Judicial activism occurs when courts interpret laws and the Constitution in ways that reflect current social values, potentially shaping public policy beyond traditional judicial boundaries. This approach often sparks debate over the balance between judicial authority and legislative power. Explore the article to understand how judicial activism impacts your legal rights and society at large.
Table of Comparison
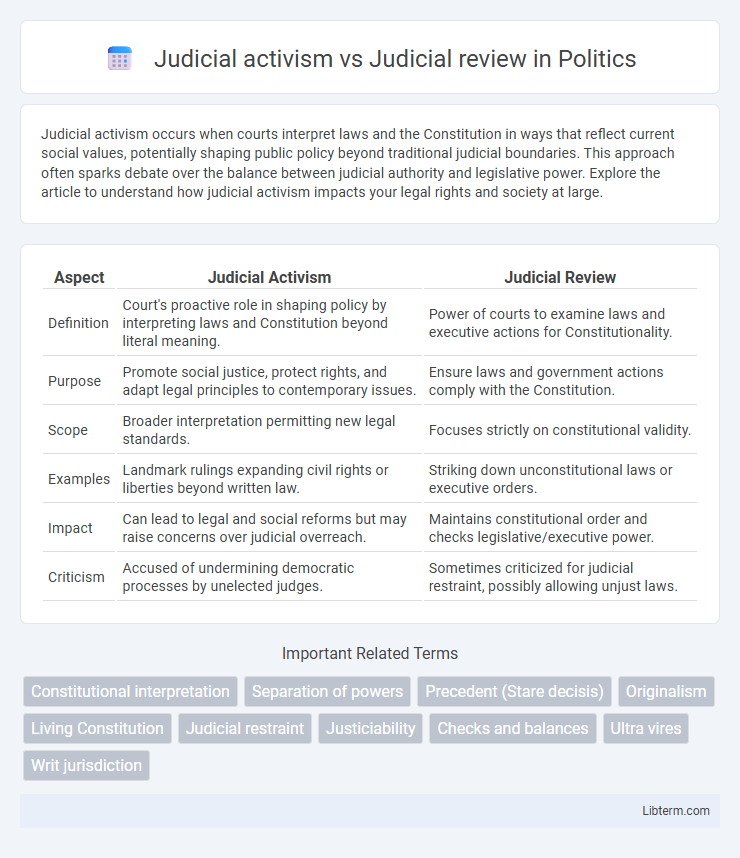
| Aspect | Judicial Activism | Judicial Review |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Court's proactive role in shaping policy by interpreting laws and Constitution beyond literal meaning. | Power of courts to examine laws and executive actions for Constitutionality. |
| Purpose | Promote social justice, protect rights, and adapt legal principles to contemporary issues. | Ensure laws and government actions comply with the Constitution. |
| Scope | Broader interpretation permitting new legal standards. | Focuses strictly on constitutional validity. |
| Examples | Landmark rulings expanding civil rights or liberties beyond written law. | Striking down unconstitutional laws or executive orders. |
| Impact | Can lead to legal and social reforms but may raise concerns over judicial overreach. | Maintains constitutional order and checks legislative/executive power. |
| Criticism | Accused of undermining democratic processes by unelected judges. | Sometimes criticized for judicial restraint, possibly allowing unjust laws. |
Introduction to Judicial Activism and Judicial Review
Judicial activism refers to judges making rulings based on personal or political considerations rather than existing law, often leading to new policies through court decisions. Judicial review is the constitutional power of courts to examine and invalidate legislative or executive actions that conflict with the constitution. Both concepts shape the balance of power among government branches and influence the interpretation and application of laws in judicial systems.
Defining Judicial Activism: Scope and Impact
Judicial activism refers to the proactive role of courts in interpreting laws and the Constitution to address societal issues, often going beyond traditional judicial restraint. Its scope includes influencing public policy, protecting minority rights, and ensuring justice when legislative or executive branches fail to act. The impact of judicial activism can reshape legal precedents and effect significant social change, but it also raises debates about the balance of power among government branches.
