Pragmatism focuses on practical consequences and real-world applications to evaluate ideas and beliefs. It emphasizes adapting to changing circumstances and prioritizing results over rigid principles. Explore how pragmatism can influence your decision-making and problem-solving by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
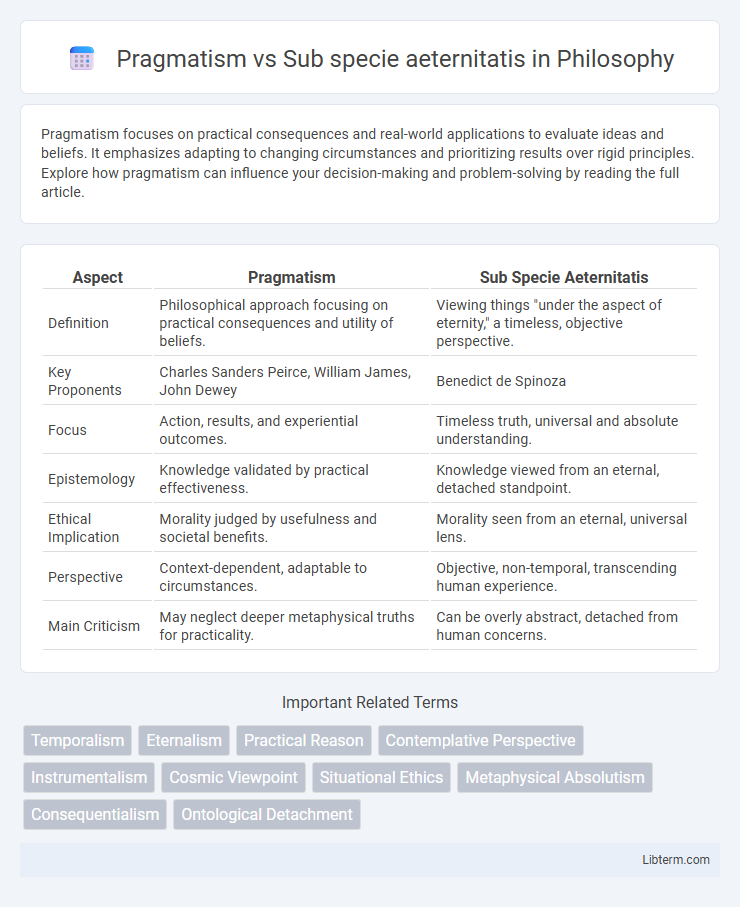
| Aspect | Pragmatism | Sub Specie Aeternitatis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical approach focusing on practical consequences and utility of beliefs. | Viewing things "under the aspect of eternity," a timeless, objective perspective. |
| Key Proponents | Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, John Dewey | Benedict de Spinoza |
| Focus | Action, results, and experiential outcomes. | Timeless truth, universal and absolute understanding. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge validated by practical effectiveness. | Knowledge viewed from an eternal, detached standpoint. |
| Ethical Implication | Morality judged by usefulness and societal benefits. | Morality seen from an eternal, universal lens. |
| Perspective | Context-dependent, adaptable to circumstances. | Objective, non-temporal, transcending human experience. |
| Main Criticism | May neglect deeper metaphysical truths for practicality. | Can be overly abstract, detached from human concerns. |
Introduction to Pragmatism and Sub Specie Aeternitatis
Pragmatism centers on practical consequences and real-world applications as the basis for meaning and truth, emphasizing experience and action. Sub specie aeternitatis, a Latin phrase meaning "under the aspect of eternity," involves viewing things from a timeless, universal perspective beyond human subjectivity. These contrasting approaches highlight the tension between immediate utility and eternal, objective truth in philosophy.
Defining Pragmatism: Core Principles and Applications
Pragmatism centers on the principle that truth is determined by practical consequences and usefulness, emphasizing action and results in belief validation. This philosophy applies to problem-solving and decision-making by focusing on outcomes that produce tangible benefits in real-world contexts. Contrasting with Sub specie aeternitatis, which seeks eternal, objective truths from a timeless perspective, pragmatism prioritizes adaptable, experiential knowledge relevant to human needs and contexts.
