Fascism is a political ideology characterized by authoritarian nationalism, centralized control, and suppression of opposition, often led by a dictatorial leader. It promotes the idea of a unified national community, prioritizing the state over individual freedoms and often relying on propaganda and militarization. Explore how fascism shaped history and its enduring impact on modern societies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
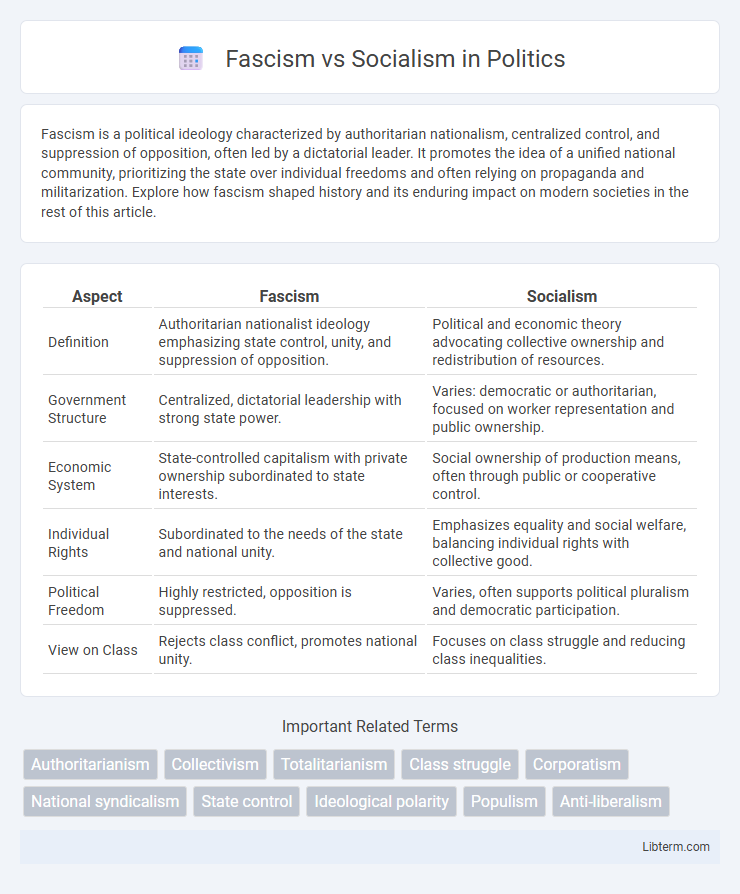
| Aspect | Fascism | Socialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authoritarian nationalist ideology emphasizing state control, unity, and suppression of opposition. | Political and economic theory advocating collective ownership and redistribution of resources. |
| Government Structure | Centralized, dictatorial leadership with strong state power. | Varies: democratic or authoritarian, focused on worker representation and public ownership. |
| Economic System | State-controlled capitalism with private ownership subordinated to state interests. | Social ownership of production means, often through public or cooperative control. |
| Individual Rights | Subordinated to the needs of the state and national unity. | Emphasizes equality and social welfare, balancing individual rights with collective good. |
| Political Freedom | Highly restricted, opposition is suppressed. | Varies, often supports political pluralism and democratic participation. |
| View on Class | Rejects class conflict, promotes national unity. | Focuses on class struggle and reducing class inequalities. |
Defining Fascism: Core Principles and History
Fascism is a far-right political ideology characterized by authoritarian nationalism, centralized control, and the suppression of opposition, originating in early 20th-century Europe, notably under Benito Mussolini's Italy. Core principles include a strong, dictatorial leadership, an emphasis on unity and collective identity over individual rights, aggressive nationalism, and often militarism. Historically, fascism arose as a reaction against liberal democracy and socialism, promoting a hierarchical society where the state exerts total control to maintain order and national strength.
Understanding Socialism: Ideologies and Variations
Socialism encompasses diverse ideologies centered on collective ownership and wealth redistribution to achieve social equality and economic justice. Variations such as democratic socialism emphasize political democracy combined with social ownership, while Marxist socialism advocates for a revolutionary transition to a classless society. Understanding these distinctions highlights socialism's broad spectrum, contrasting with fascism's authoritarian nationalism and centralized control.
