Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the votes they receive, promoting a more accurate reflection of the electorate's preferences. This electoral system enhances diversity and inclusivity within legislatures by allowing smaller parties to participate meaningfully. Explore the article to understand how proportional representation can impact your voting experience and democratic governance.
Table of Comparison
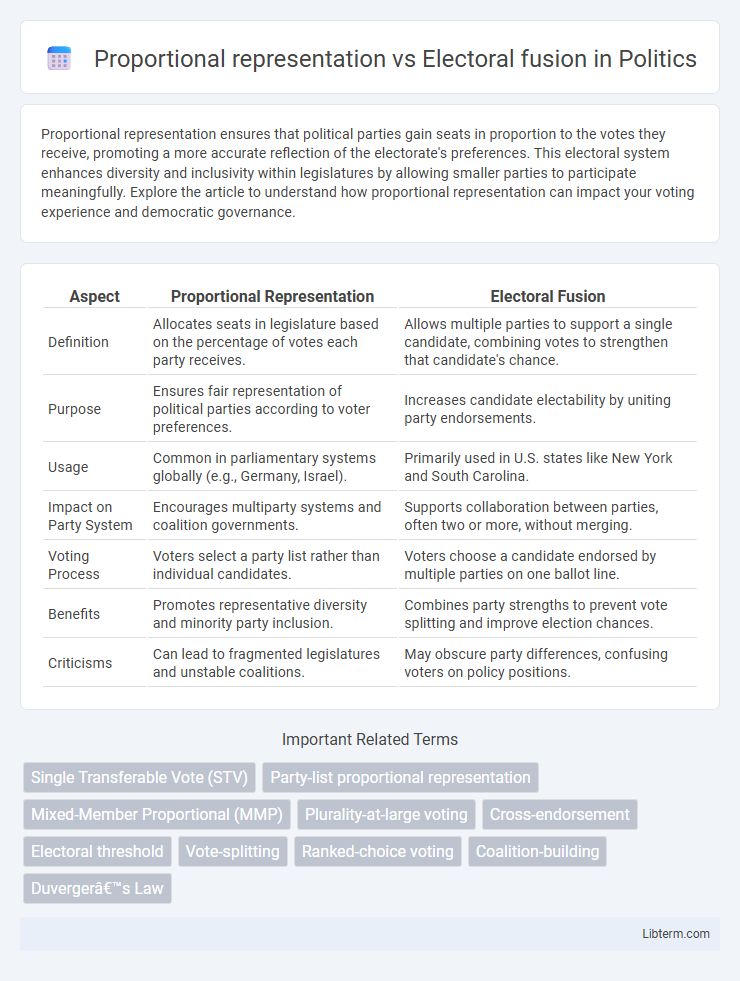
| Aspect | Proportional Representation | Electoral Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates seats in legislature based on the percentage of votes each party receives. | Allows multiple parties to support a single candidate, combining votes to strengthen that candidate's chance. |
| Purpose | Ensures fair representation of political parties according to voter preferences. | Increases candidate electability by uniting party endorsements. |
| Usage | Common in parliamentary systems globally (e.g., Germany, Israel). | Primarily used in U.S. states like New York and South Carolina. |
| Impact on Party System | Encourages multiparty systems and coalition governments. | Supports collaboration between parties, often two or more, without merging. |
| Voting Process | Voters select a party list rather than individual candidates. | Voters choose a candidate endorsed by multiple parties on one ballot line. |
| Benefits | Promotes representative diversity and minority party inclusion. | Combines party strengths to prevent vote splitting and improve election chances. |
| Criticisms | Can lead to fragmented legislatures and unstable coalitions. | May obscure party differences, confusing voters on policy positions. |
Introduction to Proportional Representation
Proportional representation is an electoral system designed to allocate seats in a legislature proportionally to the votes each party receives, ensuring minority groups obtain fair representation. Unlike electoral fusion, where multiple parties endorse the same candidate to combine votes, proportional representation emphasizes party lists or multi-member districts to reflect diverse political preferences. This system enhances political pluralism by translating vote shares directly into legislative seats, reducing the dominance of major parties.
