Advocacy groups play a crucial role in representing the interests and rights of specific communities or causes, influencing public policy and social change. Through organized campaigns, lobbying efforts, and public education, these groups strive to raise awareness and drive legislative action on important issues. Explore the rest of the article to understand how advocacy groups can amplify your voice and impact.
Table of Comparison
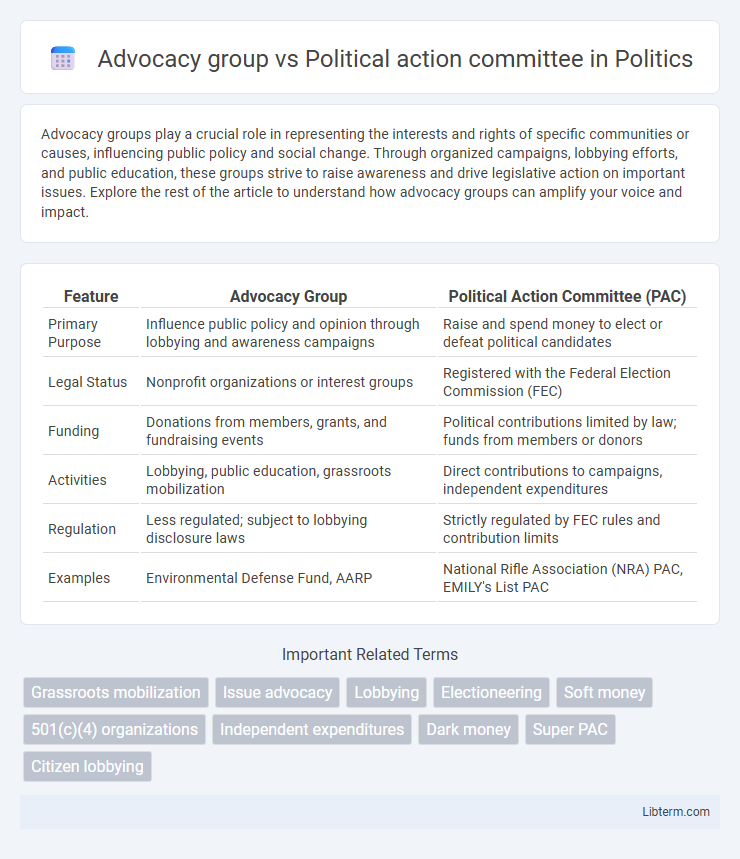
| Feature | Advocacy Group | Political Action Committee (PAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Influence public policy and opinion through lobbying and awareness campaigns | Raise and spend money to elect or defeat political candidates |
| Legal Status | Nonprofit organizations or interest groups | Registered with the Federal Election Commission (FEC) |
| Funding | Donations from members, grants, and fundraising events | Political contributions limited by law; funds from members or donors |
| Activities | Lobbying, public education, grassroots mobilization | Direct contributions to campaigns, independent expenditures |
| Regulation | Less regulated; subject to lobbying disclosure laws | Strictly regulated by FEC rules and contribution limits |
| Examples | Environmental Defense Fund, AARP | National Rifle Association (NRA) PAC, EMILY's List PAC |
Introduction: Understanding Advocacy Groups and Political Action Committees
Advocacy groups mobilize public support to influence policy changes and raise awareness on social or political issues, often operating as nonprofit organizations focused on education and lobbying efforts. Political Action Committees (PACs) collect funds to directly support or oppose political candidates, leveraging financial contributions to impact election outcomes and policymaking. Both entities play crucial roles in shaping legislation, yet PACs engage more directly in campaign financing while advocacy groups emphasize grassroots activism and public persuasion.
Defining Advocacy Groups: Purpose and Scope
Advocacy groups are organizations dedicated to influencing public policy and raising awareness on specific social, environmental, or economic issues by mobilizing community support and engaging in lobbying efforts. Their purpose is to represent the interests of a particular cause or demographic, often operating through education, grassroots campaigns, and direct communication with policymakers. Unlike political action committees, advocacy groups do not primarily focus on fundraising for election campaigns but prioritize issue-driven advocacy within legal boundaries set by campaign finance laws.
