Human intelligence encompasses the abilities to learn, reason, solve problems, and adapt to new situations, making it a cornerstone of personal and societal development. It is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, shaping how individuals acquire knowledge and apply it in various contexts. Explore the rest of the article to understand how enhancing your intelligence can lead to greater success and fulfillment.
Table of Comparison
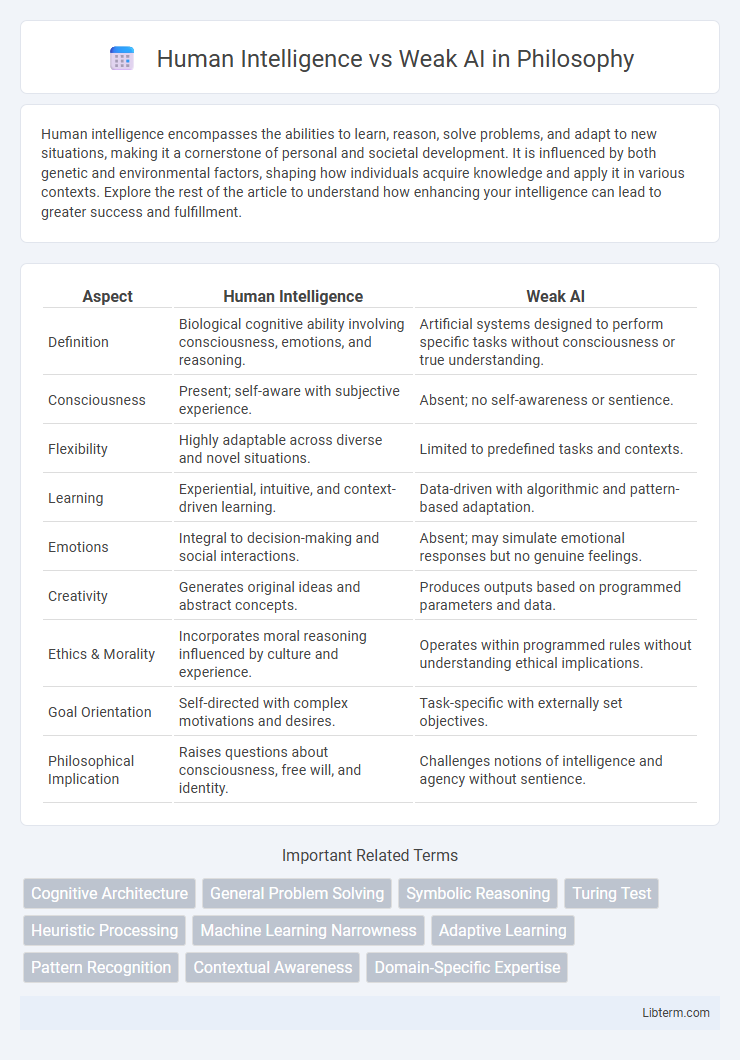
| Aspect | Human Intelligence | Weak AI |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological cognitive ability involving consciousness, emotions, and reasoning. | Artificial systems designed to perform specific tasks without consciousness or true understanding. |
| Consciousness | Present; self-aware with subjective experience. | Absent; no self-awareness or sentience. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable across diverse and novel situations. | Limited to predefined tasks and contexts. |
| Learning | Experiential, intuitive, and context-driven learning. | Data-driven with algorithmic and pattern-based adaptation. |
| Emotions | Integral to decision-making and social interactions. | Absent; may simulate emotional responses but no genuine feelings. |
| Creativity | Generates original ideas and abstract concepts. | Produces outputs based on programmed parameters and data. |
| Ethics & Morality | Incorporates moral reasoning influenced by culture and experience. | Operates within programmed rules without understanding ethical implications. |
| Goal Orientation | Self-directed with complex motivations and desires. | Task-specific with externally set objectives. |
| Philosophical Implication | Raises questions about consciousness, free will, and identity. | Challenges notions of intelligence and agency without sentience. |
Defining Human Intelligence
Human intelligence encompasses the ability to learn from experience, reason abstractly, and adapt to new situations through emotional understanding and creativity. It involves complex cognitive processes such as self-awareness, problem-solving, and ethical judgment that are deeply rooted in biological and neurological systems. Human intelligence is inherently flexible and context-aware, distinguishing it fundamentally from Weak AI, which operates under limited, predefined parameters without genuine comprehension or consciousness.
