Pragmatic ascent involves gradually refining concepts through practical applications and real-world problem-solving to achieve deeper understanding. This approach emphasizes the evolution of ideas based on their usefulness and effectiveness in specific contexts. Explore this article to discover how pragmatic ascent can enhance your critical thinking and knowledge development.
Table of Comparison
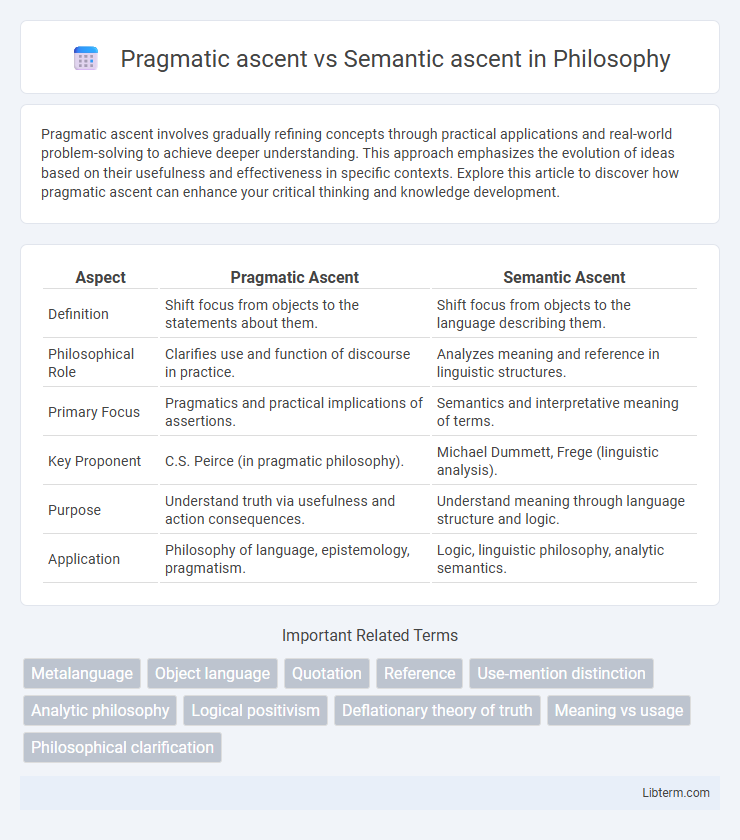
| Aspect | Pragmatic Ascent | Semantic Ascent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift focus from objects to the statements about them. | Shift focus from objects to the language describing them. |
| Philosophical Role | Clarifies use and function of discourse in practice. | Analyzes meaning and reference in linguistic structures. |
| Primary Focus | Pragmatics and practical implications of assertions. | Semantics and interpretative meaning of terms. |
| Key Proponent | C.S. Peirce (in pragmatic philosophy). | Michael Dummett, Frege (linguistic analysis). |
| Purpose | Understand truth via usefulness and action consequences. | Understand meaning through language structure and logic. |
| Application | Philosophy of language, epistemology, pragmatism. | Logic, linguistic philosophy, analytic semantics. |
Introduction to Pragmatic Ascent and Semantic Ascent
Pragmatic ascent refers to the shift from discussing specific objects or events to examining the rules and uses of the language describing them, highlighting how context and speaker intentions influence meaning. Semantic ascent involves moving from talking about particular instances to analyzing the meanings of words and sentences themselves, emphasizing formal linguistic structures and conceptual clarity. Both approaches provide distinctive methods for resolving philosophical and linguistic problems through metalinguistic reflection.
Defining Pragmatic Ascent: A Closer Look
Pragmatic ascent involves shifting the focus from specific objects or situations to the language and context used to describe them, enabling analysis of communication and meaning through metalinguistic perspectives. This contrasts with semantic ascent, which centers on examining meanings of words and phrases within language systems rather than the pragmatic use of language in interaction. Understanding pragmatic ascent provides insight into how speakers negotiate meaning and function in discourse, emphasizing context, intention, and real-world consequences over abstract semantic properties.
