Pragmatic interpretation focuses on understanding language in context, considering the speaker's intention and the listener's perception beyond the literal meaning. It plays a crucial role in effective communication, enabling you to grasp implied meanings, humor, and indirect requests. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of pragmatic interpretation and its impact on everyday conversations.
Table of Comparison
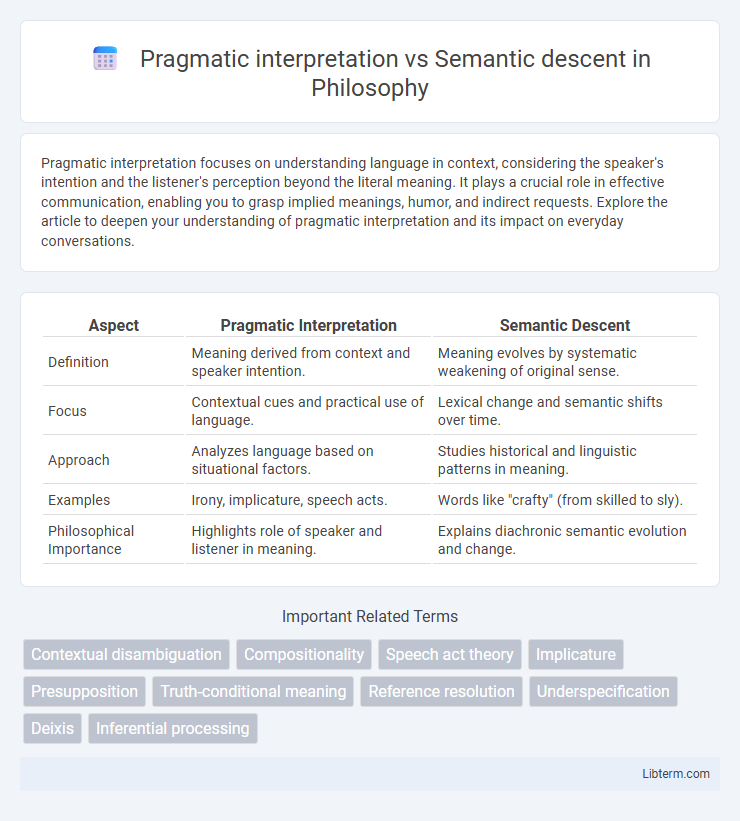
| Aspect | Pragmatic Interpretation | Semantic Descent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meaning derived from context and speaker intention. | Meaning evolves by systematic weakening of original sense. |
| Focus | Contextual cues and practical use of language. | Lexical change and semantic shifts over time. |
| Approach | Analyzes language based on situational factors. | Studies historical and linguistic patterns in meaning. |
| Examples | Irony, implicature, speech acts. | Words like "crafty" (from skilled to sly). |
| Philosophical Importance | Highlights role of speaker and listener in meaning. | Explains diachronic semantic evolution and change. |
Understanding Pragmatic Interpretation
Pragmatic interpretation focuses on how context influences the meaning of utterances beyond their literal semantic content, emphasizing speaker intention, conversational implicature, and social cues. It accounts for ambiguity resolution by integrating background knowledge, conversational maxims, and situational context to derive the intended message. This approach contrasts with semantic descent, which analyzes meaning reduction through syntactic or lexical changes without considering situational pragmatics.
Defining Semantic Descent
Semantic descent refers to the process by which a word's meaning shifts over time, often moving from a more general or positive sense to a more specific or negative one. This linguistic phenomenon highlights the evolution of language as meanings adapt to changing cultural and contextual factors. In contrast, pragmatic interpretation focuses on how context influences understanding, emphasizing speaker intent and situational factors rather than inherent changes in word meaning.
Core Differences Between Pragmatics and Semantics
Pragmatic interpretation centers on understanding language in context, emphasizing speaker intention, social cues, and situational factors, while semantic descent deals with the literal meaning and inherent relationships of words independent of context. Core differences between pragmatics and semantics include the scope of meaning analyzed--pragmatics examines implied meanings and real-world usage, whereas semantics studies formal, dictionary definitions and syntactic structures. Pragmatics adapts meaning based on context, making it dynamic, while semantics maintains stable, context-free interpretations.
Contextual Influence in Pragmatic Interpretation
Pragmatic interpretation relies heavily on contextual influence, where meaning is derived from situational factors, speaker intention, and cultural background, rather than fixed lexical definitions. Context shapes how utterances are understood by incorporating non-literal meanings, implicatures, and conversational maxims. Semantic descent, by contrast, involves the historical evolution of word meanings but does not account for immediate contextual shifts impacting interpretation in communication.
Structural Meaning in Semantic Descent
Semantic descent analyzes the evolution of word meanings through structural semantic shifts across languages, emphasizing how core meanings transform into related concepts over time. Structural meaning in semantic descent highlights the relationships between semantic components, showing how context-dependent interpretations solidify into stable lexical meanings. This contrasts with pragmatic interpretation, which relies on immediate contextual factors rather than diachronic structural patterns to derive meaning.
Real-World Examples of Pragmatic Interpretation
Pragmatic interpretation involves understanding language in context, where meaning depends on speakers' intentions and situational factors, such as interpreting "Can you pass the salt?" as a request rather than a question about ability. Semantic descent refers to the process where words lose or shift their original literal meanings over time, seen in how "awful" once meant "inspiring awe." Real-world examples of pragmatic interpretation include recognizing sarcasm in statements like "Great job!" said after a mistake, or grasping implied politeness in indirect requests like "It's cold here," prompting someone to close a window.
Case Studies Illustrating Semantic Descent
Case studies illustrating semantic descent reveal how words gradually shift meanings over time, often influenced by social and cultural contexts. For example, the word "awful" originally meant "inspiring wonder" but semantically descended to mean "very bad" due to pragmatic reinterpretations in everyday use. This phenomenon highlights the dynamic interplay between pragmatic interpretation and semantic change within linguistic evolution.
Implications for Language Processing
Pragmatic interpretation emphasizes context and speaker intent, enabling language processing systems to infer meaning beyond literal word definitions. Semantic descent, which traces the evolution of word meanings over time, provides crucial insights into polysemy and homonymy that affect accurate semantic parsing. Integrating both approaches enhances natural language understanding by combining contextual inference with historical semantic shifts, improving ambiguity resolution and user intent prediction.
Challenges in Distinguishing Pragmatics from Semantics
Distinguishing pragmatics from semantics presents challenges due to overlapping functions in meaning interpretation and context dependence. Pragmatics involves speaker intention and situational factors, while semantics focuses on inherent linguistic meaning, causing ambiguous boundaries in language processing. This ambiguity complicates computational linguistics, leading to difficulties in natural language understanding systems accurately differentiating context-driven versus encoded meanings.
Future Directions in Meaning Analysis
Future directions in meaning analysis emphasize integrating pragmatic interpretation with semantic descent to enhance natural language understanding models. Researchers aim to develop hybrid frameworks that dynamically balance contextual cues and inherent semantic hierarchies to better predict intended meanings. Advances in computational linguistics and machine learning facilitate more accurate modeling of language nuances across diverse domains and languages.
Pragmatic interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com