The Origins: Historical Emergence of Fascism and Socialism
Fascism originated in early 20th-century Italy as a reaction against liberal democracy and socialism, emphasizing authoritarian nationalism, centralized power, and militant propaganda under leaders like Benito Mussolini. Socialism emerged in the 19th century during the Industrial Revolution, advocating for social ownership of the means of production and economic equality, influenced by theorists such as Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Both ideologies arose from socioeconomic upheaval but diverged sharply in goals: fascism promotes national unity through hierarchy and dictatorship, while socialism seeks classless society through collective governance.
Key Philosophical Differences between Fascism and Socialism
Fascism centers on authoritarian nationalism, emphasizing a unified state with strict hierarchical control and suppression of individual freedoms to promote collective power. Socialism advocates for collective ownership of resources and means of production, prioritizing economic equality and social welfare through democratic or cooperative governance. While fascism enforces centralized control to maintain order and national identity, socialism seeks to redistribute power and wealth to reduce class disparities and promote social justice.
Economic Systems: State Control vs. Collective Ownership
Fascism emphasizes centralized state control over the economy, where private property exists but is subordinated to the goals of the state and controlled through corporatist structures. Socialism advocates for collective ownership of the means of production, aiming to eliminate private property and distribute resources based on egalitarian principles. Both systems reject free-market capitalism but diverge in how economic power is organized--state-directed control versus community-based ownership.
Political Structures: Authoritarianism vs. Democratic Socialism
Fascism centralizes power under a dictatorial leader, enforcing strict authoritarian control over political, social, and economic life to suppress opposition and maintain order. In contrast, Democratic Socialism embraces a political structure that combines democratic governance with social ownership of resources, promoting political pluralism and citizen participation in decision-making. While Fascism rejects democratic institutions and civil liberties, Democratic Socialism upholds these values through policies aimed at reducing inequality and enhancing social welfare.
Society and Individual Rights under Fascism and Socialism
Fascism prioritizes the collective power of the state, often suppressing individual rights to maintain strict social order and national unity, where personal freedoms are subordinate to the goals of the ruling regime. Socialism advocates for collective ownership and egalitarian distribution, aiming to balance societal welfare with individual rights by promoting economic equality and social justice. Under socialism, individual rights are protected through democratic governance and social policies designed to reduce inequality, contrasting with fascism's authoritarian control and limited personal liberties.
Cultural and Social Impacts of Each Ideology
Fascism emphasizes nationalist identity, often suppressing cultural diversity and promoting uniformity through authoritarian control, leading to the marginalization of minority groups and the erosion of social pluralism. Socialism advocates for economic equality and collective ownership, fostering inclusive cultural policies aimed at reducing class disparities and enhancing social welfare systems that prioritize education, healthcare, and workers' rights. Both ideologies profoundly shape social structures: fascism reinforces hierarchical, centralized power, whereas socialism seeks to democratize social relations and promote multicultural integration.
Historical Case Studies: Fascist and Socialist Regimes
The historical examination of fascist regimes such as Mussolini's Italy and Nazi Germany reveals centralized authoritarian control, strict nationalism, and suppression of political opposition, often accompanied by aggressive militarism and state propaganda. Socialist regimes like the Soviet Union under Lenin and Stalin emphasized state ownership of resources, planned economies, and the pursuit of classless society ideals, though both also faced criticism for authoritarian governance and limited political freedoms. Comparative analysis highlights fundamental ideological conflicts and the varied sociopolitical impacts, illustrating distinct pathways of governance and economic management in 20th-century history.
Modern Relevance: The Legacy of Fascism and Socialism Today
Fascism's legacy today manifests in authoritarian nationalist movements emphasizing centralized power and suppression of dissent, while socialism influences modern policies advocating for social welfare, economic equality, and government intervention in markets. Contemporary political landscapes reflect a tension between these ideologies, with left-wing parties drawing from socialist principles to address inequality and right-wing factions echoing fascist rhetoric to promote identity politics. Understanding these legacies is crucial for analyzing current global challenges related to governance, civil rights, and economic justice.
Fascism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com