Understanding Judicial Review: Constitutional Basis
Judicial review is the constitutional principle enabling courts to evaluate laws and executive actions for compliance with the Constitution, established by the landmark case Marbury v. Madison (1803). This foundational power ensures the supremacy of constitutional law, allowing the judiciary to nullify statutes or government acts that violate constitutional provisions. Unlike judicial activism, which involves judges making decisions based on personal or political considerations, judicial review strictly adheres to legal interpretation grounded in constitutional text and precedent.
Historical Evolution of Judicial Activism
Judicial activism traces its historical evolution to landmark cases in the early 20th century, notably in the United States, where courts began to interpret the Constitution more broadly to address social issues and protect civil rights. This approach contrasts with judicial review, established by Marbury v. Madison (1803), which primarily empowered courts to assess the constitutionality of legislative and executive actions. Over time, judicial activism expanded to challenge entrenched policies and promote social justice, reflecting changing societal values and influencing constitutional law development.
Origins and Development of Judicial Review
Judicial review originated from the landmark 1803 U.S. Supreme Court case Marbury v. Madison, which established the judiciary's authority to invalidate laws conflicting with the Constitution. This development marked a pivotal moment in constitutional law, enabling courts to act as checks on legislative and executive powers. Judicial activism, in contrast, evolves from the interpretation and application of judicial review in ways that sometimes extend beyond strict legal boundaries to influence policy and social issues.
Key Differences Between Judicial Activism and Judicial Review
Judicial activism involves judges actively interpreting the constitution to create new policies or extend rights, often reflecting contemporary values, whereas judicial review strictly limits courts to assessing the constitutionality of legislative and executive actions without creating law. Judicial activism may overstep traditional boundaries by influencing public policy, while judicial review serves as a check on government power by ensuring laws comply with constitutional mandates. The key differences lie in the scope of judicial power, with activism promoting flexible interpretations and review enforcing legal restraint.
Landmark Cases Shaping Judicial Activism
Landmark cases such as Brown v. Board of Education (1954) and Roe v. Wade (1973) exemplify judicial activism by demonstrating courts' role in actively shaping social policies and rights beyond mere constitutional interpretation. Judicial activism involves judges making decisions that address contemporary social issues, often expanding civil liberties, whereas judicial review primarily focuses on evaluating the constitutionality of legislative and executive actions. The evolving nature of judicial activism is pivotal in shaping legal precedents that impact civil rights, equality, and individual freedoms in the American legal system.
Significant Judicial Review Decisions
Significant judicial review decisions, such as Marbury v. Madison (1803), established the principle allowing courts to invalidate unconstitutional laws, solidifying judicial review as a cornerstone of constitutional law. Judicial activism manifests when courts actively interpret the Constitution to address contemporary issues, seen in landmark rulings like Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which overturned segregation. These key decisions highlight the tension between judicial restraint inherent in judicial review and the proactive role embraced in judicial activism.
Pros and Cons: Judicial Activism vs. Judicial Review
Judicial activism allows courts to interpret the constitution and laws flexibly, promoting social justice and protecting minority rights but risks overstepping judicial boundaries and disrupting legislative intent. Judicial review provides a structured mechanism to ensure laws comply with the constitution, maintaining legal stability and separation of powers, yet can be criticized for judicial passivity and limiting progressive reform. Balancing activism and review is essential to uphold democratic principles while adapting to societal changes.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Perspectives
Judicial activism empowers courts to interpret laws dynamically, addressing evolving social issues and protecting constitutional rights in contemporary society. Judicial review ensures the constitutionality of legislative and executive actions, maintaining the rule of law and checks and balances within government. Future perspectives suggest an ongoing balance between these doctrines will shape legal adaptability and institutional accountability amid rapid social and technological changes.
Judicial activism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com