Understanding Semantic Ascent: Core Principles
Semantic ascent involves shifting discussion from objects to the language or concepts describing those objects, highlighting how meaning and interpretation shape understanding. Core principles include focusing on the linguistic expressions or meta-level descriptions rather than direct reference, which clarifies abstract debates and resolves ambiguity. This approach facilitates precise analysis by examining how meaning operates within language systems rather than relying solely on empirical instances.
Historical Context and Philosophical Background
Pragmatic ascent and semantic ascent emerged from 20th-century analytic philosophy debates on language and meaning, particularly within the works of Rudolf Carnap and later philosophers like Donald Davidson. Pragmatic ascent involves shifting discussion from objects to the language or rules governing their use, rooted in Carnap's distinction between object language and metalanguage. Semantic ascent, influenced by Quine and Tarski, emphasizes moving from talk about objects to talk about linguistic expressions and their truth conditions, framing philosophical analysis within meta-linguistic perspectives.
Key Differences Between Pragmatic and Semantic Ascent
Pragmatic ascent involves shifting the focus from the literal content of an utterance to the speaker's intentions and contextual implications, emphasizing how meaning is used in communication. Semantic ascent, by contrast, shifts from discussing what words or sentences mean to discussing the meanings themselves, focusing on meta-language and the properties of linguistic expressions. The key difference lies in pragmatic ascent addressing functional use and speaker intent, while semantic ascent centers on abstract semantic properties and levels of meaning.
Illustrative Examples in Philosophical Dialogue
Pragmatic ascent occurs when a speaker shifts from discussing a concept to discussing statements or language about that concept, such as analyzing the use of the term "justice" in a debate rather than justice itself. Semantic ascent involves moving from talking about objects to talking about the meanings or interpretations of words, exemplified by examining the term "truth" in a philosophical dialogue about language. In Platonic dialogues, Socrates often employs pragmatic ascent by questioning definitions and usage, while contemporary philosophy of language illustrates semantic ascent through meta-linguistic discussions on reference and meaning.
Implications for Language and Meaning
Pragmatic ascent emphasizes the speaker's communicative intentions and contextual factors, highlighting how meaning shifts based on use and social context, which affects conversational implicatures and pragmatic enrichment. Semantic ascent involves discussing language itself rather than the world, enabling abstract reasoning about meaning but potentially detaching terms from their referential function in communication. The distinction influences linguistic theories by balancing the flexibility of pragmatic interpretation against the formal precision of semantic analysis, shaping how meaning, reference, and context interact in language understanding.
Pragmatic Ascent in Contemporary Philosophy
Pragmatic ascent in contemporary philosophy involves shifting from discussing specific propositions to examining the practical implications and uses of language within context, emphasizing how meaning is shaped by communication and action rather than abstract truth conditions. This approach contrasts with semantic ascent, which focuses on the language about language, analyzing meta-level semantics and truth-conditions of statements without direct reference to use. Philosophers like Richard Rorty and Hilary Putnam highlight pragmatic ascent as a method to dissolve traditional philosophical problems by reconsidering language's role in social practices and problem-solving.
Semantic Ascent in Analytic Philosophy
Semantic ascent in analytic philosophy involves shifting discussion from objects and their properties to the language and expressions used to describe them, enabling clearer analysis of meaning and reference. This approach allows philosophers to investigate meta-language statements, resolving ambiguities and paradoxes by focusing on linguistic frameworks rather than direct empirical claims. Semantic ascent contrasts with pragmatic ascent, which emphasizes practical consequences and use, by prioritizing the logical structure and semantics of language itself.
Conclusion: Evaluating Their Roles in Philosophical Analysis
Pragmatic ascent emphasizes shifting focus to the use and function of language in context, revealing how meaning relates to communicative intentions and practical consequences. Semantic ascent centers on analyzing the meaning of language through meta-linguistic reflection, allowing philosophers to clarify concepts and resolve ambiguities by examining language itself. Evaluating these roles reveals that pragmatic ascent aids in understanding language in action, while semantic ascent provides tools for conceptual clarity, both essential for comprehensive philosophical analysis.
Pragmatic ascent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com