Stacking is a powerful ensemble learning technique that combines multiple machine learning models to improve predictive performance. By aggregating the strengths of diverse models through a meta-learner, stacking reduces overfitting and increases accuracy compared to individual models. Explore the rest of the article to discover how stacking can elevate your machine learning projects.
Table of Comparison
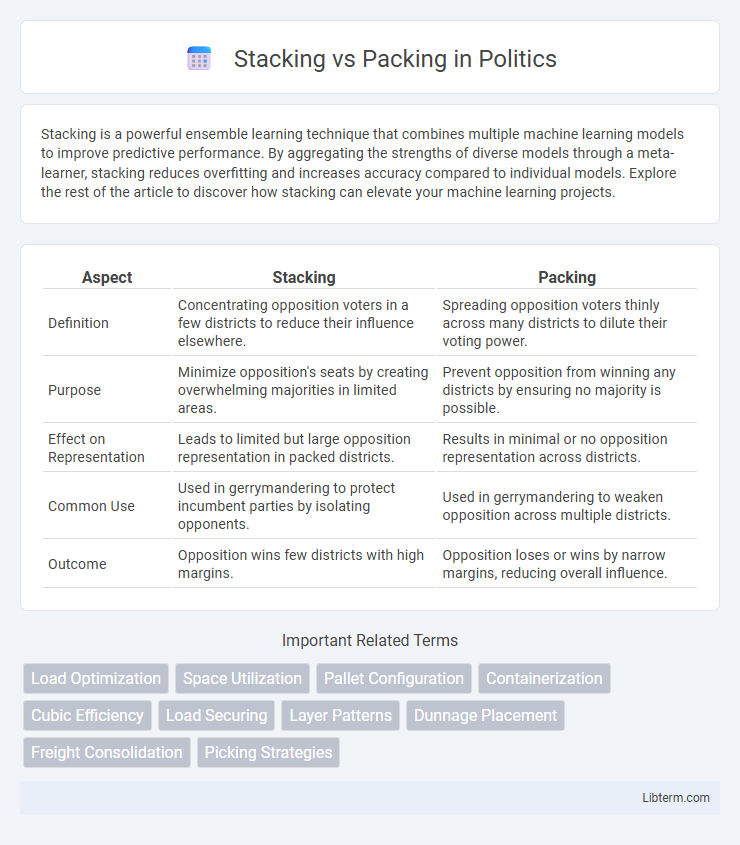
| Aspect | Stacking | Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concentrating opposition voters in a few districts to reduce their influence elsewhere. | Spreading opposition voters thinly across many districts to dilute their voting power. |
| Purpose | Minimize opposition's seats by creating overwhelming majorities in limited areas. | Prevent opposition from winning any districts by ensuring no majority is possible. |
| Effect on Representation | Leads to limited but large opposition representation in packed districts. | Results in minimal or no opposition representation across districts. |
| Common Use | Used in gerrymandering to protect incumbent parties by isolating opponents. | Used in gerrymandering to weaken opposition across multiple districts. |
| Outcome | Opposition wins few districts with high margins. | Opposition loses or wins by narrow margins, reducing overall influence. |
Introduction to Stacking and Packing
Stacking and packing are critical concepts in material handling and logistics, focusing on the efficient arrangement of items to maximize space utilization. Stacking refers to placing objects directly on top of one another, often used for uniform items like boxes or pallets to optimize vertical space. Packing involves arranging items within a container or space, considering shape and size to minimize wasted volume and ensure stability during transport.
Defining Stacking: Key Concepts
Stacking refers to the arrangement of objects in layers directly on top of each other, maximizing vertical space utilization. It involves placing items in a stable configuration, often used in warehouses or shipping to optimize load capacity. Key concepts include load-bearing capacity, stability, and weight distribution to prevent collapse.
Understanding Packing: Core Principles
Packing involves arranging objects within a defined space to maximize density and minimize wasted volume, emphasizing spatial efficiency and geometric compatibility. Core principles include understanding object shapes, size constraints, and the container's dimensions to optimize arrangement patterns. Effective packing strategies rely on mathematical models and algorithms to achieve optimal or near-optimal utilization of available space.
Applications of Stacking in Industry
Stacking technology is extensively applied in the logistics and manufacturing industries to optimize space utilization and improve material handling efficiency by arranging products or components in stable layers. In semiconductor manufacturing, stacking is crucial for creating 3D integrated circuits, enabling higher performance and miniaturization by vertically layering chips. The construction sector uses stacking methods for modular building, allowing faster assembly and enhanced structural integrity through systematically layering prefabricated elements.
Common Uses of Packing in Logistics
Packing in logistics primarily involves securely enclosing products using materials like boxes, pallets, and shrink wrap to protect goods during transportation and storage, ensuring safety and minimizing damage. Commonly used for consolidating smaller items into manageable units, packing facilitates efficient handling, space optimization, and inventory control in warehouses and distribution centers. This method supports multimodal shipping and compliance with regulatory standards, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Stacking
Stacking offers efficient use of vertical space and simplifies access to items, reducing the footprint required for storage. However, it poses risks such as potential damage to lower items due to weight and instability, especially if stacks are uneven or improperly balanced. Proper stacking techniques and weight distribution are essential to maximize safety and optimize space utilization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Packing
Packing allows efficient use of space by filling containers or areas densely, minimizing wasted volume and reducing transportation or storage costs. Its main disadvantage lies in the increased difficulty of accessing items, which can lead to higher risk of damage or longer retrieval times. Unlike stacking, packing often requires careful planning and durable materials to maintain organization and protect contents during handling.
Safety Considerations: Stacking vs Packing
Stacking safety considerations require ensuring stability by aligning weight distribution evenly and avoiding excessive height to prevent tipping hazards. Packing safety focuses on securing items within containers using appropriate cushioning materials to minimize movement and reduce damage during transit. Both practices emphasize adherence to load limits and proper handling protocols to protect workers and products.
Efficiency and Space Management Comparison
Stacking maximizes vertical space efficiency by layering items directly on top of each other, which is ideal for uniform shapes and weight distribution, reducing floor space usage. Packing optimizes space by arranging items tightly within a container, minimizing gaps and ensuring safe transport, which enhances load stability and protection. Both methods improve space management but selecting between stacking and packing depends on the item dimensions, fragility, and transportation requirements.
Choosing Between Stacking and Packing
Choosing between stacking and packing depends on factors such as space efficiency, protection requirements, and load stability. Stacking is ideal for maximizing vertical space and is commonly used in warehouses for uniform items with stable bases, while packing suits irregularly shaped goods requiring cushioning and organization within containers. Evaluating product dimensions, handling processes, and transportation methods helps optimize the decision for cost-effective storage and safe delivery.
Stacking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com