A committee chair plays a crucial role in leading discussions, organizing meetings, and ensuring that agendas are effectively followed to achieve the group's objectives. This leadership position demands strong communication skills and the ability to manage diverse opinions to facilitate productive outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to discover essential tips on becoming an effective committee chair and boosting your leadership impact.
Table of Comparison
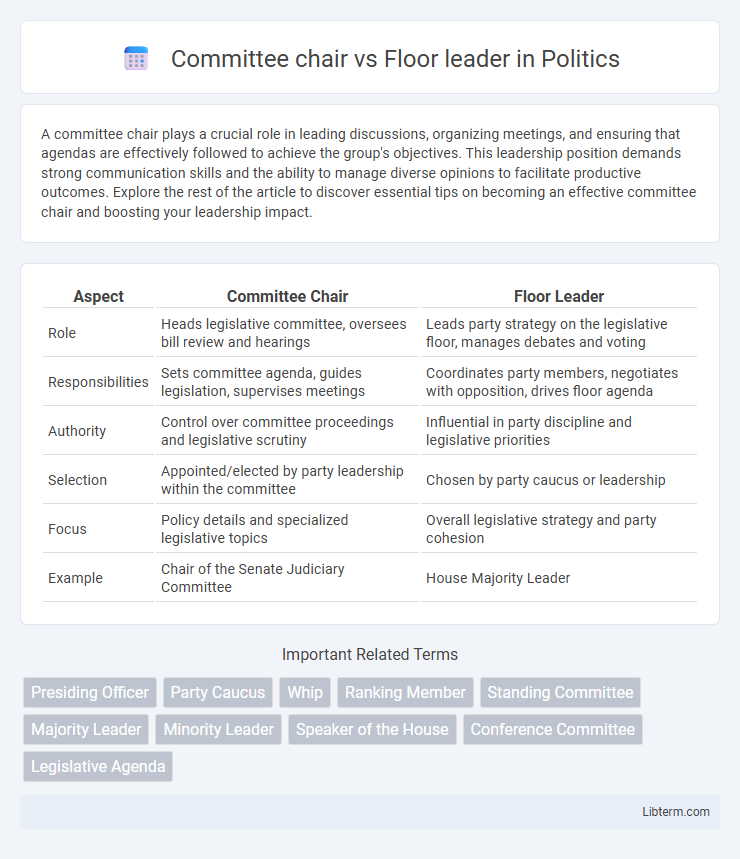
| Aspect | Committee Chair | Floor Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Heads legislative committee, oversees bill review and hearings | Leads party strategy on the legislative floor, manages debates and voting |
| Responsibilities | Sets committee agenda, guides legislation, supervises meetings | Coordinates party members, negotiates with opposition, drives floor agenda |
| Authority | Control over committee proceedings and legislative scrutiny | Influential in party discipline and legislative priorities |
| Selection | Appointed/elected by party leadership within the committee | Chosen by party caucus or leadership |
| Focus | Policy details and specialized legislative topics | Overall legislative strategy and party cohesion |
| Example | Chair of the Senate Judiciary Committee | House Majority Leader |
Introduction to Committee Chairs and Floor Leaders
Committee chairs oversee specific legislative committees, managing agenda setting and guiding policy discussions within their assigned areas. Floor leaders coordinate party strategy on the legislative floor, facilitating debate and mobilizing votes to advance party goals. Both roles are essential in shaping legislative priorities and ensuring efficient legislative processes within a parliamentary system.
Definition and Core Responsibilities
A Committee Chair is a legislative member responsible for leading a specific committee, setting agendas, guiding discussions, and managing the review of bills and policies related to the committee's focus area. A Floor Leader, often a senior party member, organizes and directs legislative strategy on the chamber floor, coordinating party members' votes and debate tactics to advance the party's legislative agenda. Both roles are pivotal for legislative efficiency, with the Committee Chair specializing in detailed policy review and the Floor Leader emphasizing overall legislative coordination and party leadership.
Historical Evolution of Both Roles
The committee chair emerged in the early 19th century as a pivotal figure responsible for steering legislative discussions and managing specialized policy areas within committees, evolving alongside the increasing complexity of parliamentary work. The floor leader role developed later, gaining prominence in the early 20th century as political parties sought organized leadership to coordinate strategy and maintain discipline during floor debates. Together, these roles reflect the adaptation of legislative structures to shifting political dynamics and the need for effective governance in democratic institutions.
Powers and Limitations
A Committee chair holds significant power over legislative agenda-setting, controlling hearings, and managing committee staff, but their influence is limited to the committee's scope and subject matter. In contrast, a Floor leader coordinates party strategy on the legislative floor, controls debate time, and guides voting, yet their authority depends on party cohesion and overall chamber rules. Both positions wield distinct yet complementary powers critical to legislative process efficiency while facing institutional and political constraints.
Selection and Appointment Processes
Committee chairs are typically selected by the majority party's leadership based on seniority, expertise, and party loyalty, often confirmed through a formal vote within the committee or party caucus. Floor leaders are appointed directly by their respective party's leadership or elected by party members in the legislative chamber to manage legislative strategy and coordinate party activities on the floor. The chair's selection emphasizes subject matter authority and committee control, while floor leader appointment prioritizes political leadership and legislative agenda management.
Influence on Legislative Proceedings
Committee chairs wield significant influence by setting agendas, controlling the flow of legislation, and overseeing detailed policy discussions within their committees. Floor leaders shape legislative proceedings by orchestrating party strategy, managing debates, and guiding voting decisions on the chamber floor. Their combined roles ensure the prioritization and passage of key legislative initiatives within the parliamentary process.
Collaboration and Conflicts Between Roles
Committee chairs and floor leaders collaborate to advance legislative agendas by coordinating bill discussions and managing party strategy; however, conflicts arise when priorities diverge or control over legislative timing becomes contested. Committee chairs hold significant influence over the detailed review and modification of bills, while floor leaders focus on navigating broader legislative procedures and vote mobilization. Effective communication and alignment between these roles are critical to minimizing conflicts and ensuring cohesive legislative progress.
Impact on Policy and Lawmaking
Committee chairs wield significant influence over policy and lawmaking by controlling the agenda, prioritizing bills, and guiding detailed legislative review within specific committees. Floor leaders impact policy by steering debate, managing party strategy during floor votes, and coordinating legislative priorities across the entire chamber. Together, these roles shape the legislative process through strategic decision-making and agenda control, directly affecting the passage and content of laws.
Notable Committee Chairs and Floor Leaders
Notable committee chairs such as Senator Richard Shelby and Representative Nancy Pelosi wield significant influence over legislative agendas by controlling committee hearings and bill markups. Prominent floor leaders, including Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer and House Minority Leader Kevin McCarthy, direct party strategy and manage floor debates to advance their party's priorities. The roles often intersect, but committee chairs focus on detailed policy development while floor leaders coordinate overall legislative tactics on the chamber floor.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Similarities
Committee chairs oversee legislative committees, managing discussions and guiding bill development, while floor leaders coordinate party strategy and manage legislative sessions on the chamber floor. Both roles are crucial in shaping legislative agendas and require strong leadership and communication skills. Their key difference lies in their scope of influence: committee chairs focus internally on specialized topics, whereas floor leaders manage broader party dynamics during floor debates.
Committee chair Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com