A well-defined policy establishes clear guidelines and expectations to ensure consistent decision-making and behavior within an organization. It helps mitigate risks, maintain compliance, and promote transparency across all levels. Discover how implementing effective policies can benefit your organization by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
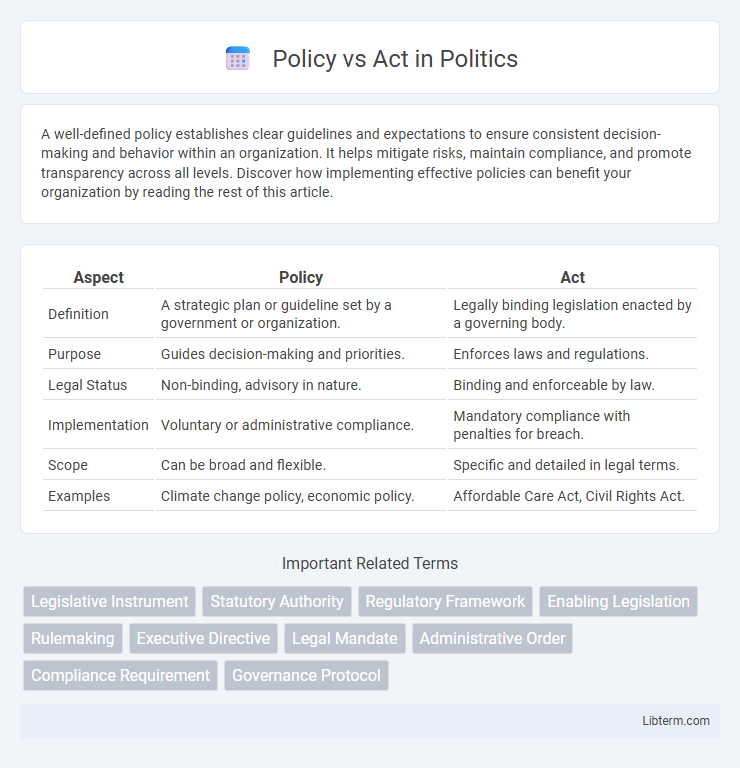
| Aspect | Policy | Act |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A strategic plan or guideline set by a government or organization. | Legally binding legislation enacted by a governing body. |
| Purpose | Guides decision-making and priorities. | Enforces laws and regulations. |
| Legal Status | Non-binding, advisory in nature. | Binding and enforceable by law. |
| Implementation | Voluntary or administrative compliance. | Mandatory compliance with penalties for breach. |
| Scope | Can be broad and flexible. | Specific and detailed in legal terms. |
| Examples | Climate change policy, economic policy. | Affordable Care Act, Civil Rights Act. |
Introduction to Policy and Act
A policy is a deliberate set of guidelines or principles designed to influence decisions and achieve rational outcomes within organizations or governments. An act, on the other hand, is a formal piece of legislation passed by a legislative body that carries legal authority and mandates specific actions or regulations. Understanding the distinction between a policy's advisory nature and an act's binding legal force is essential for effective governance and compliance.
Defining Policy
A policy is a set of guiding principles or rules established by an organization or government to influence decisions and achieve rational outcomes. Policies provide a framework for consistent decision-making and are often flexible to adapt to changing circumstances. Unlike an act, which is a formal legal statute enacted by a legislative body, a policy serves as an internal directive to guide behavior and operations within a specific context.
Defining Act
An Act refers to a formal statute enacted by a legislative body, establishing legal requirements or prohibitions with binding authority. Unlike policies, which serve as guidelines or principles to influence decisions and actions, an Act has the force of law and is enforceable by courts and regulatory agencies. Acts provide a concrete legal framework that mandates compliance and outlines specific rights, duties, or penalties.
Key Differences Between Policy and Act
A policy is a strategic guideline or principle established by an organization or government to direct decision-making and achieve long-term goals, whereas an act is a formal legal statute enacted by a legislative body to regulate behavior or enforce laws. Policies are typically flexible and can be revised internally without legislative approval, while acts require official passage through legislative procedures and have binding legal authority. Key differences include the level of formality, enforceability, and the process of implementation, with acts carrying mandatory compliance and legal penalties for violations, contrasting with policies that guide but do not impose legal obligations.
Purpose and Scope of Policy
A policy establishes guiding principles and objectives designed to influence decisions and achieve consistent outcomes within an organization or government. Its purpose is to provide a flexible framework that outlines expectations and responsibilities, applicable across various situations and departments. Unlike an act, which is a formal law enacted by a legislative body with specific legal obligations and enforcement mechanisms, a policy serves as a proactive tool for governance and strategic direction.
Purpose and Scope of Act
An Act is a formal statute enacted by a legislative body that defines legal obligations, rights, and regulations within a specific jurisdiction, establishing the foundation for governance and enforcement. The purpose of an Act is to create enforceable laws that address particular societal issues or regulatory needs, offering clear legal authority and consequences. Its scope typically delineates the extent of application, specifying the sectors, entities, or individuals affected and the limitations within which the law operates.
Legal Authority: Policy vs Act
A policy is a guiding principle set by organizations or governments to influence decisions and actions, lacking the force of law and primarily serving as an internal framework. An act, however, is a formal law enacted by a legislative body, carrying legal authority and enforceable by courts. The legal distinction lies in that acts impose binding obligations and rights, whereas policies provide non-binding directives that support compliance with the law.
Implementation and Enforcement
Policies establish guiding principles and strategic intentions that shape decision-making and resource allocation, while Acts are formal laws enacted by legislative bodies with defined legal authority. Implementation of policies often relies on administrative agencies and organizational procedures to translate objectives into actionable programs, whereas enforcement of Acts involves regulatory bodies empowered to impose penalties for non-compliance. Effective governance requires aligning policy frameworks with statutory mandates to ensure coherent application and consistent enforcement mechanisms.
Real-World Examples
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) exemplifies an act, as it is a formal legislative statute enacted by the US Congress to expand healthcare coverage. In contrast, a climate change policy like the European Green Deal outlines strategic goals and guidelines without the binding enforcement power typical of an act. Policies provide frameworks for decision-making, while acts carry legal authority and mandate specific actions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Policy and Act
Choosing between a policy and an act depends on the desired level of formality, enforcement, and flexibility; policies offer adaptable guidelines within organizations, while acts are legally binding statutes enacted by governments. Policies allow quicker modifications to address evolving needs, whereas acts require legislative approval, providing permanence and legal authority. Decision-makers must evaluate the scope, impact, and enforcement mechanisms to determine the appropriate regulatory tool for effective governance.
Policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com