Lobbying plays a crucial role in shaping public policy by influencing lawmakers and government officials to consider specific interests and perspectives. Effective lobbying requires strategic communication, relationship-building, and a deep understanding of legislative processes to ensure your voice is heard. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how lobbying works and the impact it can have on your community.
Table of Comparison
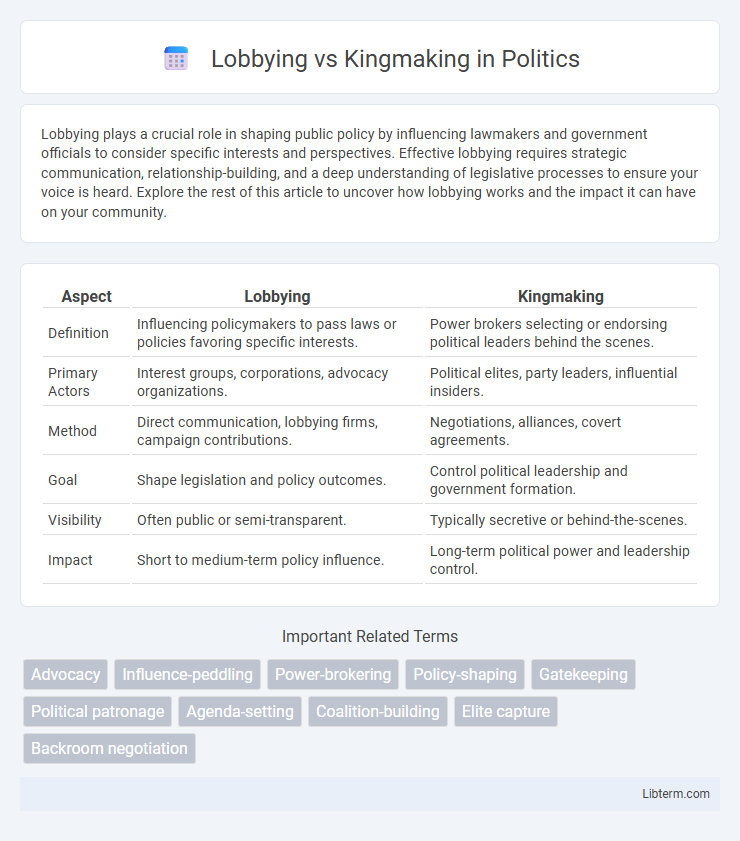
| Aspect | Lobbying | Kingmaking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Influencing policymakers to pass laws or policies favoring specific interests. | Power brokers selecting or endorsing political leaders behind the scenes. |
| Primary Actors | Interest groups, corporations, advocacy organizations. | Political elites, party leaders, influential insiders. |
| Method | Direct communication, lobbying firms, campaign contributions. | Negotiations, alliances, covert agreements. |
| Goal | Shape legislation and policy outcomes. | Control political leadership and government formation. |
| Visibility | Often public or semi-transparent. | Typically secretive or behind-the-scenes. |
| Impact | Short to medium-term policy influence. | Long-term political power and leadership control. |
Understanding Lobbying and Kingmaking
Lobbying involves influencing policymakers and legislators through advocacy, research, and strategic communication to shape decisions that favor specific interests. Kingmaking refers to the act of empowering or installing key political figures, often by behind-the-scenes support, to control power dynamics within political systems. Understanding lobbying requires analyzing legal frameworks and tactics used to sway legislation, while grasping kingmaking entails recognizing power consolidation and political patronage mechanisms.
Historical Origins of Lobbying and Kingmaking
Lobbying traces its origins to the early legislative practices of 19th-century America, where advocates sought direct access to lawmakers in hotel lobbies to influence policy decisions. Kingmaking, rooted in monarchical and feudal systems, emerged as powerful nobles and advisors manipulated royal succession and governance to extend their influence. These historical foundations highlight lobbying as a structured petitioning process, while kingmaking involved covert power plays within ruling elites.
Key Differences Between Lobbying and Kingmaking
Lobbying involves influencing policymakers and legislators to enact or oppose specific legislation through advocacy, information sharing, and strategic communication. Kingmaking refers to the act of determining or significantly shaping leadership outcomes by endorsing or installing candidates in political or organizational positions. The key difference lies in lobbying's focus on policy influence, while kingmaking centers on controlling leadership selection and power dynamics.
Methods and Strategies Used in Lobbying
Lobbying employs targeted advocacy, data-driven persuasion, and direct engagement with policymakers to influence legislation and regulatory decisions. Strategic methods include crafting tailored messages, leveraging expert testimony, and mobilizing grassroots support to create pressure on elected officials. Sophisticated lobbying strategies also utilize coalition building and continuous relationship management to sustain influence over time.
Techniques and Influence of Kingmakers
Kingmakers exert influence through strategic alliance-building, resource mobilization, and behind-the-scenes negotiation, shaping power structures without direct authority. Techniques include personalized persuasion, leveraging insider information, and orchestrating consensus among key stakeholders to install preferred leaders. Their influence often surpasses traditional lobbying by controlling critical decision points and enabling sustained political or organizational domination.
Impact on Political Decision-Making
Lobbying directly influences political decision-making by providing lawmakers with targeted information and advocating for specific policies or interests, thus shaping legislative outcomes. Kingmaking operates by determining leadership choices, often behind the scenes, impacting who holds political power and subsequently directing the broader governance agenda. Both processes significantly affect policy directions, with lobbying emphasizing issue-oriented influence and kingmaking concentrating on power distribution within political systems.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Lobbying involves legally influencing government decisions through advocacy and transparent communication, often regulated by laws requiring disclosure of activities and funding sources to ensure accountability. Kingmaking, however, crosses ethical boundaries by covertly manipulating political power or leadership selection, frequently involving bribery or undue influence that undermines democratic principles. Legal frameworks distinguish lobbying's permissible tactics from kingmaking's illicit actions, emphasizing ethical standards to maintain fair political processes and public trust.
High-Profile Examples of Lobbying and Kingmaking
High-profile lobbying examples include the tobacco industry's influence on U.S. legislation and tech giants like Google shaping data privacy laws. Kingmaking is exemplified by political figures such as Lyndon B. Johnson, who used his power to propel proteges into key positions, shaping political outcomes behind the scenes. Both lobbying and kingmaking leverage strategic relationships and influence, but lobbying operates through formal channels, while kingmaking works through personal alliances and patronage.
Societal Perceptions and Controversies
Lobbying is often perceived as a strategic influence tactic used by interest groups to shape policy, sparking debates on transparency and fairness in democratic systems. Kingmaking, viewed as the behind-the-scenes manipulation of power transitions, raises concerns about elitism and the undermining of democratic legitimacy. Both practices face societal scrutiny for prioritizing private interests over public good, fueling controversies about accountability and ethical governance.
Shaping the Future: The Evolving Roles of Lobbyists and Kingmakers
Lobbying and kingmaking are influential strategies shaping political and corporate power structures, with lobbyists advocating for specific policies and kingmakers orchestrating pivotal decisions behind the scenes. In modern governance, lobbyists leverage data-driven campaigns and strategic communication to sway legislative agendas, while kingmakers utilize network influence and coalition-building to determine leadership outcomes. The evolving roles of these actors highlight a shift towards more sophisticated, transparent, and impact-focused approaches in shaping the future of policy development and power dynamics.
Lobbying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com