Understanding Electoral Fusion
Electoral fusion refers to the practice where multiple political parties support the same candidate, allowing votes from different party lines to be aggregated, enhancing the candidate's chances without splitting the vote. This contrasts sharply with proportional representation, which allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, emphasizing party representation over individual candidates. Understanding electoral fusion requires recognizing its role in coalition-building and voter flexibility, enabling minor parties to influence elections by endorsing major party candidates while maintaining their distinct identities.
Key Differences Between PR and Electoral Fusion
Proportional representation (PR) allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences, while electoral fusion allows multiple parties to endorse a single candidate, aggregating their votes to improve the candidate's chances. PR emphasizes party-based seat distribution to enhance multi-party representation, whereas electoral fusion focuses on strategic alliances without changing the winner-takes-all nature of single-member districts. Key differences include PR's proportional allocation of seats versus electoral fusion's vote consolidation for individual candidates, impacting party influence and electoral outcomes distinctly.
Historical Context and Development
Proportional representation emerged in the late 19th century as a response to the limitations of winner-take-all electoral systems, aiming to allocate legislative seats in proportion to the votes each party receives to better reflect diverse political views. Electoral fusion, with roots in 19th-century American politics, allowed multiple parties to support a single candidate to consolidate opposition and avoid vote splitting, particularly prominent in states like New York. Both systems developed amid evolving democratic reforms, with proportional representation gaining traction in Europe and fusion influencing U.S. state-level elections, each addressing representation challenges through distinct mechanisms.
Advantages of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation ensures that political parties receive legislative seats in direct proportion to the votes they secure, promoting fairer and more accurate representation of diverse voter preferences. This system enhances political diversity and reduces wasted votes, which increases voter participation and satisfaction. It often leads to coalition governments that reflect a broader spectrum of public interests, contributing to more balanced and inclusive policymaking.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Electoral Fusion
Electoral fusion allows multiple political parties to support a single candidate, increasing coalition-building opportunities and voter choice without vote splitting. It can enhance minor party influence by allowing them to endorse major party candidates, potentially leading to more negotiated policies. However, electoral fusion may also cause voter confusion and complicate the ballot design, while possibly diluting party identity and weakening the accountability of elected officials.
Impact on Political Parties and Candidates
Proportional representation fosters multiparty systems by enabling smaller parties to gain legislative seats commensurate with their vote share, encouraging coalition-building and policy diversity. Electoral fusion allows multiple parties to endorse the same candidate, consolidating support and increasing candidates' chances of election while preserving party identities. Both systems influence party strategies; proportional representation promotes broader representation and coalition governance, whereas electoral fusion enhances strategic alliances without necessarily fragmenting the party landscape.
Voter Representation and Electoral Outcomes
Proportional representation enhances voter representation by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting diverse political voices and minimizing wasted votes. Electoral fusion allows multiple parties to endorse a single candidate, which can consolidate voter preferences and influence electoral outcomes by signaling broader coalitions. While proportional representation ensures more accurate reflection of public support in legislative bodies, electoral fusion can strategically impact outcomes by uniting similar voter blocks without altering the overall seat distribution.
Global Examples and Case Studies
Proportional representation systems, widely adopted in countries like Germany, New Zealand, and South Africa, allocate seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, enhancing multi-party representation and voter inclusivity. Electoral fusion, practiced notably in New York State and historically in parts of Italy, allows multiple parties to endorse the same candidate, consolidating votes and influencing coalition dynamics without altering vote distribution directly. Comparative analyses reveal proportional representation fosters broader political diversity, whereas electoral fusion optimizes strategic alliances and candidate viability within plurality voting frameworks.
Future Trends in Electoral Reform
Proportional representation is gaining traction globally as future electoral reforms prioritize inclusivity and accurate reflection of voter preferences. Electoral fusion, although less widespread, is being reconsidered in certain regions to enhance coalition-building and diversify candidate endorsements. Emerging trends indicate a growing synergy between these systems to balance broad representation with strategic party alliances in upcoming electoral frameworks.
Proportional representation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com