The role of a Sergeant-at-Arms is crucial in maintaining order and security during legislative sessions or formal meetings, ensuring protocols are strictly followed. This position often involves responsibilities such as enforcing rules, safeguarding officials, and managing access to restricted areas. Discover how the Sergeant-at-Arms contributes to the smooth functioning of assemblies and what your involvement might entail.
Table of Comparison
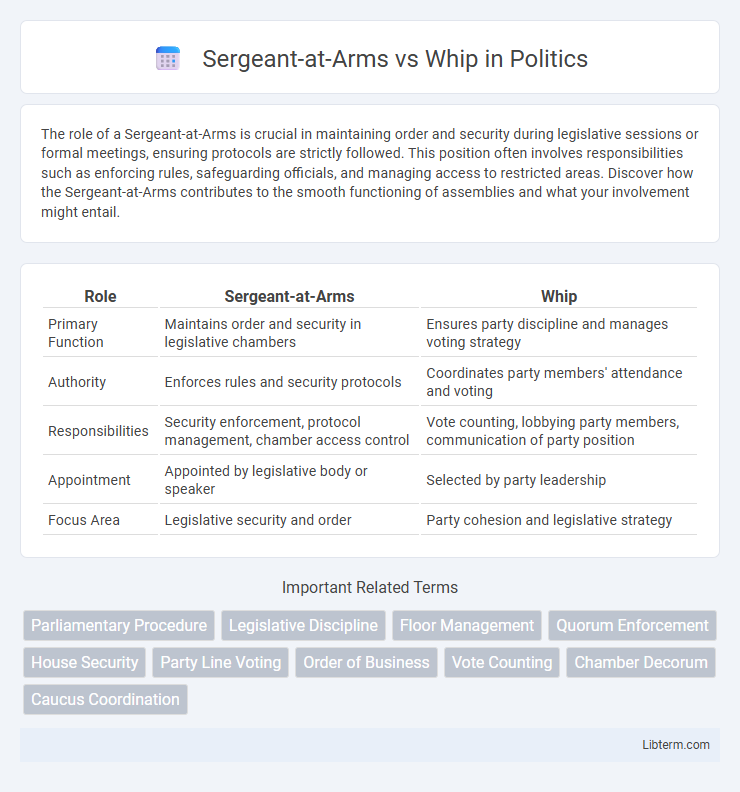
| Role | Sergeant-at-Arms | Whip |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Maintains order and security in legislative chambers | Ensures party discipline and manages voting strategy |
| Authority | Enforces rules and security protocols | Coordinates party members' attendance and voting |
| Responsibilities | Security enforcement, protocol management, chamber access control | Vote counting, lobbying party members, communication of party position |
| Appointment | Appointed by legislative body or speaker | Selected by party leadership |
| Focus Area | Legislative security and order | Party cohesion and legislative strategy |
Introduction to Parliamentary Roles
The Sergeant-at-Arms is a parliamentary officer responsible for maintaining order, security, and protocol within legislative chambers, often managing access and ensuring safety during sessions. The Whip is a party official tasked with enforcing party discipline, managing voting procedures, and ensuring members attend and vote according to party lines. Both roles are crucial in parliamentary systems, balancing procedural order with party strategy to ensure effective legislative functioning.
Defining the Sergeant-at-Arms
The Sergeant-at-Arms is a key parliamentary official responsible for maintaining order and security within legislative assemblies, ensuring that members adhere to procedural rules. Unlike the Whip, who manages party discipline and ensures attendance for votes, the Sergeant-at-Arms enforces decorum and carries out ceremonial duties such as announcing the arrival of the presiding officer. This role combines law enforcement functions with protocol management, distinguishing it from the political coordination duties handled by the Whip.
Understanding the Role of the Whip
The Whip serves as a key party official responsible for maintaining party discipline, ensuring member attendance, and managing voting strategies within legislative bodies. Unlike the Sergeant-at-Arms, whose duties center on security and order enforcement, the Whip's role emphasizes political coordination and communication among party members. Effective Whips leverage detailed legislative knowledge and interpersonal skills to secure votes and uphold party unity during critical decision-making processes.
Historical Origins of Both Positions
The Sergeant-at-Arms position originated in medieval England as a royal officer responsible for maintaining order and security within the king's court and later in legislative bodies. The Whip role emerged in the 18th century British Parliament, initially as a party official tasked with ensuring legislators' attendance and securing votes aligned with party policies. Both positions evolved to support legislative functioning, with the Sergeant-at-Arms focusing on enforcement and security, while the Whip concentrates on party discipline and vote management.
Key Responsibilities: Sergeant-at-Arms
The Sergeant-at-Arms is primarily responsible for maintaining order and security within legislative assemblies, ensuring protocol compliance, and managing access control during sessions. This role involves enforcing rules, escorting disruptive members, and overseeing the physical safety of the chamber and its participants. The Sergeant-at-Arms also coordinates security personnel and facilitates the logistical aspects of formal meetings and ceremonies.
Key Duties: Role of the Whip
The Whip is responsible for ensuring party discipline and securing attendance for votes in legislative bodies, playing a pivotal role in maintaining the party's legislative agenda. This position involves communicating party positions to members, counting votes, and persuading legislators to support key bills. Unlike the Sergeant-at-Arms, who focuses on security and order within the chamber, the Whip serves as a strategic organizer for party cohesion and legislative success.
Comparison of Authority and Influence
The Sergeant-at-Arms typically holds authority rooted in maintaining order, security, and protocol within legislative bodies, often overseeing enforcement and disciplinary actions. In contrast, the Whip exercises significant influence by managing party discipline, securing votes, and coordinating legislative strategy to ensure party cohesion. While the Sergeant-at-Arms enforces procedural rules physically, the Whip wields political influence to shape legislative outcomes and party unity.
Impact on Legislative Procedures
The Sergeant-at-Arms enforces order and security within legislative chambers, ensuring procedural compliance and preventing disruptions that could delay or obstruct legislative processes. The Whip coordinates party members' voting and attendance, directly influencing legislative outcomes by managing support for bills and motions. Together, their roles critically impact legislative efficiency, with the Sergeant-at-Arms maintaining decorum and the Whip orchestrating party strategy to facilitate or hinder the passage of legislation.
Collaboration and Differences in Practice
The Sergeant-at-Arms ensures order and security within legislative sessions, while the Whip focuses on party discipline and vote mobilization. Collaboration occurs when both coordinate to manage member attendance and maintain procedural compliance during critical votes. Differences lie in operational scope: the Sergeant-at-Arms handles enforcement of rules and physical security, whereas the Whip strategizes political alignment and communication among party members.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Sergeant-at-Arms and Whip
Choosing between Sergeant-at-Arms and Whip hinges on the specific needs of legislative or organizational discipline versus party cohesion and vote management. The Sergeant-at-Arms primarily enforces order and security within legislative chambers, ensuring protocol adherence and member safety. The Whip focuses on securing party discipline, coordinating votes, and maintaining communication among party members to advance legislative agendas effectively.
Sergeant-at-Arms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com