Nonreflective surfaces absorb light instead of bouncing it back, reducing glare and enhancing visual comfort in various settings. These surfaces are essential in fields like photography, interior design, and electronics to improve image clarity and reduce distractions. Discover how using nonreflective materials can transform your environment in the following article.
Table of Comparison
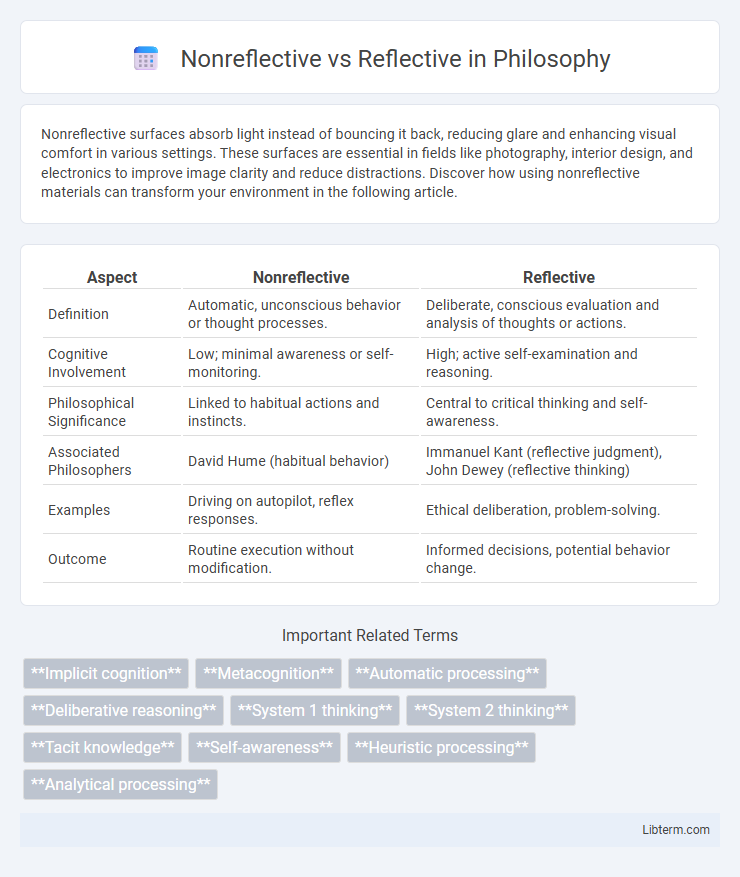
| Aspect | Nonreflective | Reflective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic, unconscious behavior or thought processes. | Deliberate, conscious evaluation and analysis of thoughts or actions. |
| Cognitive Involvement | Low; minimal awareness or self-monitoring. | High; active self-examination and reasoning. |
| Philosophical Significance | Linked to habitual actions and instincts. | Central to critical thinking and self-awareness. |
| Associated Philosophers | David Hume (habitual behavior) | Immanuel Kant (reflective judgment), John Dewey (reflective thinking) |
| Examples | Driving on autopilot, reflex responses. | Ethical deliberation, problem-solving. |
| Outcome | Routine execution without modification. | Informed decisions, potential behavior change. |
Understanding Nonreflective and Reflective Surfaces
Nonreflective surfaces absorb most incident light, reducing glare and minimizing reflections, which enhances visual comfort in environments like museums or screens. Reflective surfaces bounce light back, enabling visibility of images or surroundings, making them essential for mirrors, polished metals, and display technologies. Understanding the interaction of light with these surfaces is crucial for applications in design, optics, and safety.
Key Differences Between Nonreflective and Reflective Materials
Reflective materials efficiently bounce back light or heat, making them essential in applications like insulation, mirrors, and safety gear, whereas nonreflective materials absorb or transmit energy, reducing glare and enhancing visibility in optical devices and screens. Reflective surfaces typically feature high albedo and shiny finishes, while nonreflective materials possess matte textures and low reflectivity values to minimize light reflection. The choice between nonreflective and reflective materials significantly impacts thermal management, optical clarity, and energy efficiency across various industries.
Advantages of Nonreflective Surfaces
Nonreflective surfaces reduce glare and improve visual comfort, making them ideal for environments with bright lighting or screens. They enhance visibility and minimize eye strain by diffusing light, which is beneficial in workplaces and public spaces. These surfaces also prevent distractions caused by reflections, contributing to safety and increased productivity.
Benefits of Reflective Surfaces
Reflective surfaces enhance natural lighting by redirecting sunlight into darker areas, reducing the need for artificial illumination and lowering energy consumption. These surfaces also improve visual comfort by minimizing glare and creating a balanced light distribution in interior spaces. Furthermore, reflective materials contribute to thermal regulation by deflecting heat, which helps maintain cooler indoor temperatures and increases overall energy efficiency.
Common Applications of Nonreflective Coatings
Nonreflective coatings are widely used in optical devices such as camera lenses, eyeglasses, and microscopes to minimize glare and enhance visual clarity. These coatings improve light transmission by reducing surface reflections, thereby increasing image contrast and color fidelity. Common applications also include display screens, solar panels, and automotive windshields, where reducing reflected light boosts functionality and user experience.
Typical Uses of Reflective Materials
Reflective materials are commonly used in safety gear, road signs, and vehicle license plates to enhance visibility in low-light conditions. These materials efficiently redirect light back toward its source, improving nighttime safety for pedestrians, cyclists, and drivers. Their application extends to sportswear and outdoor equipment, where increased visibility is critical for accident prevention.
Performance Comparison: Nonreflective vs Reflective
Nonreflective performance typically outperforms reflective methods due to reduced overhead, as it avoids runtime type inspection and dynamic method invocation. Reflective operations incur additional computational costs from metadata analysis and can introduce latency, especially in large-scale or real-time applications. Benchmark tests consistently show nonreflective approaches achieving faster execution times and lower memory consumption compared to reflective counterparts.
Aesthetic Considerations in Surface Selection
Nonreflective surfaces absorb light, reducing glare and creating a matte finish that enhances visual comfort in design spaces. Reflective surfaces bounce light, intensifying brightness and highlighting textures, which can emphasize architectural details or create dynamic visual effects. Choosing between nonreflective and reflective surfaces hinges on desired ambiance and functionality, balancing aesthetic appeal with practical lighting needs.
Maintenance and Durability Insights
Reflective coatings often enhance maintenance efficiency by reducing surface degradation from UV exposure and environmental contaminants, leading to longer service intervals. Nonreflective surfaces may require more frequent cleaning and touch-ups due to higher absorption of heat and pollutants, accelerating wear and tear. Selecting reflective materials improves durability by mitigating thermal stress and preserving structural integrity over time.
Choosing the Right Surface for Your Needs
Nonreflective surfaces minimize glare and reduce eye strain, making them ideal for workspaces and display screens that require prolonged viewing. Reflective surfaces enhance brightness and color vibrancy, suitable for decorative applications or environments needing high visual impact. Selecting the right surface depends on balancing visibility requirements with ambient lighting conditions and user comfort preferences.
Nonreflective Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com