A transitional clause connects ideas smoothly by indicating relationships such as time, cause, or contrast between sentences. These clauses often begin with subordinating conjunctions like "because," "although," or "while," helping to clarify the flow of your writing. Explore the rest of this article to understand how to effectively use transitional clauses in your writing.
Table of Comparison
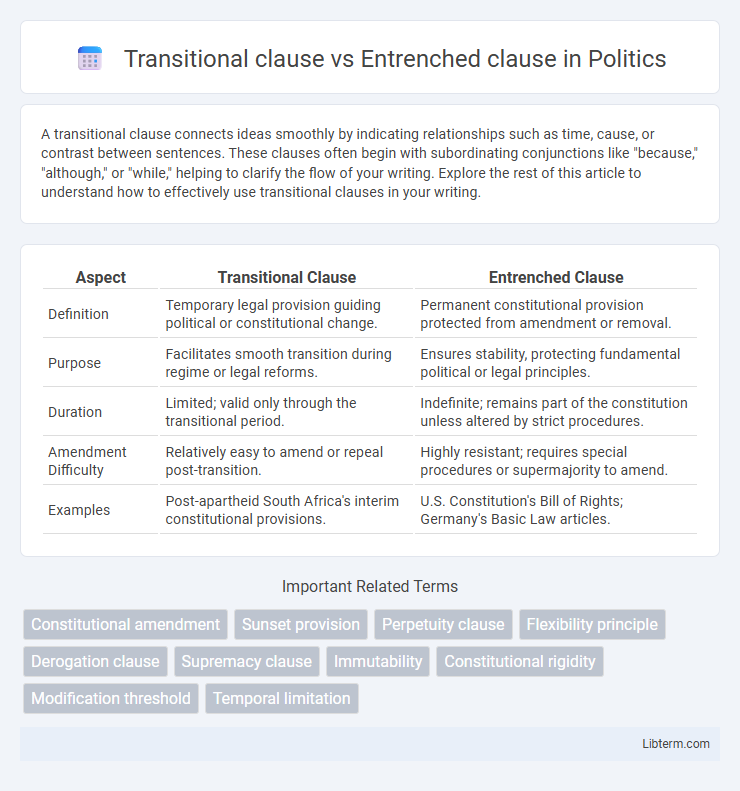
| Aspect | Transitional Clause | Entrenched Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary legal provision guiding political or constitutional change. | Permanent constitutional provision protected from amendment or removal. |
| Purpose | Facilitates smooth transition during regime or legal reforms. | Ensures stability, protecting fundamental political or legal principles. |
| Duration | Limited; valid only through the transitional period. | Indefinite; remains part of the constitution unless altered by strict procedures. |
| Amendment Difficulty | Relatively easy to amend or repeal post-transition. | Highly resistant; requires special procedures or supermajority to amend. |
| Examples | Post-apartheid South Africa's interim constitutional provisions. | U.S. Constitution's Bill of Rights; Germany's Basic Law articles. |
Introduction to Constitutional Clauses
Transitional clauses facilitate the shift from old to new legal frameworks, ensuring continuity during constitutional changes by outlining temporary provisions. Entrenched clauses, in contrast, are deeply embedded protections within a constitution, designed to be rigid and difficult to amend, preserving fundamental principles and rights. These constitutional clauses serve distinct roles in legal stability and adaptability, balancing flexibility with permanence.
Defining Transitional Clauses
Transitional clauses serve as linguistic bridges that connect ideas, events, or concepts within text, facilitating smooth progression and coherence. These clauses often introduce time-related shifts, cause-and-effect relationships, or contrast, thereby guiding readers through the narrative or argument. In contrast, entrenched clauses are fixed expressions whose meanings are deeply embedded and resistant to change, often functioning idiomatically rather than serving purely transitional purposes.
Understanding Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses are provisions within contracts or constitutions that are deliberately made difficult to amend or repeal, ensuring their stability and long-term enforceability. These clauses often require special procedures, such as supermajority votes or referendums, to prevent frequent changes and protect fundamental rights or principles. Understanding entrenched clauses is crucial for recognizing how legal systems balance flexibility with the need for constitutional or contractual continuity.
Key Differences Between Transitional and Entrenched Clauses
Transitional clauses serve as temporary provisions enacted during political or constitutional change, designed to guide the shift from an old legal framework to a new one. Entrenched clauses are permanent features within a constitution, protected by rigorous amendment procedures to preserve core principles and prevent easy alteration. Key differences lie in their durability and purpose: transitional clauses are time-bound and flexible, while entrenched clauses ensure stability and legal continuity over time.
Purposes of Transitional Clauses
Transitional clauses primarily function to guide readers through different parts of a text by linking ideas, enhancing coherence, and signaling shifts in argument or time. They enable smooth progression between sentences or paragraphs, ensuring the narrative or explanation flows logically. Unlike entrenched clauses, which firmly establish facts or states, transitional clauses emphasize relationships and transitions within the discourse.
Significance of Entrenched Clauses in Constitutions
Entrenched clauses in constitutions serve as fundamental safeguards by requiring stringent procedures for amendment, thereby preserving core principles and preventing arbitrary changes. Their significance lies in maintaining constitutional stability and protecting essential rights from transient political pressures. Unlike transitional clauses, entrenched clauses provide lasting legal continuity and reinforce the constitution's supremacy.
Amendment Procedures for Each Clause Type
Transitional clauses in constitutional law typically allow temporary or provisional amendment procedures designed to facilitate smooth shifts during periods of political or structural change, often requiring simpler majority thresholds. Entrenched clauses, by contrast, are safeguarded by stringent amendment procedures involving supermajority votes, referendums, or multiple legislative approvals to prevent frequent or easy alterations. These differentiated amendment protocols ensure stability by protecting fundamental principles in entrenched clauses while permitting flexibility through transitional provisions.
Practical Examples: Transitional vs Entrenched Clauses
Transitional clauses often include phrases like "in the meantime" or "until further notice," signaling temporary conditions or changes, such as "The office will remain closed until further notice." Entrenched clauses, embedded firmly in legal or contractual language, establish permanent rights or obligations, for example, "No employee shall disclose confidential information under any circumstances." Understanding the practical differences aids in drafting contracts where transitional clauses allow for flexibility, while entrenched clauses ensure enforceable, long-term provisions.
Legal Implications of Both Clauses
Transitional clauses facilitate the gradual application of new legal provisions, ensuring continuity and minimizing disruption in regulatory frameworks. Entrenched clauses impose strict limitations on amendments or repeal, securing fundamental rights or constitutional principles from arbitrary changes. The legal implications of transitional clauses allow flexibility in legislative evolution, whereas entrenched clauses prioritize stability and protection of core legal norms.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clause for Constitutional Stability
Transitional clauses facilitate a smooth shift from old to new constitutional frameworks by setting temporary provisions that ease institutional changes. Entrenched clauses, often found in supreme laws, provide rigidity by requiring supermajorities or referenda for amendments, thus protecting core principles from frequent alterations. Selecting the appropriate clause ensures constitutional stability by balancing adaptability with the protection of fundamental legal norms.
Transitional clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com