Effective crisis management requires quick decision-making and clear communication to minimize disruption and protect your organization's reputation. Implementing a well-structured plan ensures that teams act cohesively under pressure, reducing the impact of unexpected events. Explore the rest of the article to discover essential strategies and tools for mastering crisis management.
Table of Comparison
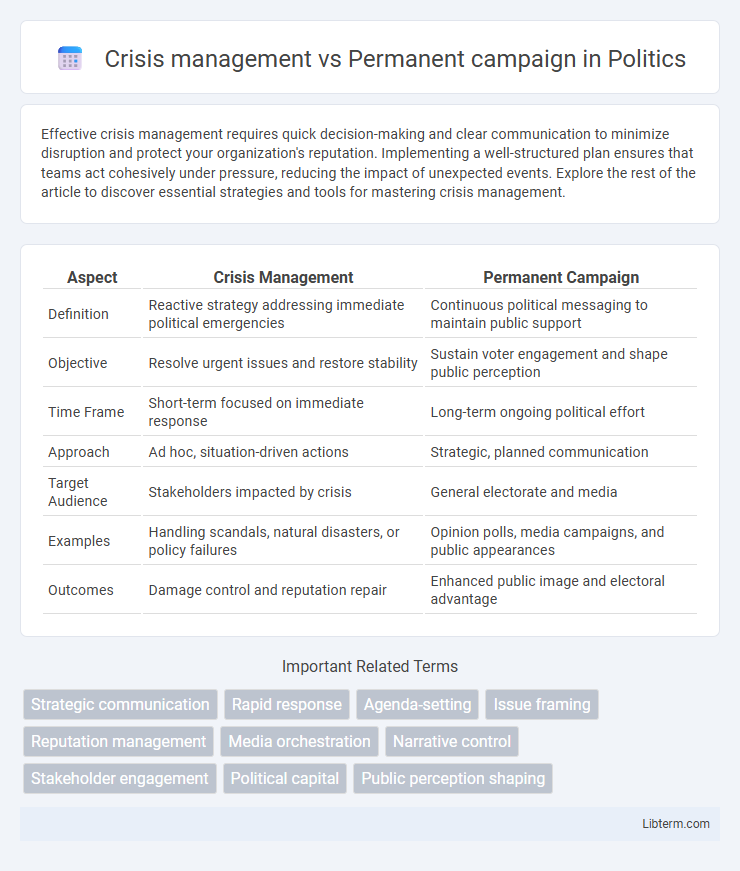
| Aspect | Crisis Management | Permanent Campaign |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reactive strategy addressing immediate political emergencies | Continuous political messaging to maintain public support |
| Objective | Resolve urgent issues and restore stability | Sustain voter engagement and shape public perception |
| Time Frame | Short-term focused on immediate response | Long-term ongoing political effort |
| Approach | Ad hoc, situation-driven actions | Strategic, planned communication |
| Target Audience | Stakeholders impacted by crisis | General electorate and media |
| Examples | Handling scandals, natural disasters, or policy failures | Opinion polls, media campaigns, and public appearances |
| Outcomes | Damage control and reputation repair | Enhanced public image and electoral advantage |
Understanding Crisis Management: Key Concepts
Crisis management involves identifying, assessing, and responding rapidly to unexpected events that threaten organizational stability or reputation, emphasizing preparedness and swift decision-making. Key concepts include risk assessment, communication strategies, and contingency planning to mitigate damage and restore normalcy. Unlike permanent campaigns, which maintain ongoing public engagement, crisis management prioritizes immediate actions to control and resolve critical incidents.
Defining the Permanent Campaign Approach
The Permanent Campaign Approach integrates ongoing strategic communication and engagement efforts to maintain public support and influence political outcomes beyond election cycles. This method prioritizes continuous messaging, media interaction, and stakeholder engagement to build a resilient political brand adaptable to shifting public opinion and external challenges. Unlike crisis management, which addresses immediate threats, the permanent campaign emphasizes proactive, long-term reputation management and issue framing.
