A political faction is a group within a larger political party or organization that shares common interests, goals, or ideologies, often competing for power and influence. These factions can shape policy decisions, leadership choices, and the overall direction of the party by advocating for specific agendas. Discover how understanding political factions can help you navigate the complex landscape of political dynamics in the full article.
Table of Comparison
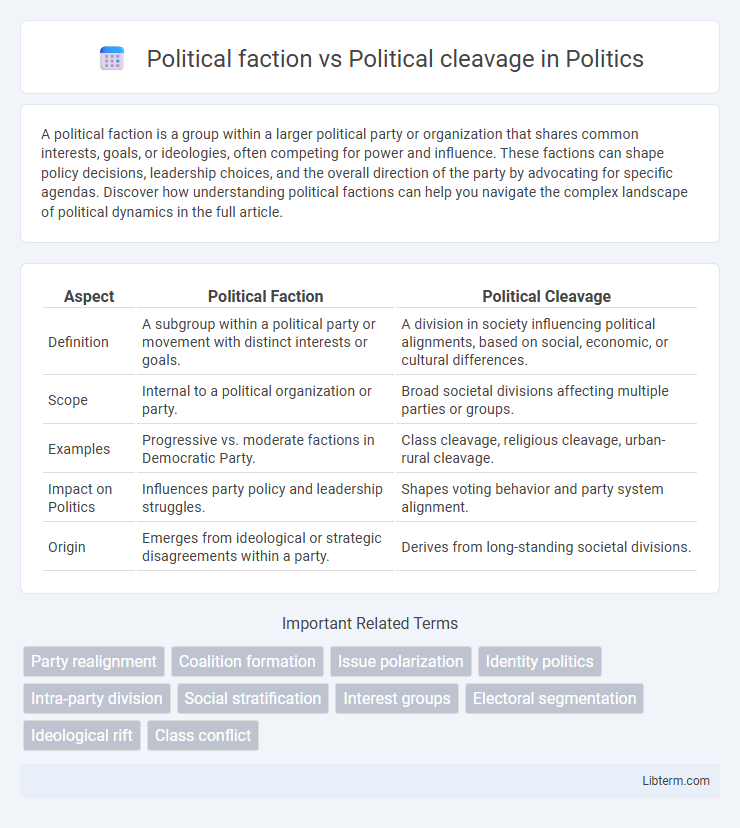
| Aspect | Political Faction | Political Cleavage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A subgroup within a political party or movement with distinct interests or goals. | A division in society influencing political alignments, based on social, economic, or cultural differences. |
| Scope | Internal to a political organization or party. | Broad societal divisions affecting multiple parties or groups. |
| Examples | Progressive vs. moderate factions in Democratic Party. | Class cleavage, religious cleavage, urban-rural cleavage. |
| Impact on Politics | Influences party policy and leadership struggles. | Shapes voting behavior and party system alignment. |
| Origin | Emerges from ideological or strategic disagreements within a party. | Derives from long-standing societal divisions. |
Understanding Political Factions
Political factions are organized groups within a larger political party or movement that advocate for specific interests, ideologies, or policy goals, often influencing leadership decisions and party platforms. These factions arise from internal divisions based on ideological, social, or economic differences, shaping party dynamics and electoral strategies. Understanding political factions requires analyzing their role in coalition-building, conflict resolution, and power distribution within the broader political system.
Defining Political Cleavages
Political cleavages are enduring social divisions that structure political preferences and party systems, often based on factors such as class, religion, ethnicity, or geography. Unlike political factions, which are temporary alliances within parties or movements, political cleavages represent deep-rooted societal conflicts influencing voter alignment and public policy. Understanding political cleavages is essential for analyzing how long-term social identities shape political behavior and institutional development.
Historical Origins of Political Factions
Political factions historically emerged from deep-seated divisions in society over governance, ideology, and power, often rooted in economic interests, religious conflicts, or social structures. These factions, unlike political cleavages which are broader and more enduring societal divisions, originated as organized groups competing for control within governments or ruling bodies, exemplified by the Federalists and Anti-Federalists in early American history. The formation of political factions reflects the dynamic process of political contestation and realignment rather than fixed societal divides represented by political cleavages.
Theoretical Frameworks for Political Cleavage
Political cleavage theory identifies deep, enduring societal divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity that shape political alignments and influence party systems. Theoretical frameworks like Lipset and Rokkan's cleavage theory highlight the historical origins and institutionalization of these cleavages, explaining how they structure voter behavior and party competition. Unlike political factions, which are transient and issue-specific groups within parties, political cleavages represent fundamental, stable social divisions embedded in the political landscape.
Key Differences Between Factions and Cleavages
Political factions represent organized groups within a larger political entity, often competing for power or influence based on shared interests or ideologies, whereas political cleavages are deep societal divisions that structure political alignments along lines such as class, ethnicity, or religion. Factions are more fluid and can form or dissolve within parties or governments, while cleavages are more enduring social divisions that shape voter behavior and party systems over time. Understanding these distinctions is essential for analyzing political dynamics, as factions influence immediate policy debates and power struggles, whereas cleavages underpin long-term political identities and alignments.
Impact on Political Systems
Political factions often lead to competition within parties, fragmenting unity and complicating decision-making processes, while political cleavages represent deeper societal divisions--such as class, religion, or ethnicity--that shape party systems and voter alignments over time. The presence of multiple factions can destabilize legislative cohesion, whereas entrenched cleavages typically result in stable, long-term patterns of political competition and policy preferences. Both dynamics significantly influence political stability, governance effectiveness, and the evolution of democratic institutions worldwide.
Examples of Political Factions Worldwide
Political factions are organized groups within larger political parties or movements competing for power, such as the Federalists and Anti-Federalists in early U.S. history or China's Communist Party factions like the Princelings and Tuanpai. Political cleavages represent deep societal divisions, such as class, ethnicity, or religion, shaping party systems; examples include the left-right economic divide in European countries or the Protestant-Catholic split in Northern Ireland. Understanding these distinctions highlights how factions operate within broader cleavages that influence political alignments globally.
Major Political Cleavages in Modern Politics
Major political cleavages in modern politics often divide societies along lines such as class, religion, ethnicity, and urban-rural residence, shaping the formation of political factions. Political factions arise from these cleavages as organized groups that seek to influence government policy and gain power within political systems. Understanding the structural basis of political cleavages is essential for analyzing factional competition and the dynamics of party systems in contemporary democracies.
How Factions and Cleavages Shape Elections
Political factions and cleavages fundamentally influence electoral dynamics by structuring voter preferences and party competition. Factions represent organized groups within parties that vie for control, impacting candidate selection and policy platforms, while cleavages are deep, societal divisions--such as class, religion, or ethnicity--that shape voter alignments and turnout. Together, these forces determine coalition-building strategies and voter mobilization, ultimately shaping election outcomes and the political landscape.
Future Trends in Political Division
Future trends in political division highlight an increasing complexity where political factions, defined as organized groups with specific agendas, evolve within broader political cleavages such as class, religion, or ethnicity. Emerging digital platforms facilitate rapid fragmentation, causing factions to multiply around niche issues, intensifying existing cleavages. This dynamic fosters a more polarized and multifaceted political landscape, influencing electoral behavior and policy-making worldwide.
Political faction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com