Running as an independent candidate allows you to bypass traditional party politics, giving you the freedom to prioritize your constituents' interests directly. This approach demands strong personal branding and grassroots support to gain visibility and influence. Explore the rest of the article to learn how an independent candidacy can shape your political journey and impact your community.
Table of Comparison
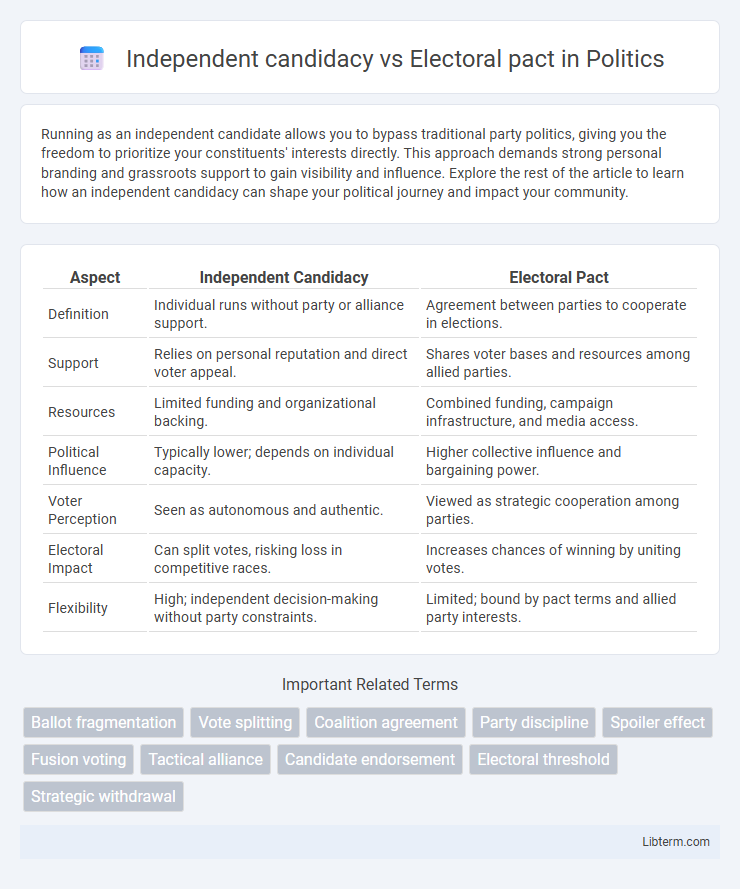
| Aspect | Independent Candidacy | Electoral Pact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual runs without party or alliance support. | Agreement between parties to cooperate in elections. |
| Support | Relies on personal reputation and direct voter appeal. | Shares voter bases and resources among allied parties. |
| Resources | Limited funding and organizational backing. | Combined funding, campaign infrastructure, and media access. |
| Political Influence | Typically lower; depends on individual capacity. | Higher collective influence and bargaining power. |
| Voter Perception | Seen as autonomous and authentic. | Viewed as strategic cooperation among parties. |
| Electoral Impact | Can split votes, risking loss in competitive races. | Increases chances of winning by uniting votes. |
| Flexibility | High; independent decision-making without party constraints. | Limited; bound by pact terms and allied party interests. |
Introduction to Independent Candidacy
An independent candidacy allows individuals to run for public office without affiliation to established political parties, emphasizing personal platforms and direct voter engagement. This approach contrasts with electoral pacts, where candidates align with parties or coalitions to consolidate support and resources. Independent candidates often appeal to voters seeking alternatives to traditional party politics and prioritize grassroots campaigning.
What is an Electoral Pact?
An electoral pact is a formal agreement between two or more political parties to coordinate their candidate nominations and voting strategies in an election to maximize their chances of winning seats. Unlike independent candidacy, where a candidate runs without party support or alliances, an electoral pact leverages combined resources, voter bases, and strategic withdrawals to avoid vote splitting. This collaboration often aims to consolidate votes against common opponents and enhance overall electoral effectiveness.
Historical Context: Independent vs Coalition Politics
Independent candidacy historically reflects individual political agency, often emerging in contexts where party disillusionment or localized issues dominate voter interests. Electoral pacts, by contrast, have roots in coalition politics aimed at consolidating opposition and maximizing electoral success against dominant parties. These dynamics illustrate evolving strategies between personal political identity and collective party cooperation in democratic systems.
Advantages of Running as an Independent
Running as an independent candidate offers freedom from party constraints, enabling a personalized platform that directly addresses constituent needs without external influence. Independent candidates often appeal to voters seeking unbiased representation and can capitalize on grassroots support, enhancing voter engagement and trust. This approach promotes accountability and transparency, as independents answer solely to their electorate rather than party agendas.
Benefits of Forming Electoral Pacts
Forming electoral pacts allows candidates or parties to pool resources, consolidate voter bases, and increase their chances of winning seats by avoiding vote splitting. Electoral alliances can enhance strategic positioning in multi-member districts, facilitating greater influence in legislative bodies. This collaboration often results in shared campaign costs and a stronger, unified front against common political opponents.
Challenges Faced by Independent Candidates
Independent candidates face significant challenges including limited access to party resources, reduced media exposure, and difficulties in mobilizing voter support compared to those within an electoral pact. The absence of established party infrastructure often results in constrained fundraising and organizational capabilities, making campaign logistics more demanding. Moreover, independent candidates typically confront barriers in gaining visibility and legitimacy, which electoral pacts help mitigate by pooling votes and consolidating political influence.
Potential Pitfalls of Electoral Alliances
Electoral alliances can lead to voter confusion when party platforms are diluted or conflicting, reducing overall voter trust. Power imbalances within the pact may marginalize smaller parties, limiting their influence and causing internal friction. Additionally, dependency on alliance partners risks election setbacks if one member faces scandals or unpopular decisions, undermining the coalition's entire campaign.
Voter Perceptions and Electability
Independent candidacy often appeals to voters seeking authenticity and direct representation, enhancing perceived trustworthiness but sometimes facing challenges in broad voter reach and resource limitations. Electoral pacts typically improve electability by consolidating votes and reducing competition among allied parties, fostering a sense of strategic unity among supporters. Voters may perceive electoral pacts as pragmatic and more likely to influence policy outcomes, while independent candidates are viewed as symbolic of political diversity and principled stands.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Failures
Independent candidacy demonstrated success in the 2016 US presidential election when outsider Donald Trump secured victory without party backing, highlighting strong personal appeal and grassroots support. Electoral pacts, such as the 2019 UK Brexit Party alliance with the Conservatives, yielded mixed results, consolidating votes in some constituencies but causing fragmentation in others. Failure cases include the 2018 French legislative elections where fragmented independent runs led to vote splitting, benefiting established parties.
Future Trends: Evolving Strategies in Political Campaigns
Independent candidacies are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to mobilize grassroots support, reflecting a shift towards personalized voter engagement. Electoral pacts, however, continue to evolve through strategic alliances that pool resources and unify messaging to counter fragmented opposition in proportional representation systems. Emerging trends indicate a hybrid approach where candidates maintain individual branding while benefiting from coalition support, optimizing both autonomy and collective influence in future elections.
Independent candidacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com