Appointing the right candidate is crucial for ensuring long-term organizational success and fostering a productive work environment. Careful evaluation of skills, experience, and cultural fit helps align new hires with your company's goals and values. Discover effective strategies to optimize your appointment process in the following article.
Table of Comparison
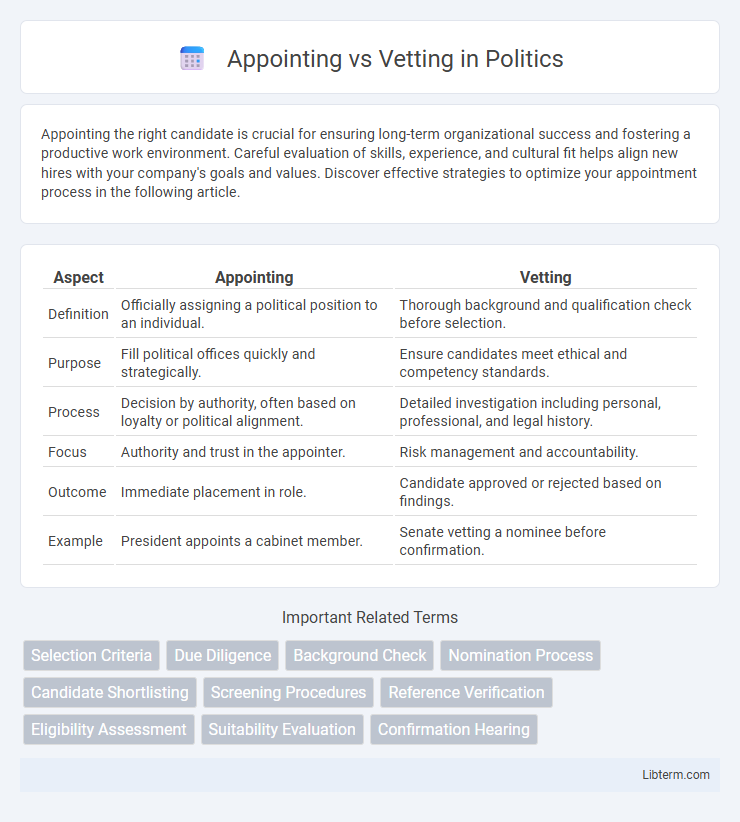
| Aspect | Appointing | Vetting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Officially assigning a political position to an individual. | Thorough background and qualification check before selection. |
| Purpose | Fill political offices quickly and strategically. | Ensure candidates meet ethical and competency standards. |
| Process | Decision by authority, often based on loyalty or political alignment. | Detailed investigation including personal, professional, and legal history. |
| Focus | Authority and trust in the appointer. | Risk management and accountability. |
| Outcome | Immediate placement in role. | Candidate approved or rejected based on findings. |
| Example | President appoints a cabinet member. | Senate vetting a nominee before confirmation. |
Understanding Appointing and Vetting
Understanding appointing involves selecting candidates based on qualifications, skills, and suitability for a specific role within an organization or government body. Vetting refers to the thorough background check and evaluation process to verify credentials, assess potential risks, and ensure compliance with legal or ethical standards. Both appointing and vetting are critical to maintaining organizational integrity and effective leadership.
Key Differences Between Appointing and Vetting
Appointing involves the formal selection and assignment of an individual to a specific role or position, emphasizing authority and responsibility transfer. Vetting refers to the thorough background check and evaluation process to assess a candidate's qualifications, credibility, and suitability before any appointment is made. Key differences include that appointing finalizes the decision-making phase, while vetting serves as a crucial preliminary screening to mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
The Importance of Vetting in Decision-Making
Vetting plays a crucial role in decision-making by thoroughly evaluating candidates' qualifications, backgrounds, and suitability before appointments are made. This detailed screening process minimizes risks, prevents potential conflicts, and ensures alignment with organizational goals and values. Effective vetting enhances the credibility of appointments and supports strategic human resource management.
Benefits of a Structured Appointment Process
A structured appointment process ensures consistent evaluation criteria, reducing biases and improving decision accuracy when selecting candidates. It enhances organizational transparency and accountability by documenting each step, which strengthens stakeholder trust and mitigates legal risks. Clearly defined procedures expedite onboarding, fostering better alignment between candidate skills and organizational needs, ultimately driving higher performance and retention rates.
Common Mistakes in Appointing Without Vetting
Appointing candidates without thorough vetting often leads to hiring individuals who lack essential qualifications or cultural fit, resulting in decreased team productivity and increased turnover rates. Common mistakes include neglecting background checks, ignoring reference validations, and failing to assess soft skills or potential ethical issues before finalizing appointments. Organizations bypassing comprehensive vetting risk costly setbacks and reputational damage that could have been prevented through diligent candidate evaluation processes.
Best Practices for Effective Vetting
Effective vetting involves thorough background checks, reference verification, and competency assessments to ensure candidate suitability before appointment. Utilizing standardized evaluation criteria and structured interviews enhances objectivity and consistency throughout the vetting process. Leveraging technology for data validation and cross-referencing minimizes risks associated with fraud or misinformation during candidate selection.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Appointing individuals to positions requires adherence to legal frameworks such as anti-discrimination laws and transparent selection processes to ensure fairness and compliance. Vetting involves thorough background checks and assessments to verify qualifications, criminal history, and conflicts of interest, aligning with data privacy regulations and ethical standards. Both practices demand rigorous documentation and accountability to uphold organizational integrity and mitigate legal liabilities.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies on appointing versus vetting highlight critical differences in organizational outcomes, where thorough vetting processes often prevent costly mis-hires and improve team cohesion. Instances of successful appointments emphasize the use of comprehensive background checks, skill assessments, and cultural fit analysis to secure ideal candidates. Failures frequently arise from rushed appointments lacking due diligence, leading to poor performance, reputational damage, and increased turnover costs.
Impact on Organizational Reputation
Appointing leaders without thorough vetting can expose organizations to reputational risks including scandals or mismanagement, damaging trust among stakeholders. Rigorous vetting processes evaluate candidates' qualifications, ethics, and background, ensuring alignment with organizational values and safeguarding public perception. Effective vetting enhances credibility, fostering stakeholder confidence and long-term organizational stability.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing between appointing and vetting hinges on organizational goals and risk tolerance; appointing accelerates decision-making by designating trusted individuals, while vetting involves thorough evaluation to mitigate risks. Organizations with high accountability demands benefit from vetting processes that include background checks, references, and competency assessments. Conversely, startups or small teams might favor appointing for agility, relying on established trust and streamlined authority allocation.
Appointing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com