Purist philosophy emphasizes maintaining authenticity and avoiding dilution of original principles, ensuring the essence of a subject remains intact. This approach can be found across various disciplines, from art and music to software development and lifestyle choices. Discover how adopting purist ideals can enhance your understanding and appreciation by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
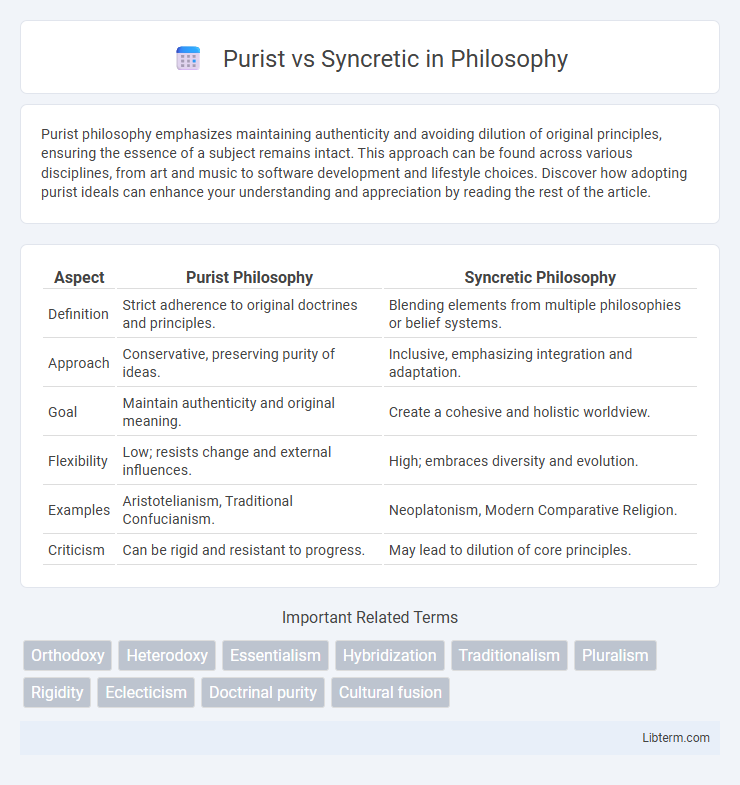
| Aspect | Purist Philosophy | Syncretic Philosophy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strict adherence to original doctrines and principles. | Blending elements from multiple philosophies or belief systems. |
| Approach | Conservative, preserving purity of ideas. | Inclusive, emphasizing integration and adaptation. |
| Goal | Maintain authenticity and original meaning. | Create a cohesive and holistic worldview. |
| Flexibility | Low; resists change and external influences. | High; embraces diversity and evolution. |
| Examples | Aristotelianism, Traditional Confucianism. | Neoplatonism, Modern Comparative Religion. |
| Criticism | Can be rigid and resistant to progress. | May lead to dilution of core principles. |
Introduction to Purist and Syncretic Approaches
Purist and syncretic approaches represent contrasting methodologies in cultural and religious studies. Purist approaches emphasize preserving original doctrines, practices, and beliefs without external influences, aiming for authenticity and continuity of tradition. Syncretic approaches involve blending elements from different cultures or religions to create hybrid systems, promoting adaptability and innovation.
Defining Purism: Core Principles and Values
Purism emphasizes maintaining linguistic or cultural elements in their original, unaltered form to preserve authenticity and purity. Core principles of purism include resistance to external influences, preserving traditional norms, and valuing historical continuity. This approach prioritizes the integrity of a system or identity by avoiding hybridization or syncretism.
Understanding Syncretism: Fusion and Adaptation
Syncretism involves the fusion and adaptation of diverse religious or cultural beliefs, creating a hybrid system that blends elements from multiple traditions. Unlike Purist approaches that seek to maintain original doctrines and practices, Syncretic systems evolve through continuous integration, reflecting dynamic social and historical contexts. This adaptive process enhances cultural resilience by accommodating change while preserving core spiritual values.
Historical Context: Origins of Purist and Syncretic Thought
Purist thought originated in contexts where maintaining cultural or religious purity was essential to identity preservation, often emerging during periods of colonization or globalization that threatened traditional values. Syncretic thought arose in multicultural societies and trading hubs, blending beliefs and practices from diverse traditions to create new, hybrid systems. Historical events such as the spread of major religions, colonial encounters, and migration significantly influenced the development of both purist and syncretic ideologies.
Cultural Impact: Tradition vs Innovation
Purist perspectives emphasize preserving cultural heritage through strict adherence to traditional practices, reinforcing identity and continuity across generations. Syncretic approaches blend diverse cultural elements, fostering innovation and adaptability in art, religion, and social customs. This dynamic interaction between tradition and innovation shapes societal evolution by balancing respect for the past with openness to change.
Purist vs Syncretic in Language and Communication
Purist language approaches emphasize preserving original linguistic forms and resist incorporating foreign words, aiming to maintain cultural and historical integrity. Syncretic language models embrace blending elements from multiple languages and dialects, fostering innovation and communication across diverse linguistic communities. In communication, purist strategies often prioritize clarity and tradition, while syncretic methods enhance adaptability and inclusivity in multilingual contexts.
Religion and Spirituality: Pure Doctrine vs Blended Belief
Purist religious perspectives emphasize strict adherence to original doctrines and scriptures, seeking to preserve unaltered beliefs and practices. Syncretic spirituality merges elements from multiple faiths, creating blended belief systems that adapt to diverse cultural contexts. These contrasting approaches influence theological interpretations, ritual expressions, and the evolution of religious identity worldwide.
Art, Music, and Literature: Authenticity vs Hybridization
Purist approaches in art, music, and literature emphasize preserving traditional techniques and cultural authenticity, often rejecting external influences to maintain original forms. Syncretic styles embrace hybridization by blending diverse cultural elements, creating innovative expressions that reflect globalization and cultural exchange. Authenticity in purist works upholds historical integrity, while syncretic creations foster evolving identities through dynamic fusion.
Societal Implications: Identity, Diversity, and Integration
Purist ideologies emphasize maintaining a distinct cultural or religious identity, often resisting outside influences to preserve traditional values, which can lead to societal fragmentation and reduced cultural diversity. Syncretic approaches encourage blending different cultural or religious elements, fostering inclusivity and promoting social integration by embracing diversity as a source of collective strength. These contrasting perspectives significantly impact social cohesion, identity formation, and the ability of communities to navigate multicultural environments.
Conclusion: Finding Balance Between Purity and Syncretism
Achieving a balance between purism and syncretism allows cultural and religious traditions to maintain their core identities while adapting to contemporary contexts and diverse influences. Embracing syncretic practices can foster inclusivity and innovation, whereas purism helps preserve authenticity and deepens understanding of original beliefs. Finding equilibrium between these approaches ensures the vitality and relevance of cultural systems across generations.
Purist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com