Finitude refers to the inherent limitations and boundaries of existence, emphasizing that all things have an end or a limit. Understanding finitude helps you appreciate the transient nature of life and the importance of living meaningfully within these constraints. Explore the rest of the article to delve deeper into the philosophical and practical implications of finitude.
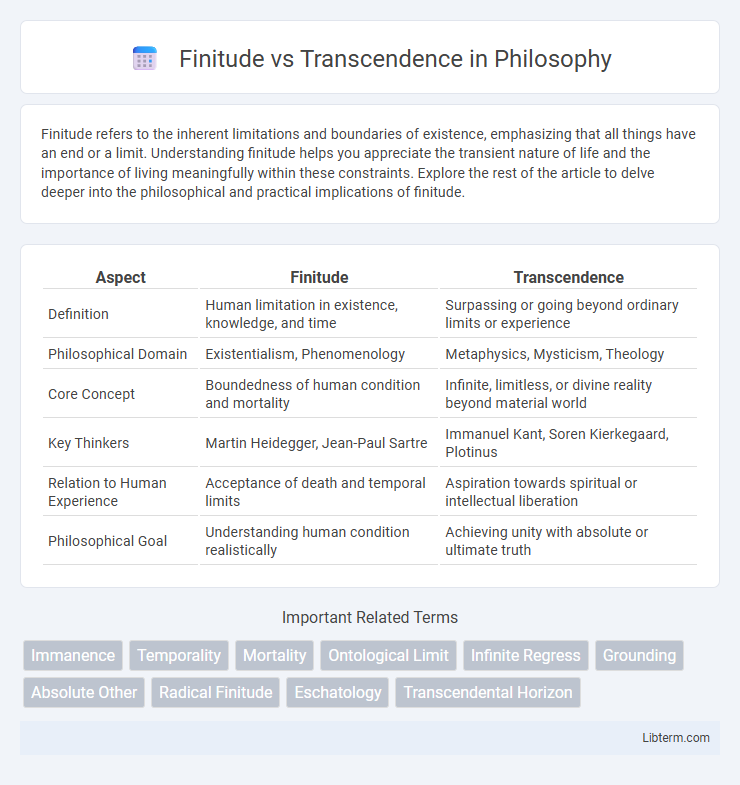
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Finitude | Transcendence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human limitation in existence, knowledge, and time | Surpassing or going beyond ordinary limits or experience |
| Philosophical Domain | Existentialism, Phenomenology | Metaphysics, Mysticism, Theology |
| Core Concept | Boundedness of human condition and mortality | Infinite, limitless, or divine reality beyond material world |
| Key Thinkers | Martin Heidegger, Jean-Paul Sartre | Immanuel Kant, Soren Kierkegaard, Plotinus |
| Relation to Human Experience | Acceptance of death and temporal limits | Aspiration towards spiritual or intellectual liberation |
| Philosophical Goal | Understanding human condition realistically | Achieving unity with absolute or ultimate truth |
Understanding Finitude: Defining Human Limits
Understanding finitude involves recognizing the inherent limitations of human existence, including mortality, cognitive boundaries, and temporal constraints. These limits shape human experience and influence how we perceive meaning, purpose, and identity in a finite lifespan. Acknowledging finitude fosters a deeper engagement with life's impermanence and the conditions that define our humanity.
The Concept of Transcendence Explained
Transcendence refers to the state of existing beyond the limitations of physical existence and material reality, often associated with spiritual or metaphysical dimensions. It involves surpassing the finite boundaries of human experience, consciousness, and temporal constraints. Philosophers and theologians interpret transcendence as the ultimate reality or divine presence that goes beyond empirical understanding and worldly phenomena.
Philosophical Roots: Finitude in Existential Thought
Finitude in existential thought centers on the inherent limitations and mortality of human existence, as extensively explored by philosophers such as Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre. Heidegger's concept of "Being-toward-death" emphasizes that recognizing one's finite nature reveals authentic existence, while Sartre highlights human freedom within these boundaries. This philosophical framework contrasts with transcendence, which implies surpassing these limits through consciousness or spiritual meaning.
Spiritual Traditions on Transcendence
Spiritual traditions often emphasize transcendence as a pathway beyond human finitude, seeking connection with the divine or ultimate reality through meditation, prayer, or mystical experiences. Practices in Buddhism aim to transcend suffering and ego by realizing Nirvana, while Christian mysticism pursues union with God as an infinite source of life and meaning. These traditions frame transcendence as a transformative journey surpassing temporal limitations and affirming a profound spiritual existence.
The Human Condition: Navigating Finitude
The human condition is defined by an inherent tension between finitude--our temporal, limited existence--and the desire for transcendence beyond those boundaries. Navigating finitude involves an existential awareness of mortality, prompting individuals to seek meaning through cultural, spiritual, or creative expressions that affirm life despite its impermanence. This dynamic interplay shapes philosophies, religions, and psychological frameworks that address how humans confront death while aspiring to transcend temporal limitations.
Bridging the Gap: Moments of Transcendence
Moments of transcendence offer fleeting breakthroughs that bridge the gap between finitude and the infinite, revealing glimpses of a reality beyond temporal limitations. These experiences often occur in encounters with nature, art, or profound reflection, where individuals sense a connection to a greater whole that surpasses individual existence. By embracing these moments, one negotiates the tension between mortal limits and the yearning for a transcendent dimension that imbues life with meaning and continuity.
Finitude and Meaning: Embracing Mortality
Embracing finitude involves acknowledging mortality as a fundamental aspect of human existence, which deepens the search for meaning in life. Awareness of life's limited duration compels individuals to prioritize authentic experiences and values, fostering a profound sense of purpose. This confrontation with finitude catalyzes personal growth and enriches the understanding of meaningful existence within temporal boundaries.
Transcendence as a Source of Hope
Transcendence offers a profound source of hope by elevating human experience beyond the limitations of finitude and mortality. It inspires individuals to seek meaning and purpose beyond temporal existence, fostering resilience amid life's uncertainties and challenges. Embracing transcendence connects people to a broader, enduring reality that affirms hope despite the inevitability of finitude.
Contemporary Debates: Reconciling Finitude and Transcendence
Contemporary debates on finitude versus transcendence center on reconciling human limitations with the quest for meaning beyond physical existence. Philosophers explore frameworks that integrate existential boundaries with aspirations toward infinite or transcendent realities, emphasizing phenomenological and metaphysical approaches. This synthesis aims to address tensions between mortality and spiritual transcendence, proposing models accommodating both finite experience and transcendent meaning.
Finitude vs. Transcendence: Implications for Human Identity
Finitude and transcendence shape human identity by defining the boundaries between mortal limitations and the aspiration for meaning beyond existence. Recognition of finitude grounds individuals in temporal reality, fostering authenticity and personal responsibility. Transcendence propels humans toward self-actualization and spiritual or philosophical pursuits, expanding identity beyond physical constraints.
Finitude Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com