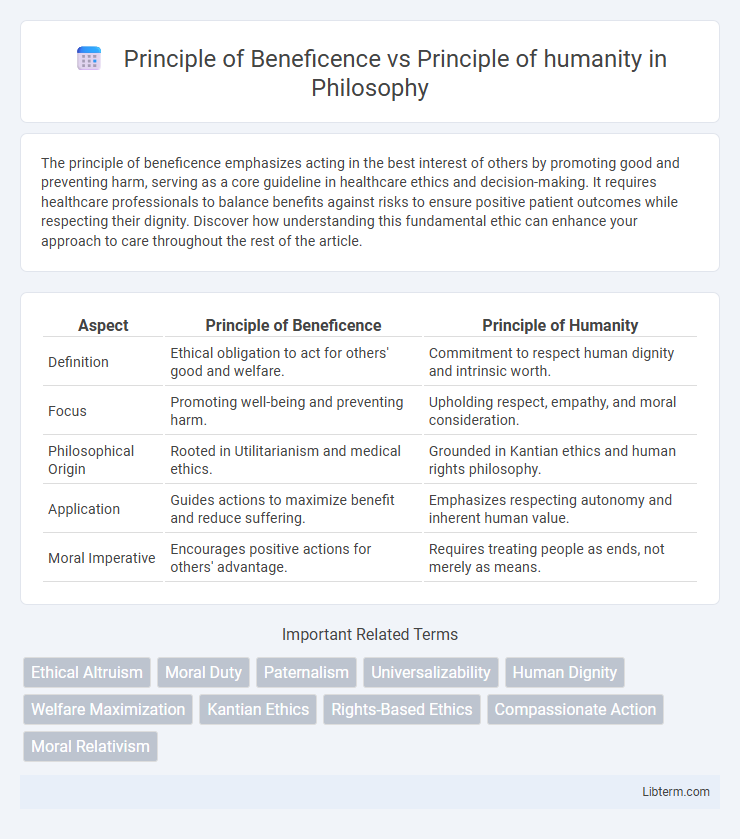
| Aspect | Principle of Beneficence | Principle of Humanity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ethical obligation to act for others' good and welfare. | Commitment to respect human dignity and intrinsic worth. |
| Focus | Promoting well-being and preventing harm. | Upholding respect, empathy, and moral consideration. |
| Philosophical Origin | Rooted in Utilitarianism and medical ethics. | Grounded in Kantian ethics and human rights philosophy. |
| Application | Guides actions to maximize benefit and reduce suffering. | Emphasizes respecting autonomy and inherent human value. |
| Moral Imperative | Encourages positive actions for others' advantage. | Requires treating people as ends, not merely as means. |
Understanding the Principle of Beneficence
The Principle of Beneficence emphasizes actively promoting the well-being of others through acts of kindness, charity, and preventing harm, making it a fundamental ethical guideline in healthcare and research. It requires professionals to balance benefits against risks, ensuring their actions contribute positively to patients' or subjects' welfare. Distinct from the broader Principle of Humanity, which centers on respect and dignity, beneficence specifically mandates proactive efforts to improve others' conditions and reduce suffering.
Exploring the Principle of Humanity
The Principle of Humanity emphasizes respecting and valuing human dignity, promoting compassion and understanding in interactions. It mandates treating individuals not merely as means to an end but as autonomous beings deserving of care and ethical consideration. This principle guides ethical decision-making by fostering empathy and prioritizing the inherent worth of every person.
Historical Origins of Beneficence and Humanity
The principle of beneficence, rooted in Hippocratic medicine and Enlightenment ethics, prioritizes actively promoting good and preventing harm in medical practice. The principle of humanity, emerging from post-World War II human rights discourse and the Nuremberg Code, emphasizes respecting human dignity and the intrinsic worth of individuals. Both principles have shaped modern bioethics by balancing the obligation to do good with the respect for human rights and moral agency.
Core Values: Comparing Beneficence and Humanity
The principle of beneficence centers on actively promoting well-being and preventing harm, emphasizing duty of care and positive action in ethical decision-making. In contrast, the principle of humanity prioritizes respect, compassion, and the intrinsic dignity of individuals, highlighting empathy and moral consideration for all human beings. Both principles share core values of respect and compassion but diverge in application: beneficence mandates proactive good deeds, while humanity focuses on honoring inherent human worth.
Ethical Foundations and Philosophical Influences
The Principle of Beneficence, rooted in utilitarian ethics, emphasizes actions that promote the greatest good and welfare for individuals or society, highlighting a proactive commitment to doing good and preventing harm. The Principle of Humanity, grounded in Kantian philosophy, insists on respecting the intrinsic dignity and autonomy of every person, treating individuals as ends in themselves rather than means to an end. Both principles form fundamental ethical foundations, with beneficence prioritizing welfare outcomes and humanity stressing moral respect and individual rights.
Applications in Healthcare and Social Policy
The Principle of Beneficence in healthcare emphasizes actions that promote patient well-being, guiding medical professionals to provide treatments that maximize benefits and minimize harm. The Principle of Humanity focuses on respecting human dignity and ensuring compassionate care, influencing social policies aimed at protecting vulnerable populations and upholding ethical standards. Together, these principles shape integrated frameworks in healthcare and social policy that prioritize both effective medical outcomes and the humane treatment of individuals.
Real-World Dilemmas: Beneficence vs Humanity
The principle of beneficence emphasizes actions that promote the well-being and welfare of others, often prioritizing tangible outcomes such as health improvements or life-saving interventions. In contrast, the principle of humanity focuses on respecting individual dignity, autonomy, and the intrinsic worth of each person, even when it conflicts with maximizing overall benefits. Real-world dilemmas arise when actions aimed at beneficence, like enforcing mandatory medical treatments, clash with respecting personal freedoms and human rights, highlighting the complex balance between doing good and honoring humanity.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Principle
The Principle of Beneficence emphasizes actively promoting good and preventing harm, offering clear ethical guidance in medical and research contexts; however, its limitation lies in potential paternalism and subjective interpretation of "benefit." The Principle of Humanity prioritizes respect for human dignity and intrinsic worth, strengthening moral consideration for individuals but sometimes lacking specific actionable directives in complex situations. Balancing these principles requires navigating between proactive welfare measures and upholding fundamental human rights, each contributing essential but distinct strengths to ethical decision-making frameworks.
Harmonizing Beneficence and Humanity in Practice
Harmonizing the Principle of Beneficence and the Principle of Humanity in practice involves ensuring actions actively promote well-being while respecting human dignity and individual rights. Effective ethical decision-making requires balancing the obligation to do good with the imperative to avoid dehumanizing treatment, fostering compassionate care and social justice. Integrating these principles enhances trust, supports equitable outcomes, and reinforces the moral foundation of healthcare and social services.
Future Directions in Ethical Decision-Making
The Principle of Beneficence emphasizes actively promoting good and preventing harm in ethical decision-making, while the Principle of Humanity centers on respecting human dignity and autonomy. Future directions include integrating artificial intelligence to enhance ethical frameworks by balancing beneficence with human rights considerations. Advancements in bioethics will focus on adaptive guidelines that prioritize both actionable well-being and respect for individual humanity in complex healthcare and technological contexts.
Principle of Beneficence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com