The administrative board plays a crucial role in overseeing organizational policies and ensuring effective governance. It establishes strategic direction, monitors performance, and manages risk to uphold the organization's mission. Explore the full article to understand how your administrative board can enhance leadership and drive success.
Table of Comparison
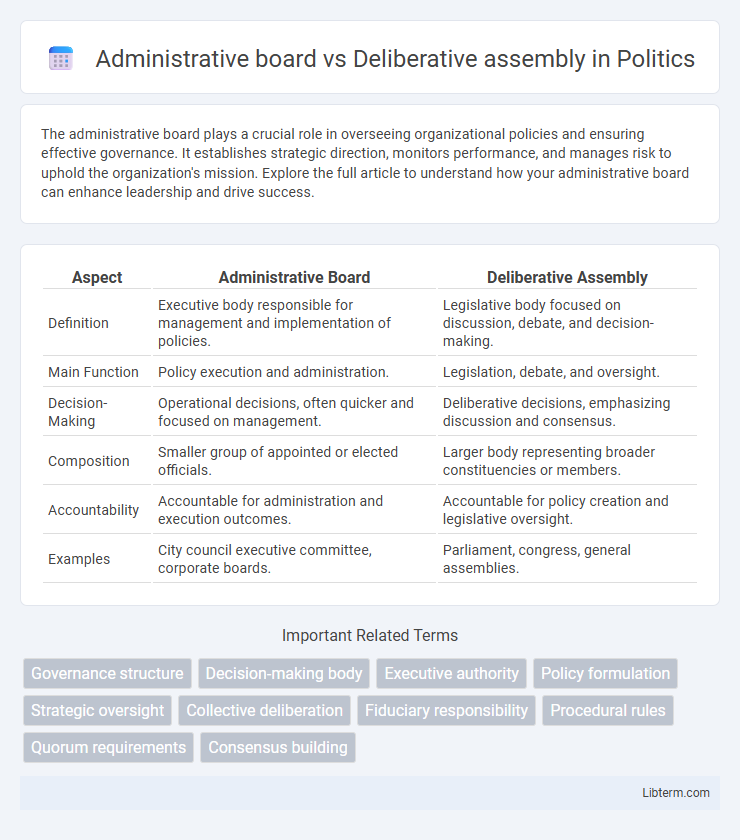
| Aspect | Administrative Board | Deliberative Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executive body responsible for management and implementation of policies. | Legislative body focused on discussion, debate, and decision-making. |
| Main Function | Policy execution and administration. | Legislation, debate, and oversight. |
| Decision-Making | Operational decisions, often quicker and focused on management. | Deliberative decisions, emphasizing discussion and consensus. |
| Composition | Smaller group of appointed or elected officials. | Larger body representing broader constituencies or members. |
| Accountability | Accountable for administration and execution outcomes. | Accountable for policy creation and legislative oversight. |
| Examples | City council executive committee, corporate boards. | Parliament, congress, general assemblies. |
Introduction to Administrative Boards and Deliberative Assemblies
Administrative boards are authoritative bodies responsible for overseeing organizational policies, financial decisions, and strategic direction, typically composed of appointed members with governance expertise. Deliberative assemblies consist of members who gather to discuss, debate, and make decisions on policies or actions, emphasizing democratic participation and collective decision-making. The distinction lies in the administrative board's focus on governance and oversight, while deliberative assemblies prioritize member involvement and consensus-building.
Defining Administrative Boards
Administrative boards are formal governing bodies responsible for overseeing organizational operations, ensuring compliance with policies, and making executive decisions through delegated authority. These boards typically consist of appointed or elected members who manage administrative functions, set strategic direction, and monitor performance metrics. Unlike deliberative assemblies, administrative boards prioritize efficient administration over open discussion, emphasizing structured decision-making processes.
Key Functions of Deliberative Assemblies
Deliberative assemblies primarily focus on decision-making through discussion, debate, and voting on policies affecting the entire organization or community. Key functions include formulating regulations, approving budgets, and electing officers, ensuring broad representation and transparent governance. Unlike administrative boards that handle executive tasks, deliberative assemblies emphasize collective input and consensus-building to shape strategic directions.
Structural Differences between Administrative Boards and Deliberative Assemblies
Administrative boards typically consist of a smaller, fixed number of appointed or elected members responsible for executive decision-making and operational oversight of an organization. Deliberative assemblies, by contrast, often include a larger, more fluid membership base representing various stakeholders, emphasizing discussion and collective decision-making through parliamentary procedures. The structural distinction lies in the administrative board's focus on governance and policy enforcement versus the assembly's role in debate, consensus-building, and legislative functions.
Authority and Decision-Making Processes
An administrative board holds executive authority, responsible for implementing policies and managing organizational operations, often making decisions within a defined scope of governance. A deliberative assembly exercises legislative authority by debating, amending, and voting on proposals, ensuring collective decision-making through majority rule or consensus. While the administrative board focuses on efficient execution and oversight, the deliberative assembly emphasizes inclusive discussion and approval of strategic directions.
Membership and Representation
The Administrative Board typically consists of a small group of appointed or elected officials responsible for executive functions, ensuring efficient management and decision-making within an organization. In contrast, the Deliberative Assembly includes a broader membership that represents various stakeholders or constituents, providing a platform for discussion, debate, and collective decision-making. Membership in the Deliberative Assembly is often more diverse and inclusive, reflecting the interests and voices of the wider organization or community.
Meeting Procedures and Protocols
Administrative boards follow structured meeting procedures emphasizing formal agendas, motion handling, and strict adherence to parliamentary rules to ensure efficient decision-making and organizational governance. Deliberative assemblies prioritize open discussion and equitable participation, using flexible protocols that encourage debate while maintaining order through recognized parliamentary procedures like Robert's Rules of Order. Both entities require accurate minute keeping and role differentiation, but administrative boards focus more on executive functions, whereas deliberative assemblies emphasize collective deliberation and consensus-building.
Accountability and Transparency
Administrative boards ensure accountability by implementing structured oversight mechanisms, regularly monitoring organizational performance, and maintaining transparent reporting practices to stakeholders. Deliberative assemblies enhance transparency through open debates, inclusive decision-making processes, and publicly accessible records, fostering collective responsibility among members. Both entities prioritize accountability and transparency, but administrative boards rely on formal control systems while deliberative assemblies emphasize participatory governance.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Model
The Administrative Board streamlines decision-making with a smaller, focused group, enhancing efficiency and quick response but may lack diverse viewpoints, potentially limiting comprehensive debate. The Deliberative Assembly encourages inclusive participation and diverse opinions, fostering thorough discussion and democratic legitimacy, yet often faces slower decision-making and risks of deadlock. Balancing efficiency and inclusiveness depends on organizational priorities, with Administrative Boards favoring centralized control and Deliberative Assemblies emphasizing collective consensus.
Choosing the Right Governance Structure
Selecting the appropriate governance structure involves understanding the distinct roles of an administrative board and a deliberative assembly. An administrative board focuses on executive decision-making, operational management, and strategic oversight, ensuring efficient organizational functioning. In contrast, a deliberative assembly emphasizes member participation, debate, and consensus-building, making it ideal for organizations valuing democratic engagement and collective decision-making.
Administrative board Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com