Administrative regulation establishes rules and procedures that govern the operations of government agencies, ensuring compliance and accountability in public administration. These regulations impact businesses, individuals, and organizations by setting standards for licensing, safety, and enforcement. Explore the rest of this article to understand how administrative regulations affect your daily interactions with government entities.
Table of Comparison
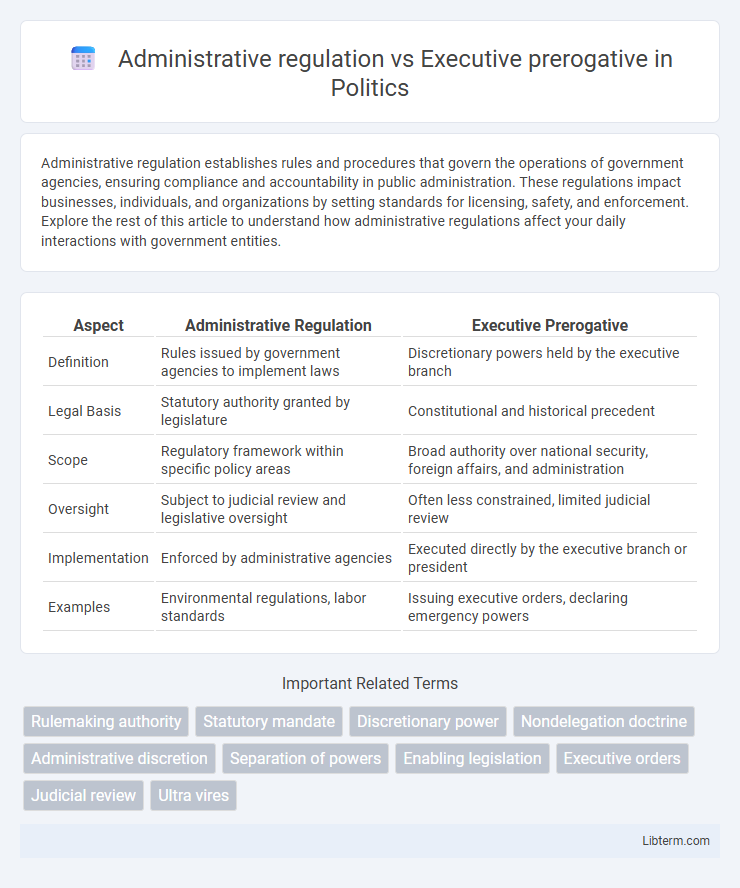
| Aspect | Administrative Regulation | Executive Prerogative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules issued by government agencies to implement laws | Discretionary powers held by the executive branch |
| Legal Basis | Statutory authority granted by legislature | Constitutional and historical precedent |
| Scope | Regulatory framework within specific policy areas | Broad authority over national security, foreign affairs, and administration |
| Oversight | Subject to judicial review and legislative oversight | Often less constrained, limited judicial review |
| Implementation | Enforced by administrative agencies | Executed directly by the executive branch or president |
| Examples | Environmental regulations, labor standards | Issuing executive orders, declaring emergency powers |
Introduction to Administrative Regulation and Executive Prerogative
Administrative regulation involves rules and standards set by government agencies to implement legislative mandates, ensuring consistent public policy enforcement. Executive prerogative refers to the discretionary powers granted to executive authorities, allowing swift decision-making in areas where legislation is silent or ambiguous. Understanding the balance between formal regulations and executive discretion is crucial for effective governance and legal accountability.
Defining Administrative Regulation
Administrative regulation refers to the rules and standards established by government agencies to implement laws passed by the legislature, ensuring consistent enforcement and compliance across various sectors. These regulations have the force of law and are designed to address complex issues that require specialized knowledge beyond legislative capabilities. Unlike executive prerogative, which involves discretionary actions taken by the executive branch without explicit statutory authority, administrative regulations are formally codified and subject to public review and legal challenges.
Understanding Executive Prerogative
Executive prerogative refers to the discretionary powers granted to the executive branch, allowing decisions without prior legislative approval, typically in matters of national security, foreign affairs, or emergencies. Unlike administrative regulation, which involves rulemaking subject to procedural oversight and public input, executive prerogative operates under inherent authority rooted in constitutional or statutory provisions. Understanding this distinction highlights how executive prerogative enables swift action while administrative regulation ensures transparency and accountability in government decision-making.
Historical Evolution of Both Concepts
Administrative regulation evolved from early 20th-century efforts to address industrialization's complexities, establishing formal rules by government agencies to ensure public welfare and market stability. Executive prerogative traces its roots to monarchical powers and colonial governance, granting the executive branch discretionary authority to act swiftly in matters of national security and foreign policy. Over time, the balance between these concepts has been shaped by legal precedents and constitutional interpretations emphasizing checks and accountability.
Legal Basis and Framework
Administrative regulation derives its legal basis from statutes enacted by legislatures, establishing detailed rules and procedures for implementing laws; regulatory agencies operate within a framework defined by enabling legislation and adhere to procedural standards such as the Administrative Procedure Act. Executive prerogative stems from constitutional powers vested in the executive branch, allowing discretionary actions, especially in matters of national security and foreign policy, often grounded in inherent or delegated authority without explicit statutory mandates. The contrast lies in administrative regulation's reliance on legislative authorization and procedural oversight, while executive prerogative emphasizes constitutional or inherent powers exercised independently of detailed legislative frameworks.
Scope and Limitations
Administrative regulation involves rules created by government agencies to implement and enforce legislation within defined legal frameworks, ensuring public accountability and procedural transparency. Executive prerogative refers to discretionary powers exercised by the executive branch, particularly in areas like national security or foreign affairs, often with broader latitude but subject to constitutional or judicial limits. The scope of administrative regulation is generally narrower and more procedural, while executive prerogative holds a wider yet more politically sensitive authority, both constrained by legal boundaries to prevent abuse of power.
Key Differences: Administrative Regulation vs Executive Prerogative
Administrative regulation involves formal rules issued by government agencies based on legislative authority to ensure compliance and implement policy, whereas executive prerogative refers to discretionary powers exercised by the executive branch, often without requiring legislative approval. Administrative regulations are subject to public comment, judicial review, and adherence to procedural standards, while executive prerogatives typically involve decisions made unilaterally by the president or executive officials in areas like national security or emergency responses. The key difference lies in the legal basis and oversight mechanisms: administrative regulations derive authority from statutes and regulatory frameworks, whereas executive prerogative stems from inherent executive powers and constitutional interpretations.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Administrative regulation shapes government agency actions through detailed rules, as seen in the landmark Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, where court deference highlighted agency expertise in environmental policy interpretation. Executive prerogative allows presidents to act independently in national security and foreign affairs, exemplified by Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer, which limited executive power during wartime. These cases illustrate the balance between regulatory frameworks and executive discretion in U.S. governance.
Impacts on Governance and Public Administration
Administrative regulation establishes formal rules that ensure transparency, accountability, and consistency in public administration, directly shaping policy implementation and service delivery. Executive prerogative allows discretion in decision-making, enabling rapid responses to emerging issues but risks undermining bureaucratic checks and balances. The tension between these mechanisms influences governance effectiveness by balancing regulatory certainty with administrative flexibility.
Future Trends and Challenges
Future trends in administrative regulation emphasize increased reliance on data analytics and artificial intelligence to enhance regulatory precision and responsiveness. Challenges include balancing executive prerogative with transparency and accountability, as expanding digital governance tools raise concerns about oversight and public trust. Navigating these dynamics requires integrating regulatory innovation with robust legal frameworks to ensure equitable and effective administration.
Administrative regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com