Suspension in vehicles plays a crucial role in enhancing ride comfort and handling by absorbing shocks from uneven road surfaces. The system's components, such as springs, shock absorbers, and linkages, work together to maintain tire contact with the road, ensuring safety and stability. Explore the rest of this article to understand how suspension impacts your driving experience and vehicle performance.
Table of Comparison
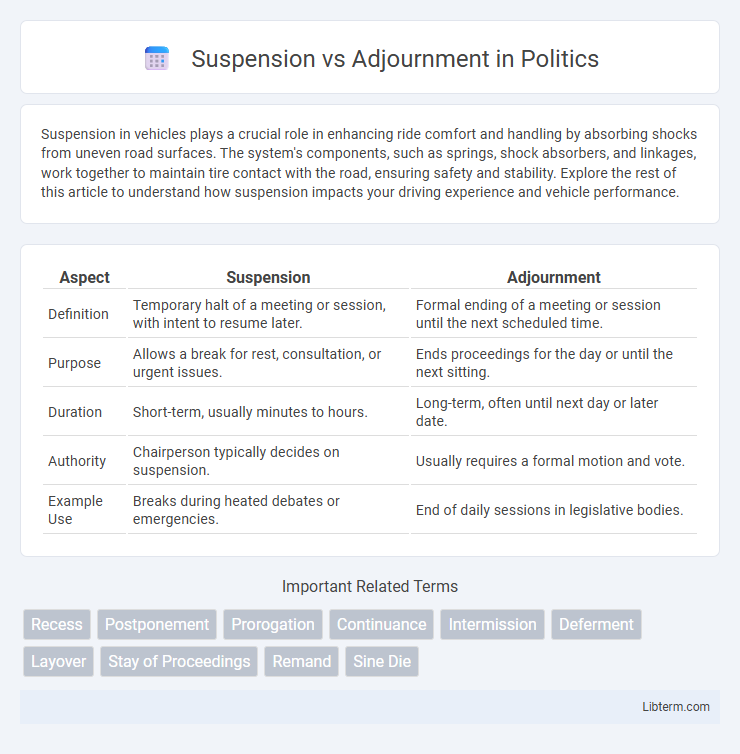
| Aspect | Suspension | Adjournment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary halt of a meeting or session, with intent to resume later. | Formal ending of a meeting or session until the next scheduled time. |
| Purpose | Allows a break for rest, consultation, or urgent issues. | Ends proceedings for the day or until the next sitting. |
| Duration | Short-term, usually minutes to hours. | Long-term, often until next day or later date. |
| Authority | Chairperson typically decides on suspension. | Usually requires a formal motion and vote. |
| Example Use | Breaks during heated debates or emergencies. | End of daily sessions in legislative bodies. |
Understanding Suspension and Adjournment
Suspension refers to a temporary halt in proceedings with the intention to resume at a later time, often due to specific issues such as technical difficulties or the need for additional information. Adjournment signifies the formal ending of a session or meeting, with no immediate resumption planned, usually scheduled to continue at a later date. Understanding the difference between suspension and adjournment is crucial for managing legal, legislative, or organizational meetings effectively.
Key Differences Between Suspension and Adjournment
Suspension refers to temporarily halting a meeting with an intention to resume after a short break, while adjournment signifies the formal ending of a meeting or session, often without a specified time to reconvene. Suspension is typically used for short intervals like recesses, allowing participants to pause and continue later the same day, whereas adjournment marks the conclusion of proceedings until the next scheduled meeting. The key difference lies in the purpose and duration: suspension is a brief pause within the same session, adjournment is the official closure requiring a new session to restart the discussion.
Legal Definitions and Context
Suspension in legal terms refers to the temporary halting of proceedings or the enforcement of a legal action while maintaining the case's active status. Adjournment denotes the formal postponement of a court session or hearing to a later date, often to allow for additional evidence gathering or procedural requirements. Both terms affect case timelines but differ in operational impact and legal ramifications within judicial contexts.
Procedures for Suspension in Meetings
Procedures for suspension in meetings typically require a formal motion proposed by a member and subsequently seconded to halt the ongoing discussion temporarily without dissolving the meeting. The suspension motion often mandates a specific duration or a condition under which the meeting will resume, ensuring clarity and preventing confusion among participants. Approval usually needs a majority vote, adhering to established parliamentary rules like Robert's Rules of Order to maintain procedural integrity.
Procedures for Adjournment in Meetings
Procedures for adjournment in meetings typically require a formal motion, seconding by another attendee, and a majority vote to pass. The chairperson may also have the authority to adjourn the meeting if the agenda is completed or in case of emergency, based on the organization's bylaws. Proper documentation of the adjournment time and reason is essential for accurate meeting minutes and compliance with governance standards.
Reasons for Suspending vs Adjourning
Suspension occurs when proceedings are temporarily halted due to specific issues such as the need for additional evidence, procedural errors, or health emergencies affecting key participants. Adjournment is generally granted to allow more time for preparation, to accommodate scheduling conflicts, or when a party requests postponement for strategic reasons. Understanding the procedural context and underlying causes is essential for distinguishing between suspension and adjournment in legal and organizational settings.
Impact on Parliamentary Proceedings
Suspension temporarily halts parliamentary proceedings without concluding the session, allowing for short-term breaks or urgent discussions to resume later. Adjournment ends the current session, often deferring unfinished business to a later date or a new session, impacting legislative timelines and priorities. Suspension maintains procedural continuity, while adjournment significantly influences the scheduling and momentum of parliamentary decision-making.
Case Studies: Suspension and Adjournment in Practice
Suspension and adjournment in legal case studies reveal distinct applications: suspension temporarily halts proceedings due to specific issues like evidence review or party unavailability, as seen in criminal trials paused for DNA testing. Adjournment postpones sessions to a later date for reasons such as witness absence or further investigation, commonly used in civil litigation to accommodate additional discovery. Analyzing case outcomes highlights that suspension often addresses immediate procedural needs, while adjournment allows courts flexibility in managing complex schedules.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Suspension temporarily halts proceedings without setting a specific resumption date, allowing flexibility to address urgent issues or gather information but may cause uncertainty and delays. Adjournment ends a session with a scheduled continuation, providing clear timelines but potentially disrupting momentum and extending the overall duration. Both measures offer strategic benefits in managing workflow but carry risks of inefficiency if overused or poorly timed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Suspension temporarily pauses a legal proceeding or meeting with the intention to resume later, while adjournment ends it until a specified future time or date. Suspension is often used during hearings to address urgent matters without concluding the session, whereas adjournment schedules a formal break or postponement. Courts and meetings frequently employ suspension to handle unforeseen interruptions, and adjournment to allow participants preparation time or to comply with procedural requirements.
Suspension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com