Historical Evolution of Crisis Management and Permanent Campaign
The historical evolution of crisis management traces back to early organizational responses to sudden disruptions, with formal frameworks developing post-World War II to address complex political, economic, and social crises. Permanent campaigns emerged in the late 20th century, driven by the rise of mass media and political communication strategies aiming to sustain continuous public engagement beyond election periods. Both concepts evolved from reactive measures to proactive, strategic processes integrating communication, decision-making, and stakeholder management in dynamic environments.
Core Objectives: Reactive vs Proactive Strategies
Crisis management focuses on reactive strategies aimed at addressing immediate threats and minimizing damage during unforeseen events, prioritizing swift response and containment. Permanent campaigns employ proactive strategies designed to build and maintain favorable public perception over time, emphasizing continuous engagement and reputation management. Both approaches serve distinct core objectives: crisis management mitigates risks after they emerge, while permanent campaigns strive to prevent crises by fostering long-term stakeholder trust.
Tools and Techniques in Crisis Management
Crisis management relies heavily on real-time monitoring tools such as social media analytics platforms, crisis simulation software, and emergency communication systems to rapidly identify and respond to emerging threats. Techniques include scenario planning, stakeholder mapping, and rapid decision-making protocols designed to minimize reputational damage and operational disruption. Integrating AI-driven sentiment analysis and automated alert systems enhances the ability to anticipate crises and deploy targeted responses efficiently.
Communication Strategies in a Permanent Campaign
Communication strategies in a permanent campaign emphasize continuous engagement, message consistency, and proactive reputation management to maintain public trust and influence voter behavior over time. Unlike crisis management, which prioritizes rapid response and damage control during unforeseen events, permanent campaigns utilize data-driven targeting, narrative framing, and multi-channel outreach to build long-term emotional connections with key audiences. This approach leverages real-time analytics and social media monitoring to adapt messaging dynamically and reinforce brand identity across diverse stakeholder segments.
Leadership Roles: Crisis Response vs Continuous Mobilization
Leadership roles in crisis management require rapid decision-making, clear communication, and decisive action to address immediate threats and restore stability. In contrast, leadership in a permanent campaign emphasizes continuous mobilization, strategic planning, and sustained engagement to maintain support and adapt to evolving political landscapes. Effective leaders balance crisis response skills with long-term vision to navigate both urgent disruptions and ongoing organizational goals.
Impact on Public Trust and Institutional Legitimacy
Crisis management often temporarily restores public trust by addressing urgent issues promptly, but repeated reliance on reactive strategies can erode institutional legitimacy over time. Permanent campaigns maintain continuous engagement with the public, fostering sustained trust through transparency and consistent communication, yet risk politicizing governance processes. Balancing immediate crisis responses with ongoing proactive outreach is crucial to preserving both public confidence and institutional credibility.
Case Studies: Successful and Failed Applications
Crisis management involves rapid, strategic responses to unexpected events, as seen in Johnson & Johnson's Tylenol recall, which successfully protected brand reputation through transparency and swift action. In contrast, the permanent campaign strategy, exemplified by Apple, maintains continuous engagement and brand loyalty, effectively preempting crises by fostering strong customer relationships. Failed applications such as BP's Deepwater Horizon response highlight the pitfalls of inadequate crisis management, while Microsoft's initially faltering Windows Vista launch demonstrated the risks of poor permanent campaign execution in product positioning.
Choosing the Right Approach: Contextual Decision-Making
Crisis management demands rapid response strategies that prioritize damage control and stakeholder communication, while a permanent campaign emphasizes sustained engagement and reputation building over time. Organizations must assess factors such as urgency, resource availability, and long-term objectives to determine the optimal approach. Contextual decision-making involves analyzing the specific scenario to balance immediate actions with ongoing strategic initiatives.
Crisis management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com