Categorical grants provide federal funds to state and local governments for specific, narrowly-defined purposes, ensuring targeted use of resources in areas such as education, transportation, or health services. These grants often require matching funds and strict adherence to federal guidelines to qualify for funding. Explore the rest of the article to understand how categorical grants impact your community and governance.
Table of Comparison
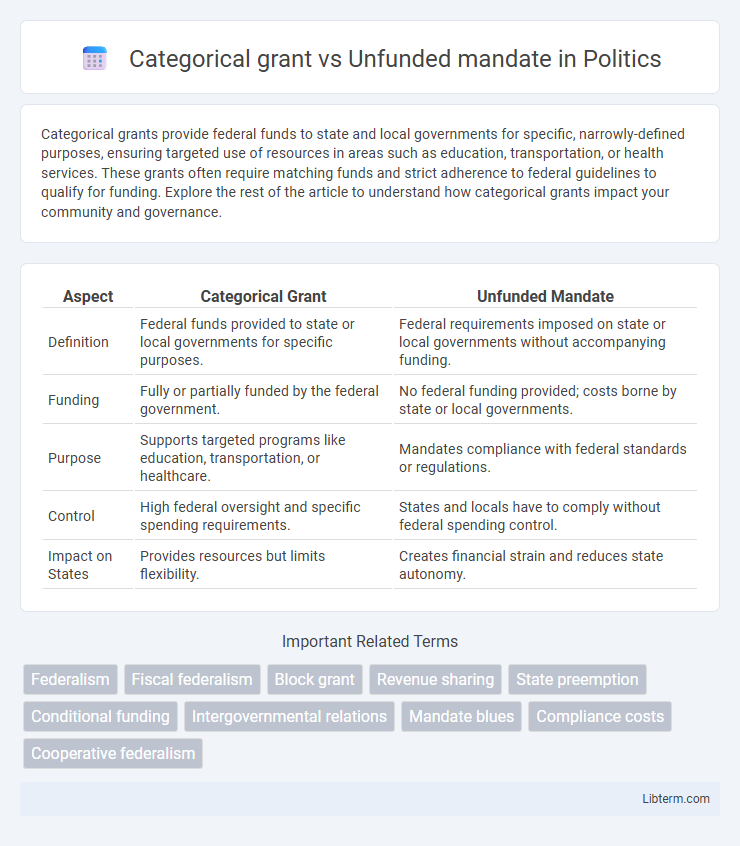
| Aspect | Categorical Grant | Unfunded Mandate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Federal funds provided to state or local governments for specific purposes. | Federal requirements imposed on state or local governments without accompanying funding. |
| Funding | Fully or partially funded by the federal government. | No federal funding provided; costs borne by state or local governments. |
| Purpose | Supports targeted programs like education, transportation, or healthcare. | Mandates compliance with federal standards or regulations. |
| Control | High federal oversight and specific spending requirements. | States and locals have to comply without federal spending control. |
| Impact on States | Provides resources but limits flexibility. | Creates financial strain and reduces state autonomy. |
Introduction to Categorical Grants and Unfunded Mandates
Categorical grants are federal funds provided to state and local governments for specific purposes, often requiring strict compliance with federal guidelines, which ensures targeted allocation of resources. Unfunded mandates impose federal requirements on lower governments without accompanying funding, creating financial burdens that can strain local budgets. Understanding the distinctions clarifies how federal policies impact state and local governance through either supported initiatives or cost-shifting obligations.
Definition and Key Features of Categorical Grants
Categorical grants are federal funds provided to state and local governments for specific, narrowly defined purposes such as education or transportation, requiring adherence to strict guidelines and reporting standards. These grants typically involve detailed conditions on how the money must be spent, ensuring targeted use and accountability. Unlike unfunded mandates, which impose obligations without financial support, categorical grants offer designated funding to assist governments in meeting federal requirements.
What Are Unfunded Mandates?
Unfunded mandates are regulations or requirements imposed by the federal government on state or local governments without providing corresponding funding to cover the costs. Unlike categorical grants, which allocate federal funds for specific purposes with defined criteria, unfunded mandates shift financial responsibility to lower levels of government, often straining their budgets. This lack of federal financial support can lead to challenges in compliance and service delivery at the state and local levels.
Historical Context and Development
Categorical grants originated in the 1930s as part of New Deal federal policies, designed to provide states with specific funding for narrowly defined programs, enhancing federal control over state expenditures. Unfunded mandates emerged prominently in the 1970s and 1980s as federal regulations required state and local governments to comply with federal standards without providing accompanying funding, creating fiscal burdens. The development of these mechanisms reflects evolving federal-state relations, with categorical grants promoting cooperative federalism and unfunded mandates often sparking debates over state sovereignty and fiscal responsibility.
Federal vs. State Government Roles
Categorical grants are specific funds provided by the federal government to state governments for particular projects or programs, ensuring targeted use of resources aligned with federal priorities. Unfunded mandates require state governments to comply with federal regulations or policies without accompanying financial support, often creating budgetary challenges at the state level. The federal government leverages categorical grants to influence state policy implementation, while unfunded mandates impose obligations without direct funding, highlighting tensions in federal-state government roles and fiscal responsibilities.
Funding Mechanisms and Fiscal Impact
Categorical grants provide targeted federal funding to states or local governments for specific programs, ensuring designated use of funds and often requiring matching contributions, which directly supports local initiatives without broad fiscal strain. Unfunded mandates impose requirements on lower governments without accompanying financial support, leading to increased fiscal burdens as states or localities must allocate existing resources or raise funds to comply. The fiscal impact of categorical grants is more predictable and limited by federal budgets, whereas unfunded mandates can create significant budgetary pressures and strain public services.
Examples of Categorical Grants
Categorical grants provide federal funds to state or local governments for specific, narrowly defined purposes such as highway construction, Medicaid, or school lunch programs, with strict compliance requirements. Examples include the Medicaid program, which offers targeted health coverage for eligible low-income individuals, and the National School Lunch Program, aimed at providing nutritious meals to students. Unlike unfunded mandates, which compel states to perform actions without federal funding, categorical grants supply resources but limit flexibility in usage.
Notable Unfunded Mandate Cases
Notable unfunded mandate cases often involve federal requirements imposed on state or local governments without providing corresponding financial support, leading to significant budget strains. For example, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) required local governments to improve accessibility without direct federal funding, sparking litigation over financial burdens. In contrast, categorical grants provide targeted federal funds to states with specific conditions, ensuring financial assistance aligns with mandated programs.
Advantages and Disadvantages Compared
Categorical grants provide targeted federal funding with specific conditions, ensuring states allocate resources to designated programs, which enhances accountability and program effectiveness but may limit state flexibility. Unfunded mandates impose federal requirements without accompanying funds, compelling states to comply at their own expense, which ensures uniform standards but can strain state budgets and reduce autonomy. The trade-off lies in the balance between federal oversight and state discretion, where categorical grants promote compliance with financial support, whereas unfunded mandates risk burdening states financially without offering resources.
Implications for Policy and Governance
Categorical grants provide targeted funding with specific conditions, enabling governments to implement and prioritize designated programs while maintaining fiscal accountability and oversight. Unfunded mandates impose requirements on state or local governments without accompanying financial support, often straining budgets and limiting flexibility in policy execution. The contrast impacts policy effectiveness by balancing resource allocation with autonomy, influencing governance through varying degrees of control and fiscal pressure.
Categorical grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com