General elections determine the leadership and future policies of a country by allowing citizens to vote for their preferred candidates or parties. These elections impact every aspect of daily life, from healthcare and education to economic growth and national security. Discover how general elections shape your community and why your participation matters by reading the full article.
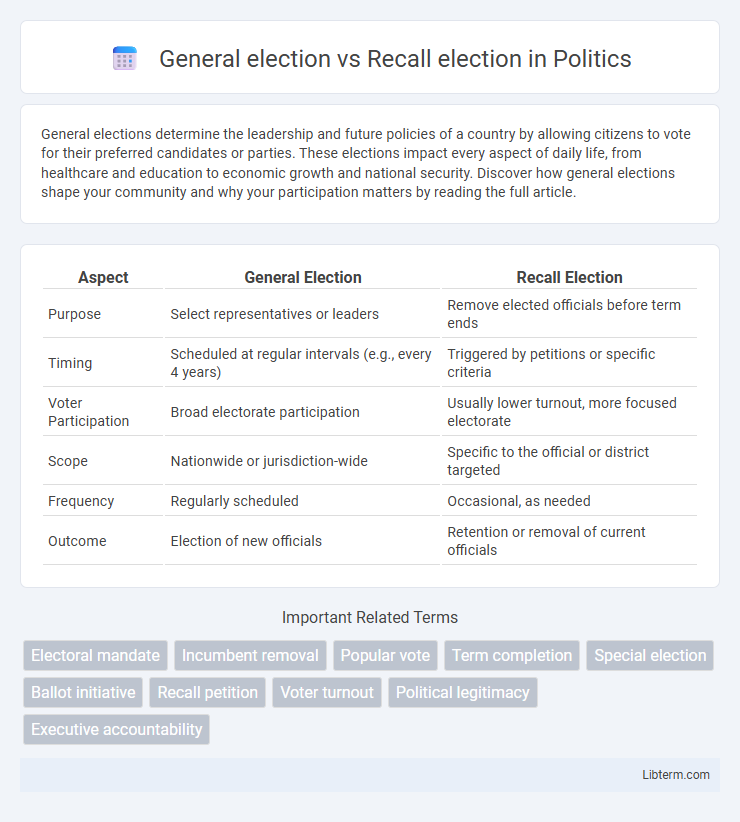
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | General Election | Recall Election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Select representatives or leaders | Remove elected officials before term ends |
| Timing | Scheduled at regular intervals (e.g., every 4 years) | Triggered by petitions or specific criteria |
| Voter Participation | Broad electorate participation | Usually lower turnout, more focused electorate |
| Scope | Nationwide or jurisdiction-wide | Specific to the official or district targeted |
| Frequency | Regularly scheduled | Occasional, as needed |
| Outcome | Election of new officials | Retention or removal of current officials |
Introduction to General and Recall Elections
General elections are regularly scheduled events where voters select candidates for public office across various levels of government, including local, state, and federal positions. Recall elections allow citizens to remove elected officials from office before their term expires through a petition process and subsequent vote. Both election types serve democratic purposes but differ in timing, initiation, and scope, with general elections determining standard leadership and recall elections addressing voter dissatisfaction with specific incumbents.
Definition of General Election
A general election is a regular electoral event where voters choose candidates for public offices, including legislative and executive positions, across all participating jurisdictions. It determines the composition of government representatives who will serve fixed terms and is typically held on a scheduled cycle, such as every four years. Unlike a recall election, which is initiated to remove an incumbent before their term ends, a general election establishes leadership through a standard democratic process.
Definition of Recall Election
A recall election is a procedure that allows voters to remove an elected official from office before their term ends by voting on whether to retain or dismiss the official. Unlike a general election, which is regularly scheduled for electing representatives or officials, a recall election is initiated through a petition process driven by voter dissatisfaction or allegations of misconduct. This direct democracy tool serves as a mechanism for accountability, enabling citizens to intervene between general elections.
Key Differences Between General and Recall Elections
General elections are scheduled events where voters choose candidates for public office across multiple positions, often occurring at fixed intervals such as every four years. Recall elections are unscheduled, initiated by citizen petitions to remove an elected official before their term ends, requiring a threshold number of signatures to trigger the vote. Key differences include the purpose--electing officials versus removing them--and the initiation process, with general elections being routine and recall elections being reactive to specific grievances.
Legal Framework Governing Both Election Types
General elections are governed by comprehensive electoral laws that establish voting procedures, candidate eligibility, and the regular schedule mandated by constitutional or statutory provisions. Recall elections operate under specific legal frameworks allowing voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, often requiring petition thresholds and strict timelines defined by state or local laws. Both election types must comply with overarching election laws ensuring transparency, voter rights, and fair administration, but recall elections involve additional rules tailored to the initiation and verification of recall petitions.
Purpose and Objectives of Each Election
General elections serve the purpose of selecting public officials or representatives for fixed terms, enabling voters to influence government policy and leadership through scheduled voting. Recall elections aim to remove an incumbent from office before their term ends by allowing voters to express dissatisfaction with their performance or conduct. The primary objective of general elections is democratic governance through regular transitions, while recall elections focus on accountability and direct voter intervention.
Process and Procedures: General Election
General elections involve a comprehensive voting process where eligible citizens elect public officials at various government levels, typically following a fixed schedule determined by law. The procedure includes candidate nominations, official ballot preparation, voter registration verification, and the actual casting and counting of votes under strict regulatory oversight to ensure fairness and transparency. Election authorities administer the entire process, including monitoring for election fraud, enforcing campaign finance rules, and certifying final results before offices are officially assigned.
Process and Procedures: Recall Election
Recall elections initiate when a significant percentage of voters sign a petition to remove an elected official before their term ends, triggering a special vote. The process involves verifying petition signatures, holding a public notice period, and scheduling a separate ballot where voters decide to retain or remove the official. Unlike general elections that follow fixed schedules, recall elections are reactive, demanding rapid organization and strict adherence to legal timelines to ensure legitimacy.
Impacts on Political Stability and Governance
General elections determine the overall political leadership and policy direction, fostering legitimacy and long-term government stability through broad voter participation. Recall elections introduce accountability by enabling removal of officials before their term ends, but frequent recalls can disrupt governance continuity and create political volatility. Balancing these mechanisms impacts political stability, where general elections build structured transitions, while recalls act as corrective tools that may either strengthen or undermine governance depending on their use.
Real-World Examples of General and Recall Elections
General elections determine representational leadership across various government levels, as seen in the 2020 U.S. presidential election where voters elected Joe Biden as president. Recall elections, such as the 2003 California gubernatorial recall that removed Governor Gray Davis and installed Arnold Schwarzenegger, provide a mechanism for voters to remove officials before their terms end. These elections highlight the contrast between regular, scheduled electoral processes and targeted, issue-driven votes to address specific governance concerns.
General election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com