Dissolution refers to the formal closing or termination of a business entity, legal partnership, or contract. Understanding the legal, financial, and operational implications is crucial to ensure compliance and protect your interests during this process. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to navigate dissolution effectively.
Table of Comparison
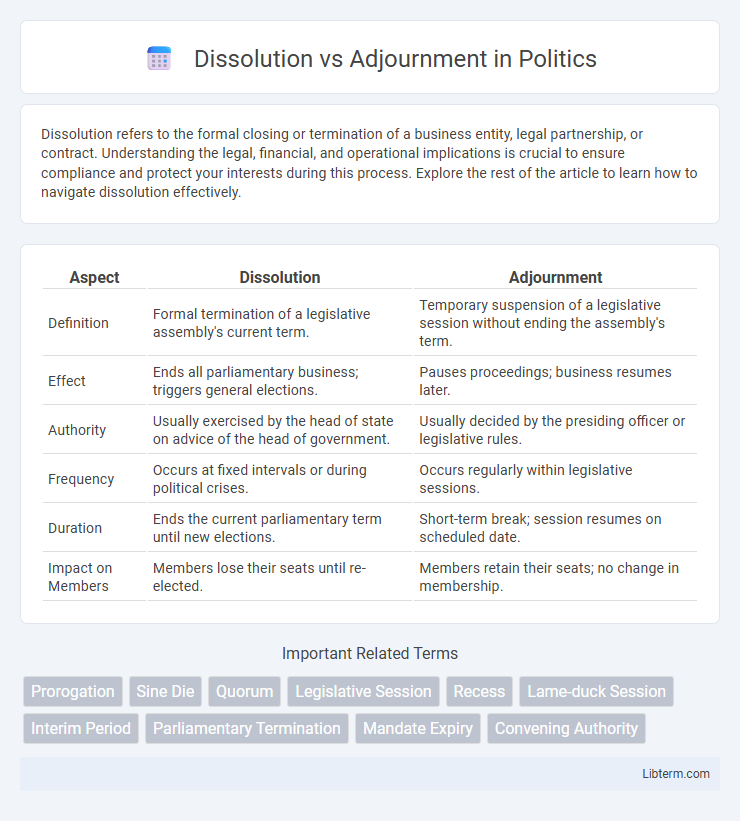
| Aspect | Dissolution | Adjournment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal termination of a legislative assembly's current term. | Temporary suspension of a legislative session without ending the assembly's term. |
| Effect | Ends all parliamentary business; triggers general elections. | Pauses proceedings; business resumes later. |
| Authority | Usually exercised by the head of state on advice of the head of government. | Usually decided by the presiding officer or legislative rules. |
| Frequency | Occurs at fixed intervals or during political crises. | Occurs regularly within legislative sessions. |
| Duration | Ends the current parliamentary term until new elections. | Short-term break; session resumes on scheduled date. |
| Impact on Members | Members lose their seats until re-elected. | Members retain their seats; no change in membership. |
Introduction to Dissolution and Adjournment
Dissolution refers to the formal termination of a meeting or assembly, ending all discussions and actions permanently until the next scheduled session. Adjournment temporarily halts the meeting with the intention to resume at a later time or date, preserving the agenda and pending items. Understanding the distinction is crucial for proper procedural compliance in organizational and legislative contexts.
Definitions: Dissolution vs Adjournment
Dissolution refers to the formal termination or disbanding of a legal entity, such as a corporation or partnership, ending its existence and operations permanently. Adjournment is the temporary suspension or postponement of a meeting, session, or legal proceeding to resume at a later time without concluding the matter. While dissolution signifies a final closure, adjournment allows for continuation and resumption of activities.
Key Differences Between Dissolution and Adjournment
Dissolution refers to the formal termination of a meeting or organization, marking the end of its existence or session, while adjournment is a temporary pause or suspension of proceedings with the intention to resume later. Dissolution permanently concludes business and legal activities, often requiring official documentation, whereas adjournment merely delays decision-making without ending the entity's operation. The key difference lies in permanence: dissolution ends an entity or meeting entirely, whereas adjournment preserves continuity by postponing action.
Legal Framework Governing Both Processes
Dissolution is governed by specific corporate or partnership laws that outline the formal termination of a legal entity's existence, including settling liabilities and distributing assets according to jurisdictional statutes like the Companies Act or Partnership Acts. Adjournment, regulated under procedural rules such as court rules or legislative procedures, temporarily halts proceedings without ending the entity's legal status, subject to conditions set by relevant legal frameworks like civil procedure codes. Both processes require compliance with statutory requirements to ensure legal validity and prevent disputes related to the cessation or continuation of legal activities.
Purpose and Implications of Dissolution
Dissolution signifies the formal termination of a legal entity or organization, ending its existence and operations permanently. Its primary purpose is to conclude all affairs, including settling debts, distributing assets, and ceasing business activities. The implications involve legal finality, loss of corporate status, and the need for regulatory compliance to ensure proper winding up.
Purpose and Implications of Adjournment
Adjournment serves as a temporary pause in a meeting or legal proceeding, allowing participants to reconvene at a later time without concluding the matter. Its purpose includes accommodating scheduling conflicts, gathering additional information, or awaiting necessary parties to be present, ensuring thorough deliberation. Unlike dissolution, which permanently ends an organization's existence or a proceeding, adjournment preserves the status quo and maintains legal or organizational continuity.
Process and Procedures for Dissolution
The process for dissolution involves legally terminating a business entity by filing articles of dissolution with the relevant state authority, settling outstanding liabilities, and distributing remaining assets among shareholders. Formal procedures require the approval of the board of directors and shareholders, followed by notification to creditors and compliance with state-specific regulations. Documentation must include a final tax return and certificates confirming the completion of all dissolution steps to ensure the entity is officially closed.
Process and Procedures for Adjournment
Adjournment is the temporary suspension of a meeting or legal proceeding to be resumed later, typically requiring a formal motion, majority vote, or preset agreement among participants. The process involves notifying all parties of the new date, time, and location to ensure continued participation and compliance with procedural rules. Unlike dissolution, which permanently ends an entity or session, adjournment maintains the entity's existence while pausing activities for strategic, logistical, or operational reasons.
Real-World Examples of Dissolution and Adjournment
Dissolution occurs when an organization or governmental body officially ceases to exist, as seen when the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991, marking the end of its political structure. Adjournment, in contrast, refers to the temporary suspension of meetings or sessions, exemplified by the U.S. Congress adjourning at the end of a legislative day or session to resume later. These distinctions highlight how dissolution results in permanent termination, while adjournment allows for continuation at a later time.
Significance in Legislative Contexts
Dissolution in legislative contexts marks the formal termination of a parliamentary session or the entire legislature, often triggering general elections and enabling a reset of political mandates. Adjournment temporarily pauses legislative proceedings without ending the session, allowing time for further discussion, committee work, or external events to unfold. Understanding these distinctions clarifies the procedural mechanisms that maintain legislative continuity and political stability.
Dissolution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com