Understanding Weak AI
Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is designed to perform specific tasks without possessing genuine understanding or consciousness, unlike human intelligence which exhibits awareness, emotions, and reasoning across diverse domains. Weak AI operates through algorithms and data processing, excelling in pattern recognition and problem-solving within predefined parameters but lacking the intuitive and adaptive learning capabilities inherent in human cognition. Understanding weak AI involves recognizing its reliance on programmed instructions and datasets, distinguishing it from the flexible, self-aware thought processes characteristic of human intelligence.
Core Differences Between Human Intelligence and Weak AI
Human intelligence exhibits adaptive learning capabilities, emotional understanding, and abstract reasoning, enabling complex decision-making in unpredictable environments. Weak AI, or narrow AI, operates based on predefined algorithms and specific tasks without genuine understanding or consciousness. Core differences include human creativity, self-awareness, and generalization, contrasting with weak AI's rule-based processing and limited scope of functionality.
Cognitive Abilities: Humans Versus Machines
Human intelligence exhibits complex cognitive abilities such as abstract reasoning, emotional understanding, and contextual learning, which surpass the current capabilities of weak AI systems designed to perform narrow, specific tasks. Weak AI relies on preprogrammed algorithms and lacks true comprehension or self-awareness, limiting its ability to adapt beyond its predefined scope. While machines process large datasets efficiently, human cognition integrates experience, intuition, and creativity, enabling flexible problem-solving in unpredictable environments.
Learning and Adaptation: Biological Minds vs. Algorithms
Human intelligence excels in learning and adaptation through complex neural plasticity, enabling nuanced understanding and emotional context integration. Weak AI relies on pre-programmed algorithms and vast data sets, which limit its capacity for genuine creativity or deep contextual learning. While algorithms can rapidly process information and improve within specified parameters, they lack the intrinsic flexibility and experiential growth characteristic of biological minds.
Emotional Intelligence: Human Uniqueness
Human intelligence excels in emotional intelligence, enabling deep empathy, social understanding, and nuanced emotional responses that weak AI cannot replicate. While weak AI uses predefined algorithms to simulate basic interactions, it lacks genuine emotional awareness and the ability to adapt creatively to complex social cues. Emotional intelligence remains a distinctive human trait critical for authentic interpersonal relationships and effective communication.
Limitations of Weak AI
Weak AI systems operate within narrowly defined tasks and lack genuine understanding or consciousness, limiting their ability to adapt to novel situations beyond pre-programmed scenarios. These systems rely heavily on large datasets and predefined algorithms, resulting in brittleness when encountering ambiguous or unexpected inputs. Human intelligence surpasses Weak AI by integrating emotional reasoning, common sense, and contextual awareness, essential for complex decision-making and creativity.
Real-World Applications of Weak AI
Weak AI, designed for specific tasks, excels in real-world applications such as virtual personal assistants, fraud detection systems, and recommendation algorithms, enabling efficient data-driven decision-making. Unlike human intelligence, which encompasses general reasoning and emotional understanding, Weak AI operates within narrowly defined parameters to automate repetitive or data-intensive functions. This specialization allows industries like healthcare, finance, and customer service to enhance productivity and accuracy through targeted AI solutions.
Ethical Considerations in Human-AI Interaction
Human intelligence embodies ethical reasoning, empathy, and moral judgment derived from consciousness and values, while Weak AI operates within predefined parameters lacking genuine understanding or ethical awareness. Ethical considerations in human-AI interaction emphasize the importance of transparency, accountability, and preventing biases embedded in AI algorithms that can lead to discrimination or harm. Ensuring that Weak AI systems align with human values requires continuous oversight, ethical frameworks, and inclusive design to safeguard human dignity and autonomy.
Future Prospects: Bridging the Intelligence Gap
Future prospects for bridging the intelligence gap between human intelligence and weak AI involve advancements in machine learning algorithms, enabling AI to perform complex cognitive tasks with greater accuracy and adaptability. Integration of neuromorphic computing and increased computational power could mimic human brain processes, enhancing AI's contextual understanding and decision-making abilities. Collaborative frameworks combining human intuition with AI's data processing strengths may lead to hybrid intelligence systems that revolutionize industries and problem-solving.
Human Intelligence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com