Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the number of votes they receive, promoting a fairer and more inclusive electoral system. This method enhances the diversity of viewpoints in legislatures, giving smaller parties a better chance to influence policy decisions. Discover how proportional representation can transform your voting experience by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
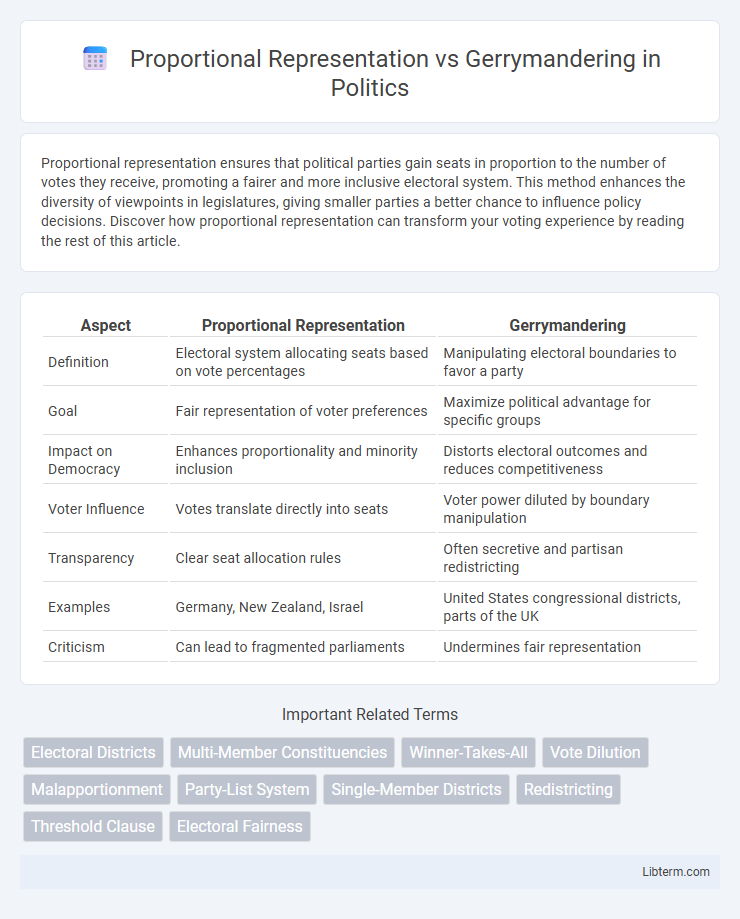
| Aspect | Proportional Representation | Gerrymandering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electoral system allocating seats based on vote percentages | Manipulating electoral boundaries to favor a party |
| Goal | Fair representation of voter preferences | Maximize political advantage for specific groups |
| Impact on Democracy | Enhances proportionality and minority inclusion | Distorts electoral outcomes and reduces competitiveness |
| Voter Influence | Votes translate directly into seats | Voter power diluted by boundary manipulation |
| Transparency | Clear seat allocation rules | Often secretive and partisan redistricting |
| Examples | Germany, New Zealand, Israel | United States congressional districts, parts of the UK |
| Criticism | Can lead to fragmented parliaments | Undermines fair representation |
Understanding Proportional Representation
Proportional representation ensures that political parties receive seats in legislative bodies in direct proportion to the percentage of votes they secure, promoting fairer and more diverse representation. This electoral system minimizes the distortions often caused by gerrymandering, a practice where electoral district boundaries are manipulated to favor specific parties or candidates. By reflecting the actual voter preferences more accurately, proportional representation enhances democratic legitimacy and reduces partisan bias in election outcomes.
What Is Gerrymandering?
Gerrymandering is the practice of manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor a specific political party or group, often resulting in distorted representation. This tactic undermines the principle of proportional representation by concentrating or diluting voter influence to secure electoral advantage. Courts and reform advocates seek to address gerrymandering through independent commissions and algorithmic districting methods to promote fair and equitable elections.
Historical Origins of Electoral Systems
Proportional representation emerged in the late 19th century as a response to the limitations of winner-takes-all systems, aiming to allocate seats in legislatures based on the percentage of votes each party receives, thereby ensuring more equitable representation. Gerrymandering, with origins tracing back to the early 19th century in the United States, involves manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor a particular party or group, skewing democratic outcomes. While proportional representation strives for fairness by reflecting voter preferences accurately, gerrymandering undermines this principle by distorting district lines to influence election results.
How Proportional Representation Works
Proportional representation allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of the electorate's preferences. Unlike winner-takes-all systems susceptible to gerrymandering, proportional representation reduces district manipulation by emphasizing party lists or multi-member constituencies. This voting system enhances fairness and diversity by enabling smaller parties to gain representation proportional to their actual support.
Mechanisms and Tactics of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering manipulates electoral district boundaries through mechanisms like "cracking," which dilutes opposition voters across multiple districts, and "packing," which concentrates them into a few districts to minimize their overall influence. These tactics exploit geographic distributions to engineer safe seats and skew representation despite actual voter preferences. In contrast, proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, reducing opportunities for such boundary-based manipulation.
Impacts on Voter Representation
Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to their share of the vote, significantly enhancing voter representation by reflecting diverse political preferences more accurately than winner-takes-all systems. Gerrymandering manipulates electoral district boundaries to favor specific parties or candidates, often diluting certain voter groups' influence and leading to misrepresentation in legislative bodies. This distortion undermines democratic fairness by skewing election outcomes away from the actual voter distribution, reducing the effectiveness of each vote.
Electoral Fairness: A Comparative Analysis
Proportional representation ensures electoral fairness by allocating seats in legislative bodies based on the percentage of votes each party receives, minimizing vote wastage and enhancing minority representation. Gerrymandering manipulates district boundaries to create an unfair advantage for particular parties, often diluting voter influence and skewing election outcomes. Comparative analysis highlights that proportional representation promotes equitable voter influence, whereas gerrymandering undermines democratic fairness by distorting constituency boundaries for partisan gain.
Case Studies: Countries and Outcomes
Proportional Representation systems, as implemented in countries like Germany and New Zealand, consistently produce more equitable electoral outcomes by closely matching the percentage of votes with legislative seats, enhancing minority representation and political diversity. In contrast, Gerrymandering in the United States has led to skewed district boundaries that disproportionately favor one party, resulting in decreased electoral competitiveness and distorted voter influence. Case studies reveal that proportional representation frameworks tend to foster fairer democratic processes, while gerrymandering undermines electoral integrity and public trust.
Reform Movements and Policy Solutions
Reform movements addressing gerrymandering emphasize adopting proportional representation systems, which allocate seats based on the percentage of votes received, ensuring fairer political outcomes and reducing partisan manipulation. Policy solutions include independent redistricting commissions that draw electoral boundaries transparently, minimizing biases that favor incumbents or dominant parties. Implementing multi-member districts and ranked-choice voting further strengthens proportional representation, promoting diverse and equitable legislative bodies.
Future of Electoral Systems: Trends and Predictions
Proportional representation systems are gaining momentum globally as they offer more equitable voter representation compared to gerrymandering-prone district-based models, which often manipulate boundaries to favor specific parties. Emerging trends suggest increased adoption of mixed-member proportional frameworks and algorithmic redistricting tools aimed at minimizing bias and enhancing transparency. Predictions for future electoral systems emphasize technological integration and legal reforms that prioritize fairness, inclusivity, and voter confidence over traditional, partisan-driven district manipulation.
Proportional Representation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com