Understanding Sub Specie Aeternitatis: The Eternal Perspective
Understanding Sub Specie Aeternitatis involves contemplating existence from an eternal or infinite perspective, transcending temporal and subjective limitations to grasp the absolute nature of reality. This philosophical viewpoint contrasts sharply with Pragmatism, which emphasizes practical consequences and human experiences as the basis for truth and meaning. Sub Specie Aeternitatis encourages detachment from immediate contexts, aiming to perceive events and values as part of an unchanging, timeless whole.
Historical Context: Origins and Philosophical Roots
Pragmatism emerged in the late 19th century United States, pioneered by thinkers like Charles Sanders Peirce and William James, emphasizing practical consequences and human experiences as the basis for meaning and truth. In contrast, Sub specie aeternitatis, a concept rooted in Stoic philosophy and later popularized by Baruch Spinoza in the 17th century, advocates viewing life from an "eternal perspective," suggesting an objective, timeless truth beyond human concerns. These distinct historical contexts underscore pragmatism's focus on immediate, pragmatic results versus Sub specie aeternitatis' emphasis on an overarching, unchanging viewpoint.
Key Thinkers: William James vs. Baruch Spinoza
William James, a central figure in Pragmatism, emphasized practical consequences and lived experience as the core of truth, advocating for beliefs that work effectively in everyday life. In contrast, Baruch Spinoza's Sub specie aeternitatis perspective advocates viewing reality from an eternal, infinite standpoint, transcending human biases and temporal limitations to grasp the cosmos' essential nature. The fundamental tension between James' focus on contingent, actionable truths and Spinoza's pursuit of immutable, absolute understanding illustrates divergent approaches to reality and knowledge.
Worldview Comparison: Practicality vs. Timelessness
Pragmatism emphasizes a worldview centered on practicality, valuing ideas and beliefs based on their tangible outcomes and real-world applications. In contrast, the Sub specie aeternitatis perspective adopts a timeless, universal viewpoint, considering truths and values beyond immediate circumstances or subjective experiences. This comparison highlights the tension between focusing on actionable, present-oriented understanding and seeking eternal, context-independent insights.
Pragmatic Approaches to Meaning and Value
Pragmatic approaches to meaning emphasize the practical consequences and usefulness of ideas, grounding truth and value in their effects on human actions and experiences. Unlike the Sub specie aeternitatis perspective, which considers meaning and value from an eternal, objective viewpoint, pragmatism assesses significance through context-dependent, dynamic interactions. This framework aligns meaning with real-world applications, prioritizing outcomes and adaptability over absolute or timeless standards.
Sub Specie Aeternitatis: Ethics and Ultimate Significance
Sub specie aeternitatis, a Latin phrase meaning "from the perspective of eternity," frames ethics in terms of ultimate significance beyond immediate human concerns, emphasizing timeless values and universal truths. This perspective challenges pragmatic ethics, which prioritize practical outcomes and situational benefits, by demanding moral judgments that withstand the test of infinite time and cosmic scale. Ethical decisions under sub specie aeternitatis are evaluated for their alignment with permanent principles rather than transient consequences, fostering a more abstract and enduring moral philosophy.
Pragmatism vs Sub Specie Aeternitatis in Everyday Life
Pragmatism emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications, making decisions based on what works effectively in everyday scenarios. In contrast, Sub Specie Aeternitatis, a perspective meaning "under the aspect of eternity," encourages viewing situations from an eternal or timeless viewpoint, often leading to more detached or philosophical considerations. In daily life, pragmatism guides adaptive problem-solving and immediate action, while Sub Specie Aeternitatis invites reflection on long-term significance and universal truths beyond immediate circumstances.
Conclusion: Bridging Practicality and Eternity
Pragmatism emphasizes practical outcomes and adaptive problem-solving, while Sub specie aeternitatis offers a timeless, universal perspective on existence and morality. Bridging these philosophies requires integrating immediate, context-sensitive actions with enduring, objective truths that transcend individual circumstances. This synthesis fosters decision-making that is both grounded in real-world applicability and guided by eternal principles.
Pragmatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com