What is a Political Action Committee (PAC)?
A Political Action Committee (PAC) is a type of organization that collects and pools campaign contributions from members or supporters to donate funds to political candidates, parties, or legislation advocates. Unlike advocacy groups that focus on influencing public opinion and policy through education and lobbying, PACs directly finance electoral campaigns to support candidates aligned with their interests. PACs operate under strict federal regulations limiting donation amounts and requiring financial transparency to ensure accountability in political fundraising.
Key Differences Between Advocacy Groups and PACs
Advocacy groups primarily aim to influence public opinion and policy through education, lobbying, and grassroots campaigns, whereas Political Action Committees (PACs) focus on raising and donating funds to support political candidates or legislation. Advocacy groups can operate as nonprofit organizations and often engage in issue-based activism without direct candidate endorsements, while PACs are regulated entities specifically designed to contribute financially to electoral campaigns. The key distinction lies in their methods and legal restrictions: advocacy groups emphasize awareness and policy change, while PACs emphasize financial contributions within legal limits to electoral processes.
The Role of Advocacy Groups in Policy Influence
Advocacy groups play a crucial role in shaping public policy by mobilizing grassroots support, conducting research, and engaging with policymakers to promote specific social or political causes. Unlike Political Action Committees (PACs), which primarily focus on fundraising and supporting candidates through financial contributions, advocacy groups emphasize public education and lobbying efforts to influence legislative agendas. Their strategic use of media campaigns and coalition-building enhances their capacity to affect policy decisions and foster legislative change.
How PACs Participate in the Political Process
Political Action Committees (PACs) actively engage in the political process by directly contributing funds to candidates, political parties, and campaigns, enabling them to influence elections and policy decisions. PACs also organize fundraising events, run advertisements, and mobilize voters to support preferred candidates, thereby amplifying their impact on electoral outcomes. Unlike advocacy groups, PACs operate under strict federal regulations regarding fundraising limits and disclosure requirements, ensuring transparency in their political involvement.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks Governing Advocacy Groups and PACs
Advocacy groups operate under regulations that emphasize issue advocacy and typically cannot coordinate directly with candidates, governed primarily by the Federal Trade Commission and IRS rules for nonprofit status. Political Action Committees (PACs) are strictly regulated by the Federal Election Commission (FEC), which enforces contribution limits, disclosure requirements, and coordination rules with candidates and political parties. PACs must adhere to stringent reporting obligations and contribution limits, whereas advocacy groups benefit from fewer constraints but face restrictions on direct political campaigning to maintain tax-exempt status.
Funding Sources: Advocacy Groups vs PACs
Advocacy groups primarily rely on donations from individuals, membership fees, grants, and fundraising events to support their missions, whereas Political Action Committees (PACs) fund their activities through contributions from members, employees, or shareholders of connected organizations. PACs face strict federal limits on donation amounts and must regularly report their contributions and expenditures to the Federal Election Commission (FEC), ensuring transparency in political funding. Advocacy groups, especially 501(c)(3) nonprofits, have restrictions on direct political contributions but can engage in issue advocacy, often leveraging unrestricted donations.
Impact on Elections and Legislation
Advocacy groups influence elections and legislation primarily through awareness campaigns, lobbying efforts, and public mobilization, shaping voter opinions and pressuring lawmakers to adopt specific policies. Political Action Committees (PACs) directly impact elections by raising and spending funds to support or oppose candidates, thereby affecting electoral outcomes and legislative agendas. While advocacy groups focus on long-term policy influence, PACs play a critical role in financing campaigns that determine legislative power balances.
Choosing the Right Approach: Advocacy or Political Action?
Choosing the right approach depends on the desired impact: advocacy groups primarily focus on influencing public opinion and shaping policy through education and lobbying, while political action committees (PACs) directly support candidates or legislation by raising and spending money on campaigns. Advocacy groups engage in grassroots mobilization and issue awareness, making them ideal for long-term social change, whereas PACs provide strategic financial contributions to influence electoral outcomes more immediately. Understanding the goals, resources, and legal limitations of each entity ensures the selection of the most effective method for political influence and policy advancement.
Advocacy group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com