Understanding the difference between subject and substance is crucial in various fields such as law, philosophy, and literature to grasp the core meaning behind concepts and arguments. While the subject refers to the main topic or focus, the substance denotes the essential content or meaning that gives the subject its depth and relevance. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how subject and substance shape interpretation and communication.
Table of Comparison
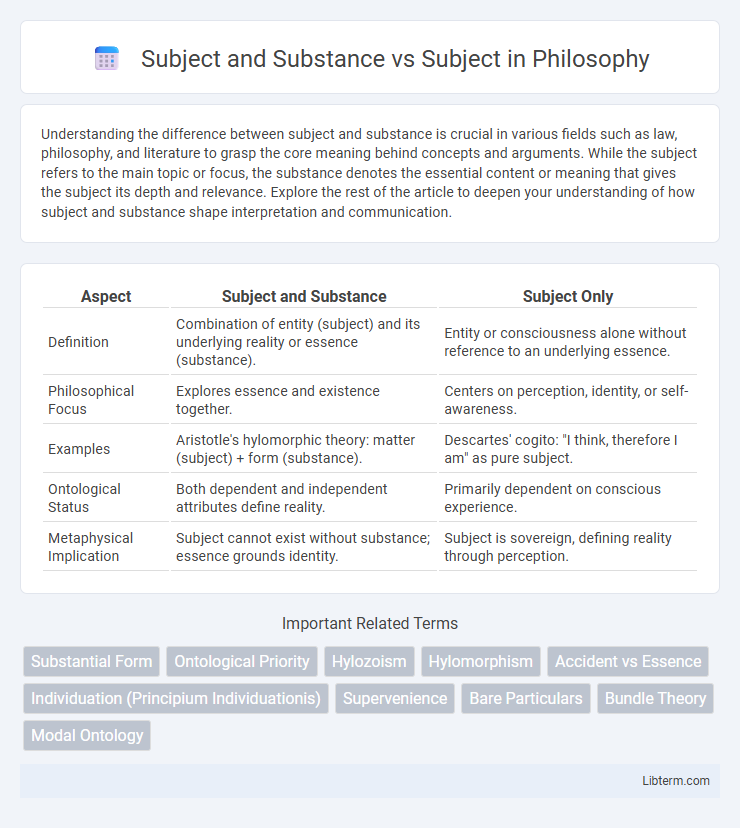
| Aspect | Subject and Substance | Subject Only |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of entity (subject) and its underlying reality or essence (substance). | Entity or consciousness alone without reference to an underlying essence. |
| Philosophical Focus | Explores essence and existence together. | Centers on perception, identity, or self-awareness. |
| Examples | Aristotle's hylomorphic theory: matter (subject) + form (substance). | Descartes' cogito: "I think, therefore I am" as pure subject. |
| Ontological Status | Both dependent and independent attributes define reality. | Primarily dependent on conscious experience. |
| Metaphysical Implication | Subject cannot exist without substance; essence grounds identity. | Subject is sovereign, defining reality through perception. |
Understanding the Concepts: Subject and Substance vs Subject
Understanding the concepts of Subject and Substance versus Subject involves distinguishing the underlying essence from the entity itself, where Subject refers to the entity experiencing or acting, and Substance denotes the inherent nature or material that constitutes the subject. Philosophically, Substance is often viewed as the foundational reality that persists through changes, while Subject emphasizes consciousness or agency within that framework. Analyzing these distinctions aids in clarifying metaphysical discussions about identity, existence, and the relationship between mind and matter.
Defining "Subject" in Academic and Philosophical Contexts
The term "subject" in academic and philosophical contexts refers to the entity that experiences, observes, or acts within a discourse or investigation, often distinguished from the "object" of study. Subject signifies the conscious self or perspective that engages with phenomena, serving as the locus of thought and perception in phenomenology and epistemology. Understanding "subject" is crucial for analyzing the relationship between knowledge and reality, especially when contrasted with "substance," which denotes the underlying essence or entity that exists independently of perception.
What is "Substance"? A Semantic Overview
Substance refers to the essential nature or underlying reality that defines an entity beyond its mere attributes or appearances, serving as the foundational "stuff" that persists through change. In philosophy, substance is considered the bearer of properties, providing the concrete existence to which predicates apply, distinguishing it from the abstract concept of subject as merely the topic of discussion. Understanding substance involves exploring its role as the core entity in metaphysics that underpins and sustains the subject's identity across time and conditions.
The Relationship Between Subject and Substance
The relationship between subject and substance is pivotal in philosophical discourse, where the subject represents consciousness or the observer, and substance denotes the underlying essence or matter of existence. Substance provides the foundation that persists through change, while the subject perceives and interacts with this stable essence, allowing for identity and continuity in experience. Understanding their interdependence reveals how subjective awareness is rooted in, yet distinct from, the material or metaphysical substance that constitutes reality.
Distinctions: Subject Standalone vs Subject with Substance
The distinction between Subject standalone and Subject with Substance lies in the depth of meaning and context provided; Subject standalone refers to the primary topic or entity without additional qualifiers, while Subject with Substance includes underlying attributes, qualities, or contextual information that enrich its understanding. Semantic analysis reveals that Subject with Substance offers a more comprehensive representation by integrating descriptive elements, enabling nuanced interpretation and precise knowledge extraction. This differentiation is crucial in fields such as linguistics, artificial intelligence, and knowledge management, where the clarity and depth of subject identification impact data accuracy and relevance.
Historical Perspectives on Subject and Substance
Historical perspectives on subject and substance emerge prominently in classical philosophy, where Aristotle defined substance as the fundamental reality underpinning attributes, distinguishing it from the subject that bears properties. Early modern philosophers like Descartes shifted focus to the subject, emphasizing consciousness as the essence of existence, thus redefining substance as a thinking entity rather than just material. This evolution highlights the changing ontological framework from substance as matter to subject as self-aware mind in the development of metaphysical thought.
Subject and Substance in Modern Discourse
Subject and Substance in modern discourse emphasize the essential qualities or core essence defining an entity, distinguishing the underlying reality from mere attributes or descriptions. This concept contrasts with a mere focus on Subject, which often refers to the thematic or grammatical role in communication without addressing the deeper ontological significance. Contemporary philosophy and analytic semantics prioritize understanding Subject and Substance to unravel identity and persistence conditions across varying contexts.
Practical Implications: Subject vs Subject with Substance
Subject with substance enhances depth and credibility in discussions, providing concrete information and practical examples that support the main idea. Pure subject statements often lack context, making them less effective for decision-making or problem-solving scenarios. Emphasizing substance transforms abstract concepts into actionable insights, improving understanding and application in real-world situations.
Analyzing Examples: Subject and Substance in Action
Subject and Substance explore the foundational elements of meaning and existence within linguistic and philosophical contexts. Analyzing examples such as "The cat (subject) purrs" reveals the subject as the actor, while substance pertains to its inherent qualities or essence that persist through different states. This distinction clarifies how subjects are identified by their substantive attributes, shaping interpretations in semantics and metaphysics.
Conclusion: The Importance of Substance in Identifying Subjects
The distinction between subject and substance is pivotal in accurately identifying subjects within legal and philosophical contexts. Substance provides the essential characteristics that define and anchor the subject's identity, ensuring clarity and consistency in interpretation. Recognizing the importance of substance prevents misclassification and supports precise conclusions about the nature and rights of the subject.
Subject and Substance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com