Inclusivism promotes embracing diverse perspectives and fostering unity by recognizing the value in different beliefs and cultures. It encourages understanding and respect, bridging gaps between varied worldviews to create a more harmonious society. Explore the rest of the article to discover how inclusivism can transform your outlook and community interactions.
Table of Comparison
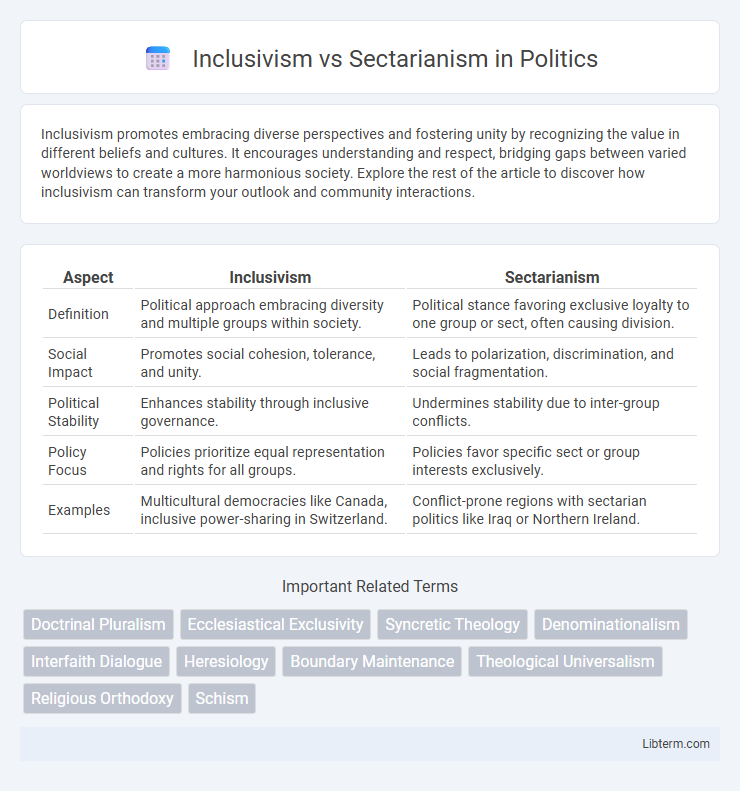
| Aspect | Inclusivism | Sectarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach embracing diversity and multiple groups within society. | Political stance favoring exclusive loyalty to one group or sect, often causing division. |
| Social Impact | Promotes social cohesion, tolerance, and unity. | Leads to polarization, discrimination, and social fragmentation. |
| Political Stability | Enhances stability through inclusive governance. | Undermines stability due to inter-group conflicts. |
| Policy Focus | Policies prioritize equal representation and rights for all groups. | Policies favor specific sect or group interests exclusively. |
| Examples | Multicultural democracies like Canada, inclusive power-sharing in Switzerland. | Conflict-prone regions with sectarian politics like Iraq or Northern Ireland. |
Understanding Inclusivism: A Broad Embrace
Inclusivism promotes understanding and tolerance by recognizing the validity of diverse religious beliefs while maintaining a core commitment to one's own faith, fostering harmony among different traditions. This approach encourages dialogue, mutual respect, and a broad embrace of spiritual insights across various sects, reducing conflict and promoting unity. By valuing shared ethical principles and spiritual goals, inclusivism bridges divides and cultivates an environment of coexistence and cooperation.
Defining Sectarianism: Barriers and Boundaries
Sectarianism establishes rigid social and religious barriers that enforce group identity through exclusion and discrimination, often leading to conflict and division within a society. These boundaries manifest in distinct cultural, ideological, and territorial separations that hinder mutual understanding and cooperation among different communities. The emphasis on maintaining exclusive membership contrasts sharply with inclusivist approaches that seek to bridge divides and promote shared values across diverse groups.
Historical Roots of Inclusivism and Sectarianism
Inclusivism traces its historical roots to ancient religious and philosophical traditions that emphasized the acceptance of diverse beliefs within a unified framework, such as early Vedantic thought and the ecumenical approaches of some Christian theologians. Sectarianism, by contrast, often emerged from socio-political conflicts and doctrinal disputes that reinforced group identity and exclusivity, seen in schisms like the Sunni-Shia split in Islam or the Protestant Reformation in Christianity. These divergent origins reflect how inclusivism promotes pluralism and unity, while sectarianism fosters division and rigid boundaries based on interpreted orthodoxy.
Inclusivism in Religious and Social Contexts
Inclusivism in religious and social contexts promotes the acceptance and integration of diverse beliefs and practices, affirming that truth and value exist beyond a single tradition. This approach fosters interfaith dialogue and social cohesion by recognizing the validity of multiple pathways to spiritual and moral understanding. Emphasizing shared values and common human experiences, inclusivism counters sectarian divisions and encourages unity amid diversity.
Sectarianism’s Impact on Communities and Society
Sectarianism fosters division within communities by promoting exclusive loyalty to particular religious or ideological groups, resulting in social fragmentation and mistrust. It escalates conflict and violence by amplifying differences and undermining social cohesion, often leading to discrimination and marginalization of minority groups. The societal impact includes weakened institutions and hindered economic development as resources are diverted to manage tensions and maintain order.
Benefits of Inclusive Ideologies
Inclusive ideologies promote social cohesion by encouraging acceptance and respect for diverse beliefs, reducing conflicts and fostering peaceful coexistence. They enhance innovation and creativity by integrating varied perspectives and experiences, leading to more holistic problem-solving. Inclusive frameworks also support equitable resource distribution and social justice, improving overall community well-being and stability.
Dangers of Sectarian Divisions
Sectarian divisions dangerously undermine social cohesion by fostering exclusion, intolerance, and conflict among different religious or ideological groups. These divisions often lead to discrimination, violence, and the breakdown of shared values, weakening national unity and stability. Emphasizing inclusivism encourages mutual respect and understanding, which are essential for peaceful coexistence and sustainable development in diverse societies.
Comparing Inclusivist and Sectarian Approaches
Inclusivism promotes acceptance and integration of diverse beliefs, emphasizing common values to foster social cohesion, whereas sectarianism upholds exclusive adherence to a specific ideology, often leading to division and conflict. Inclusivist approaches prioritize dialogue and mutual respect to accommodate pluralism, while sectarian approaches reinforce boundaries and resist compromise, limiting intergroup understanding. Research shows inclusivism correlates with lower social tensions, whereas sectarianism frequently exacerbates polarization and discrimination.
Modern Movements Toward Inclusivity
Modern movements toward inclusivity emphasize embracing diverse religious traditions and promoting interfaith dialogue, challenging rigid sectarian boundaries. Inclusivism fosters mutual respect and understanding by recognizing shared values and common ethical principles among different faiths. Such efforts contribute to reducing religious conflicts and encouraging global cooperation through pluralistic spiritual perspectives.
Overcoming Sectarianism: Paths to Unity
Overcoming sectarianism requires fostering inclusive dialogue that respects diverse religious and cultural identities while promoting shared values and common goals. Emphasizing mutual understanding and cooperation through interfaith initiatives and community-building efforts helps bridge divisions that fuel sectarian conflict. Education and policymaking focused on inclusivism facilitate social cohesion by addressing the root causes of sectarianism and encouraging collective identity beyond narrow group affiliations.
Inclusivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com